GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Quaternary Structure
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
| Quaternary Structure: Subunits |
| RAMP1 (Accessory protein) |
| CT receptor |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| CTR/RAMP1 |
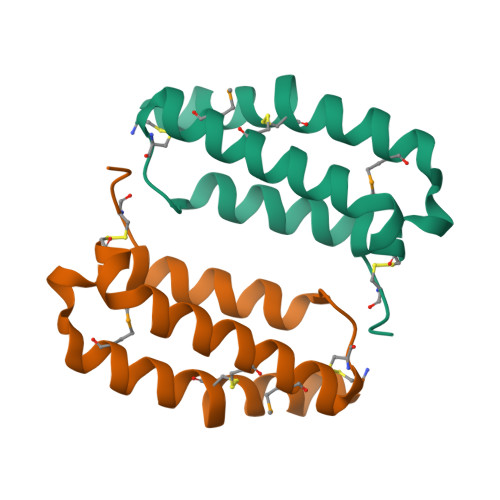
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| adrenomedullin {Sp: Human} |
| adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Human} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Mouse} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Rat} |
| amylin {Sp: Human} , amylin {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| calcitonin {Sp: Human} , calcitonin {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Human} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Human} , β-CGRP {Sp: Mouse} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Rat} |
| Comments: Amylin, α-CGRP, and β-CGRP are the most potent endogenous agonists |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| amylin (IAPP, P10997) ≥ α-CGRP (CALCA, P06881), β-CGRP (CALCB, P10092) > adrenomedullin 2/intermedin (ADM2, Q7Z4H4) ≥ calcitonin (CALCA, P01258) > adrenomedullin (ADM, P35318) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The AMY1 receptor is a heterodimeric complex of the calcitonin receptor and RAMP1 [17]. The variability in potency values reported is likely to reflect cell background such as the presence of other endogenous RAMPs and the calcitonin receptor-like receptor [20]. It is difficult to ascertain the contribution of such factors to the reported values. Human amylin is rarely used because of its propensity to aggregate. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 3,7,11-12,14,17 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
References
1. Armour SL, Foord S, Kenakin T, Chen WJ. (1999) Pharmacological characterization of receptor-activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs) and the human calcitonin receptor. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods, 42 (4): 217-24. [PMID:11033437]
2. Bhogal R, Smith DM, Bloom SR. (1992) Investigation and characterization of binding sites for islet amyloid polypeptide in rat membranes. Endocrinology, 130 (2): 906-13. [PMID:1310282]
3. Christopoulos G, Perry KJ, Morfis M, Tilakaratne N, Gao Y, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Foord SM, Sexton PM. (1999) Multiple amylin receptors arise from receptor activity-modifying protein interaction with the calcitonin receptor gene product. Mol Pharmacol, 56 (1): 235-42. [PMID:10385705]
4. Cooper GJ, Leighton B, Dimitriadis GD, Parry-Billings M, Kowalchuk JM, Howland K, Rothbard JB, Willis AC, Reid KB. (1988) Amylin found in amyloid deposits in human type 2 diabetes mellitus may be a hormone that regulates glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 85 (20): 7763-6. [PMID:3051005]
5. Gingell JJ, Burns ER, Hay DL. (2014) Activity of pramlintide, rat and human amylin but not Aβ1-42 at human amylin receptors. Endocrinology, 155 (1): 21-6. [PMID:24169554]
6. Gorn AH, Rudolph SM, Flannery MR, Morton CC, Weremowicz S, Wang TZ, Krane SM, Goldring SR. (1995) Expression of two human skeletal calcitonin receptor isoforms cloned from a giant cell tumor of bone. The first intracellular domain modulates ligand binding and signal transduction. J Clin Invest, 95: 2680-2691. [PMID:7769107]
7. Hay DL, Christopoulos G, Christopoulos A, Poyner DR, Sexton PM. (2005) Pharmacological discrimination of calcitonin receptor: receptor activity-modifying protein complexes. Mol Pharmacol, 67 (5): 1655-65. [PMID:15692146]
8. Hay DL, Christopoulos G, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM. (2006) Determinants of 1-piperidinecarboxamide, N-[2-[[5-amino-l-[[4-(4-pyridinyl)-l-piperazinyl]carbonyl]pentyl]amino]-1-[(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxoethyl]-4-(1,4-dihydro-2-oxo-3(2H)-quinazolinyl) (BIBN4096BS) affinity for calcitonin gene-related peptide and amylin receptors--the role of receptor activity modifying protein 1. Mol Pharmacol, 70: 1984-1991. [PMID:16959943]
9. Hong Y, Hay DL, Quirion R, Poyner DR. (2012) The pharmacology of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin. Br J Pharmacol, 166 (1): 110-20. [PMID:21658025]
10. Kusano S, Kukimoto-Niino M, Akasaka R, Toyama M, Terada T, Shirouzu M, Shindo T, Yokoyama S. (2008) Crystal structure of the human receptor activity-modifying protein 1 extracellular domain. Protein Sci, 17 (11): 1907-14. [PMID:18725456]
11. Kuwasako K, Cao YN, Nagoshi Y, Tsuruda T, Kitamura K, Eto T. (2004) Characterization of the human calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor subtypes associated with receptor activity-modifying proteins. Mol Pharmacol, 65 (1): 207-13. [PMID:14722252]
12. Kuwasako K, Kitamura K, Nagoshi Y, Eto T. (2003) Novel calcitonin-(8-32)-sensitive adrenomedullin receptors derived from co-expression of calcitonin receptor with receptor activity-modifying proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 301 (2): 460-4. [PMID:12565884]
13. Leighton B, Cooper GJ. (1988) Pancreatic amylin and calcitonin gene-related peptide cause resistance to insulin in skeletal muscle in vitro. Nature, 335 (6191): 632-5. [PMID:3050530]
14. Leuthauser K, Gujer R, Aldecoa A, McKinney RA, Muff R, Fischer JA, Born W. (2000) Receptor-activity-modifying protein 1 forms heterodimers with two G-protein-coupled receptors to define ligand recognition. Biochem J, 351: 347-351. [PMID:11023820]
15. Lutz TA. (2006) Amylinergic control of food intake. Physiol Behav, 89 (4): 465-71. [PMID:16697020]
16. Pan KS, Siow A, Hay DL, Walker CS. (2020) Antagonism of CGRP Signaling by Rimegepant at Two Receptors. Front Pharmacol, 11: 1240. [PMID:32973499]
17. Poyner DR, Sexton PM, Marshall I, Smith DM, Quirion R, Born W, Muff R, Fischer JA, Foord SM. (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXII. The mammalian calcitonin gene-related peptides, adrenomedullin, amylin, and calcitonin receptors. Pharmacol Rev, 54 (2): 233-46. [PMID:12037140]
18. Qi T, Dong M, Watkins HA, Wootten D, Miller LJ, Hay DL. (2013) Receptor activity-modifying protein-dependent impairment of calcitonin receptor splice variant Δ(1-47)hCT((a)) function. Br J Pharmacol, 168 (3): 644-57. [PMID:22946511]
19. Roth JD, Erickson MR, Chen S, Parkes DG. (2012) GLP-1R and amylin agonism in metabolic disease: complementary mechanisms and future opportunities. Br J Pharmacol, 166 (1): 121-36. [PMID:21671898]
20. Tilakaratne N, Christopoulos G, Zumpe ET, Foord SM, Sexton PM. (2000) Amylin receptor phenotypes derived from human calcitonin receptor/RAMP coexpression exhibit pharmacological differences dependent on receptor isoform and host cell environment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 294 (1): 61-72. [PMID:10871296]
21. Venkatanarayan A, Raulji P, Norton W, Chakravarti D, Coarfa C, Su X, Sandur SK, Ramirez MS, Lee J, Kingsley CV et al.. (2015) IAPP-driven metabolic reprogramming induces regression of p53-deficient tumours in vivo. Nature, 517 (7536): 626-30. [PMID:25409149]
22. Walker CS, Eftekhari S, Bower RL, Wilderman A, Insel PA, Edvinsson L, Waldvogel HJ, Jamaluddin MA, Russo AF, Hay DL. (2015) A second trigeminal CGRP receptor: function and expression of the AMY1 receptor. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 2 (6): 595-608. [PMID:26125036]
23. Young AA, Gedulin B, Vine W, Percy A, Rink TJ. (1995) Gastric emptying is accelerated in diabetic BB rats and is slowed by subcutaneous injections of amylin. Diabetologia, 38 (6): 642-8. [PMID:7672483]