|
Abbreviated name: TDF
Synonyms: (R)-PMPA | PMPA | tenofovir (anhydrous)
tenofovir is an approved drug
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
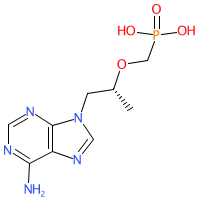
Comment: Tenofovir is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NtRTI) antiretroviral compound. The R-enantiomer, as shown here, is more effective at inhibiting retroviruses than the S-enantiomer [1]. Tenofovir has poor oral bioavailability and is delivered as either the prodrug tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread®) or tenofovir alafenamide fumerate (Vemlidy®).
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Tenofovir is approved for the treatment of HIV (in combination with other antiretroviral agents) and chronic hepatitis B infections. Compared to other nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors, tenofovir demonstrates a favourable safety profile. Renal toxicity has been found to be a modest, but significant risk [2]. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: A number of Phase 2/3 clinical trials are planned to evaluate the use of emtricitabine/tenofovir to prevent SARS-COV-2 transmission to healthcare professionals. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Tenofovir is an acyclic nucleotide diester analogue of adenosine 5'-monophosphate, reverse transciptase inhibitor, preventing viral replication. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT04334928 | Randomized Clinical Trial for the Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19) in Healthcare Personnel | Phase 3 Interventional | Plan Nacional sobre el Sida (PNS) | ||
| NCT04519125 | Daily Regimen of Tenofovir/Emtricitabine as Prevention for COVID-19 in Health Care Personnel in Colombia | Phase 2/Phase 3 Interventional | Hospital Universitario San Ignacio | ||
| NCT04405271 | TAF/FTC for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis of COVID-19 in Healthcare Workers (CoviPrep Study) | Phase 3 Interventional | Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires | ||
Pharmacokinetics  |
| Biotransformation/Metabolism |
| Bi-phosphorylation to the active compound tenofovir biphosphate. |
| Elimination |
| Tenofovir is eliminated in the urine by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. |
| Organ function impairment |
| In the kidney, tenofovir can cause proximal tubule dysfunction leading to Fanconi syndrome, acute tubular necrosis [7] and acute kidney injury (AKI) [5,7]. Severe AKI can cause chronic kidney disease (CKD) and even lead to end stage renal disease (ESRD). Tenofovir can enter mitochondria of tubule cells where it inhibits mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ [3], giving structural mitochondrial abnormalities. This causes apoptosis via mitochondrial protein release. Injured proximal tubule cells are unable to reabsorb small molecules, secrete H+ or synthesize calcitriol [3]. Proximal tubule cell loss is caused from persistent injury, this decreases glomerular filtration rate and injures the kidney. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Drugs.com |