GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: 29060-LE | Velban® | Velbe® | vincaleucoblastin | vincaleukoblastine
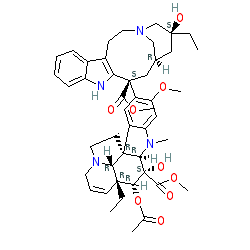
vinblastine is an approved drug (FDA (1965))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: A pan tubulin inhibitor that is a chemical analogue of vincristine (from Catharanthus roseus, also known as Vinca rosea). There is some ambiguity surrounding the exact stereochemistry of vinblastine. The chirality shown here corresponds to the PubChem CID provided on the Summary tab. However, bioactivity data for the compound is also listed against CID 241903, and some of the external resource links refer to this chiral specification or others. Marketed formulations contain vinblastine sulfate (PubChem CID 5388983).
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: vinblastine |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Causes cell cycle arrest by inhibiting microtubule assembly. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com |