GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1
 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target id: 1843
Nomenclature: discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1
Abbreviated Name: DDR1
Contents:
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 1 | 913 | 6p21.33 | DDR1 | discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 | |
| Mouse | 1 | 911 | 17 18.7 cM | Ddr1 | discoidin domain receptor family, member 1 | |
| Rat | 1 | 910 | 20p12 | Ddr1 | discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 | |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q08345 (Hs), Q03146 (Mm), Q63474 (Rn) |
| BRENDA | 2.7.10.1 |
| CATH/Gene3D | 2.60.120.260 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL5319 (Hs), CHEMBL4523274 (Mm), CHEMBL4295859 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000204580 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000003534 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000057125 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 780 (Hs), 12305 (Mm), 25678 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000204580 (Hs) |
| KEGG Enzyme | 2.7.10.1 |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:780 (Hs), mmu:12305 (Mm), rno:25678 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600408 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q08345 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001202521 (Hs), NM_001198833 (Mm), NM_013137 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_001945 (Hs), NP_001185760 (Mm), NP_031610 (Mm), NP_766550 (Mm), NP_001185762 (Mm), NP_037269 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q08345 (Hs), Q03146 (Mm), Q63474 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | DDR1 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
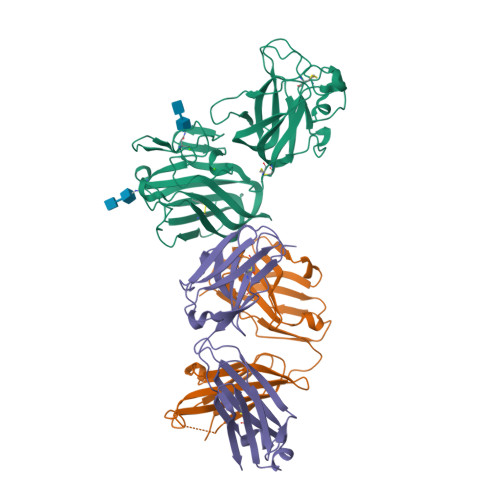
|
|
||||||||||||
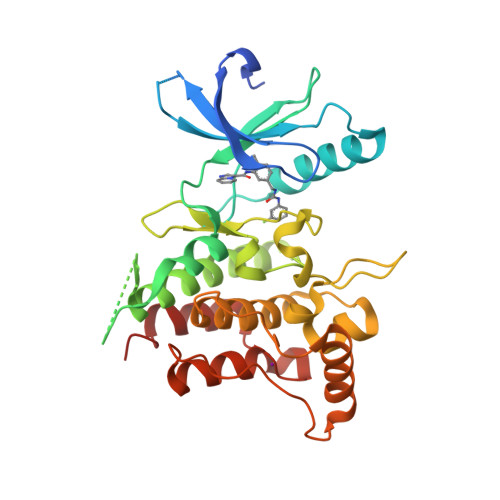
|
|
||||||||||||
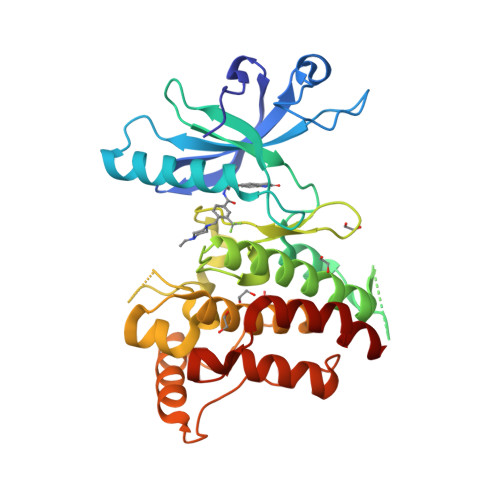
|
|
||||||||||||
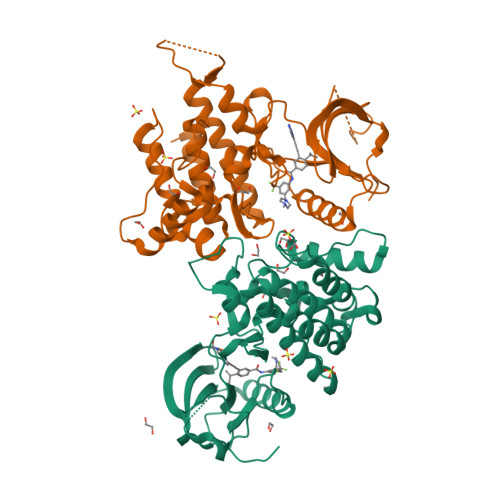
|
|
||||||||||||
Enzyme Reaction  |
||||
|
||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibodies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DiscoveRx KINOMEscan® screen  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A screen of 72 inhibitors against 456 human kinases. Quantitative data were derived using DiscoveRx KINOMEscan® platform. http://www.discoverx.com/services/drug-discovery-development-services/kinase-profiling/kinomescan Reference: 3,15 |
 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Target used in screen: DDR1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displaying the top 10 most potent ligands View all ligands in screen » | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| The DDR1 and DDR2 receptor tyrosine kinases are new potential targets for anti-inflammatory drug discovery, as they are critical mediators of inflammatory-cytokine secretion whose dysregulation is implicated in the progression of various human inflammatory diseases, including fibrosis, arthritis, and cancer [1,6]. DDR1 appears to promote inflammation in atherosclerosis, lung fibrosis and kidney injury. Small molecule inhibitors of these kinases are being developed and investigated for potential anti-inflammatory activity [1,7]. |
References
1. Borza CM, Pozzi A. (2014) Discoidin domain receptors in disease. Matrix Biol, 34: 185-92. [PMID:24361528]
2. Carafoli F, Mayer MC, Shiraishi K, Pecheva MA, Chan LY, Nan R, Leitinger B, Hohenester E. (2012) Structure of the discoidin domain receptor 1 extracellular region bound to an inhibitory Fab fragment reveals features important for signaling. Structure, 20 (4): 688-97. [PMID:22483115]
3. Davis MI, Hunt JP, Herrgard S, Ciceri P, Wodicka LM, Pallares G, Hocker M, Treiber DK, Zarrinkar PP. (2011) Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol, 29 (11): 1046-51. [PMID:22037378]
4. Gao M, Duan L, Luo J, Zhang L, Lu X, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Tu Z, Xu Y, Ren X et al.. (2013) Discovery and optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)ethynyl)benzamides as novel selective and orally bioavailable discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. J Med Chem, 56 (8): 3281-95. [PMID:23521020]
5. Kim HG, Tan L, Weisberg EL, Liu F, Canning P, Choi HG, Ezell SA, Wu H, Zhao Z, Wang J et al.. (2013) Discovery of a potent and selective DDR1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol, 8 (10): 2145-50. [PMID:23899692]
6. Leitinger B. (2014) Discoidin domain receptor functions in physiological and pathological conditions. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 310: 39-87. [PMID:24725424]
7. Li Y, Lu X, Ren X, Ding K. (2015) Small molecule discoidin domain receptor kinase inhibitors and potential medical applications. J Med Chem, 58 (8): 3287-301. [PMID:25569119]
8. Li Y, Xiong Y, Zhang G, Zhang L, Yang W, Yang J, Huang L, Qiao Z, Miao Z, Lin G et al.. (2018) Identification of 5-(2,3-Dihydro-1 H-indol-5-yl)-7 H-pyrrolo[2,3- d]pyrimidin-4-amine Derivatives as a New Class of Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 (RIPK1) Inhibitors, Which Showed Potent Activity in a Tumor Metastasis Model. J Med Chem, 61 (24): 11398-11414. [PMID:30480444]
9. Liu J, Chiang HC, Xiong W, Laurent V, Griffiths SC, Dülfer J, Deng H, Sun X, Yin YW, Li W et al.. (2023) A highly selective humanized DDR1 mAb reverses immune exclusion by disrupting collagen fiber alignment in breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer, 11 (6). [PMID:37328286]
10. Murray CW, Berdini V, Buck IM, Carr ME, Cleasby A, Coyle JE, Curry JE, Day JE, Day PJ, Hearn K et al.. (2015) Fragment-Based Discovery of Potent and Selective DDR1/2 Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett, 6 (7): 798-803. [PMID:26191369]
11. Ramurthy S, Taft BR, Aversa RJ, Barsanti PA, Burger MT, Lou Y, Nishiguchi GA, Rico A, Setti L, Smith A et al.. (2020) Design and Discovery of N-(3-(2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)-6-morpholinopyridin-4-yl)-4-methylphenyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)isonicotinamide, a Selective, Efficacious, and Well-Tolerated RAF Inhibitor Targeting RAS Mutant Cancers: The Path to the Clinic. J Med Chem, 63 (5): 2013-2027. [PMID:31059256]
12. Tröster A, Heinzlmeir S, Berger BT, Gande SL, Saxena K, Sreeramulu S, Linhard V, Nasiri AH, Bolte M, Müller S et al.. (2018) NVP-BHG712: Effects of Regioisomers on the Affinity and Selectivity toward the EPHrin Family. ChemMedChem, 13 (16): 1629-1633. [PMID:29928781]
13. Wang Z, Bian H, Bartual SG, Du W, Luo J, Zhao H, Zhang S, Mo C, Zhou Y, Xu Y et al.. (2016) Structure-Based Design of Tetrahydroisoquinoline-7-carboxamides as Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors. J Med Chem, 59 (12): 5911-6. [PMID:27219676]
14. Wang Z, Zhang Y, Pinkas DM, Fox AE, Luo J, Huang H, Cui S, Xiang Q, Xu T, Xun Q et al.. (2018) Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 3-(Imidazo[1,2- a]pyrazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-isopropyl- N-(3-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide as a Dual Inhibitor of Discoidin Domain Receptors 1 and 2. J Med Chem, 61 (17): 7977-7990. [PMID:30075624]
15. Wodicka LM, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Hunt JP, Floyd M, Salerno S, Hua XH, Ford JM, Armstrong RC, Zarrinkar PP et al.. (2010) Activation state-dependent binding of small molecule kinase inhibitors: structural insights from biochemistry. Chem Biol, 17 (11): 1241-9. [PMID:21095574]
16. Wu Y, Wang B, Wang J, Qi S, Zou F, Qi Z, Liu F, Liu Q, Chen C, Hu C et al.. (2019) Discovery of 2-(4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-N-(4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)acetamide (CHMFL-KIT-64) as a Novel Orally Available Potent Inhibitor against Broad-Spectrum Mutants of c-KIT Kinase for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. J Med Chem, 62 (13): 6083-6101. [PMID:31250638]
17. Yan SB, Peek VL, Ajamie R, Buchanan SG, Graff JR, Heidler SA, Hui YH, Huss KL, Konicek BW, Manro JR et al.. (2013) LY2801653 is an orally bioavailable multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against MET, MST1R, and other oncoproteins, and displays anti-tumor activities in mouse xenograft models. Invest New Drugs, 31 (4): 833-44. [PMID:23275061]
18. Zhavoronkov A, Ivanenkov YA, Aliper A, Veselov MS, Aladinskiy VA, Aladinskaya AV, Terentiev VA, Polykovskiy DA, Kuznetsov MD, Asadulaev A et al.. (2019) Deep learning enables rapid identification of potent DDR1 kinase inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol, 37 (9): 1038-1040. [PMID:31477924]











