GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
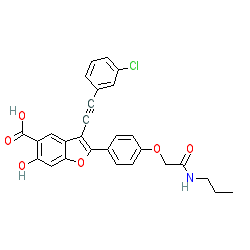
Comment: Compound 8a was designed as a small-molecule inhibitor of the lymphoid-specific non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase, LYP (PTPN22) [1]. PTPN22 directly dephosphorylates several kinase enzymes, effecting negative regulation of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling [3], and is implicated in autoimmune diseases [4].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. He Y, Liu S, Menon A, Stanford S, Oppong E, Gunawan AM, Wu L, Wu DJ, Barrios AM, Bottini N et al.. (2013)
A potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor for the lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (LYP), a target associated with autoimmune diseases. J Med Chem, 56 (12): 4990-5008. [PMID:23713581] |
|
2. Vang T, Congia M, Macis MD, Musumeci L, Orrú V, Zavattari P, Nika K, Tautz L, Taskén K, Cucca F et al.. (2005)
Autoimmune-associated lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is a gain-of-function variant. Nat Genet, 37 (12): 1317-9. [PMID:16273109] |
|
3. Wu J, Katrekar A, Honigberg LA, Smith AM, Conn MT, Tang J, Jeffery D, Mortara K, Sampang J, Williams SR et al.. (2006)
Identification of substrates of human protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22. J Biol Chem, 281 (16): 11002-10. [PMID:16461343] |
|
4. Yu X, Sun JP, He Y, Guo X, Liu S, Zhou B, Hudmon A, Zhang ZY. (2007)
Structure, inhibitor, and regulatory mechanism of Lyp, a lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase implicated in autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (50): 19767-72. [PMID:18056643] |