GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: LAM-002A (apilimod dimesylate) | LAM002A | STA 5326 | STA-5326 | STA5326
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Apilimod was originally identified as an inhibitor of IL-12/IL-23 production [12], but the molecular mechanism behind this biological effect was undetermined. Inhibition of IL-12/IL-23 production has application for the treatment Th1-and Th17-mediated immunologic pathologies (which are driven by IL-12 and IL-23 respectively) [11-12]. Apilimod has subsequently been identified as a selective inhibitor of the type III phosphoinostol kinase, PIKfyve [4-5].
We provide structural details for the parent molecule, but some bioactivity data may relate to use of the mesylate salt form as stipulated by the compound's USAN (see PubChem CID 115273300). PIKfyve has been reported as being required for Ebola virus (EBOV) infection of host cells [9], and indeed apilimod has anti-EBOV activity in vitro. More broad-spectrum antiviral activity against Lassa virus (LASV), Marburg virus (MARV) [8] and SARS-CoV-2 [6,10] is supported in the literature. Activity of PIKfyve is markedly modulated by SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, and indicates potential hijacking of phosphatidylinositol enzyme activities by the coronavirus [3]. Pharmacological inhibition of this kinase with apilimod has anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in two model cell lines, A549-ACE2 cells (IC50 7 nM) and Vero E6 cells (IC50 80 nM), and in human iPSC-derived pneumocyte-like cells Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Classification  |
|
| Compound class | Synthetic organic |
IUPAC Name  |
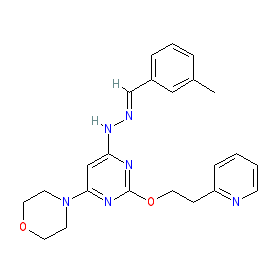
| N-[(3-methylphenyl)methylideneamino]-6-morpholin-4-yl-2-(2-pyridin-2-ylethoxy)pyrimidin-4-amine |
International Nonproprietary Names  |
|
| INN number | INN |
| 8763 | apilimod |
Synonyms  |
| LAM-002A (apilimod dimesylate) | LAM002A | STA 5326 | STA-5326 | STA5326 |
Database Links  |
|
| CAS Registry No. | 541550-19-0 (source: WHO INN record) |
| GtoPdb PubChem SID | 363894153 |
| PubChem CID | 10173277 |
| Search Google for chemical match using the InChIKey | HSKAZIJJKRAJAV-KOEQRZSOSA-N |
| Search Google for chemicals with the same backbone | HSKAZIJJKRAJAV |
| Search PubMed clinical trials | apilimod |
| Search PubMed titles | apilimod |
| Search PubMed titles/abstracts | apilimod |
| UniChem Compound Search for chemical match using the InChIKey | HSKAZIJJKRAJAV-KOEQRZSOSA-N |
| UniChem Connectivity Search for chemical match using the InChIKey | HSKAZIJJKRAJAV-KOEQRZSOSA-N |
Product suppliers
View disclaimer
Sponsored products disclaimer
Product supplier links are provided as a service to assist in identifying commercial suppliers of reagents that are mentioned on the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database website, and do not imply their endorsement by NC-IUPHAR.
Links are provided in return for sponsorship, used to fund improvements to this database. The sponsorship account is managed and audited by the University of Edinburgh, a charitable body registered in Scotland, SC005336. If you are interested in sponsoring the database, please contact us.
✖
Sponsored products disclaimer
Product supplier links are provided as a service to assist in identifying commercial suppliers of reagents that are mentioned on the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY database website, and do not imply their endorsement by NC-IUPHAR.
Links are provided in return for sponsorship, used to fund improvements to this database. The sponsorship account is managed and audited by the University of Edinburgh, a charitable body registered in Scotland, SC005336. If you are interested in sponsoring the database, please contact us.
✖|
Apilimod (links to external site)
Cat. No. HY-14644 |