GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
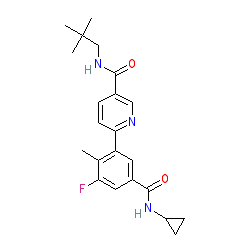
Synonyms: GS856553 | GW856553
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Losmapimod is a p38 mitogen-activated kinase α/β inhibitor. It was originally developed by GlaxoSmithKline for cardiovascular disease, but this failed to show efficacy. Fulcrum acquired the drug and are repurposing it for the treatment of the progressive muscle wasting disorder facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) based on evidence that p38α regulates expression of the FSHD-related gene DUX4 [4-5].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Losmapimod has been evaluated in clinical trials for cardiovascular disease [2], inflammatory conditions and a muscle wasting disease [4-5]. It has failed to provide significant efficacy in trials for cardiovascular disease, and has failed to meet the primary endpoint in a Phase 2 facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) study (NCT04264442). |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT02145468 | A Phase 3 Clinical Outcomes Study to Compare the Incidence of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects Presenting With Acute Coronary Syndrome Treated With Losmapimod Compared to Placebo (LATITUDE-TIMI 60) | Phase 3 Interventional | GlaxoSmithKline | Losmapimod fared no better than placebo and not reduce the risk of major ischemic cardiovascular events in this study. It was not progressed further. | 3 |
| NCT01541852 | Losmapimod in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients Stratified by Fibrinogen. | Phase 2 Interventional | Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust | ||
| NCT02000440 | A Phase II, Repeat Dose, Proof of Mechanism Study of Losmapimod to Reduce Proteinuria in Patients With Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) | Phase 2 Interventional | GlaxoSmithKline | ||
| NCT04003974 | Efficacy and Safety of Losmapimod in Subjects With Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD) | Phase 2 Interventional | Fulcrum Therapeutics | ||
| NCT04264442 | Efficacy and Safety of Losmapimod in Treating Subjects With Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD) With Open-Label Extension (OLE) | Phase 2 Interventional | Fulcrum Therapeutics | ReDUX4 study: testing the hypothesis that losmapimod might block expression of the transcriptional activator DUX4, as a mechanism for treating FSHD. Despite having no effect on DUX4 expression after 48 weeks of losmapimod treatment, other signals of potential benefit have been detected and as of June 2021 Fulcrum have committed to continuing development in FSHD. | |