GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Voltage Dependence
- Rank order lists
- Activators
- Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 6 | 1 | 871 | 12q24.11 | TRPV4 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 | 32 |
| Mouse | 6 | 1 | 871 | 5 F | Trpv4 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 | 32 |
| Rat | 6 | 1 | 871 | 12q16 | Trpv4 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 | 32 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q9HBA0 (Hs), Q9EPK8 (Mm), Q9ERZ8 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 1.25.40.20 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL3119 (Hs), CHEMBL6126 (Mm), CHEMBL2775 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000111199 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000014158 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000001195 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 59341 (Hs), 63873 (Mm), 66026 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000111199 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:59341 (Hs), mmu:63873 (Mm), rno:66026 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 605427 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA171081 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q9HBA0 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_021625 (Hs), NM_022017 (Mm), NM_023970 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_067638 (Hs), NP_071300 (Mm), NP_076460 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q9HBA0 (Hs), Q9EPK8 (Mm), Q9ERZ8 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | TRPV4 (Hs) |
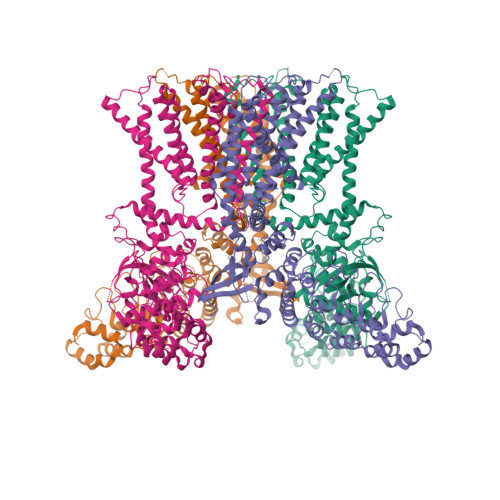
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
| Ion Selectivity and Conductance Comments | ||||||
| Conductance is ~30-60 pS at -60 mV, and ~88-100 pS at +60 mV. |
| Voltage Dependence Comments |
| Activation of TRPV4 is not voltage dependent. |
| Other chemical activators (Human) |
| Epoxyeicosatrieonic acids and NO-mediated cysteine S-nitrosylation |
| Physical activators (Human) |
| Constitutively active, heat (> 24°C - 32°C), mechanical stimuli |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific inhibitor tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paracetamol (acetaminophen) dose-dependently suppresses TRPV4 agonist-induced calcium entry into rat PC12 cells in vitro [38]. In cells exogenously expressing TRPV4 the paracetamol effect is TRPV4 dependent, which indicates a direct interaction of paracetamol with this calcium channel. The nature of paracetamol's interaction with the channel remains unclear. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Expressed on mouse neutrophils [39]. |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
1. Ai C, Wang Z, Li P, Wang M, Zhang W, Song H, Cai X, Lv K, Chen X, Zheng Z. (2023) Discovery and pharmacological characterization of a novel benzimidazole TRPV4 antagonist with cyanocyclobutyl moiety. Eur J Med Chem, 249: 115137. [PMID:36696767]
2. Alessandri-Haber N, Dina OA, Joseph EK, Reichling D, Levine JD. (2006) A transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-dependent mechanism of hyperalgesia is engaged by concerted action of inflammatory mediators. J Neurosci, 26 (14): 3864-74. [PMID:16597741]
3. Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD. (2003) Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron, 39 (3): 497-511. [PMID:12895423]
4. Alvarez DF, King JA, Weber D, Addison E, Liedtke W, Townsley MI. (2006) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-mediated disruption of the alveolar septal barrier: a novel mechanism of acute lung injury. Circ Res, 99 (9): 988-95. [PMID:17008604]
5. Atobe M, Nagami T, Muramatsu S, Ohno T, Kitagawa M, Suzuki H, Ishiguro M, Watanabe A, Kawanishi M. (2019) Discovery of Novel Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) Agonists as Regulators of Chondrogenic Differentiation: Identification of Quinazolin-4(3 H)-ones and in Vivo Studies on a Surgically Induced Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. J Med Chem, 62 (3): 1468-1483. [PMID:30629441]
6. Auer-Grumbach M, Olschewski A, Papić L, Kremer H, McEntagart ME, Uhrig S, Fischer C, Fröhlich E, Bálint Z, Tang B et al.. (2010) Alterations in the ankyrin domain of TRPV4 cause congenital distal SMA, scapuloperoneal SMA and HMSN2C. Nat Genet, 42 (2): 160-4. [PMID:20037588]
7. Benfenati V, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Caprini M, Mylonakou MN, Rapisarda C, Ottersen OP, Ferroni S. (2007) Expression and functional characterization of transient receptor potential vanilloid-related channel 4 (TRPV4) in rat cortical astrocytes. Neuroscience, 148 (4): 876-92. [PMID:17719182]
8. Birder L, Kullmann FA, Lee H, Barrick S, de Groat W, Kanai A, Caterina M. (2007) Activation of urothelial transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 by 4alpha-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate contributes to altered bladder reflexes in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 323 (1): 227-35. [PMID:17636010]
9. Brooks CA, Barton LS, Behm DJ, Eidam HS, Fox RM, Hammond M, Hoang TH, Holt DA, Hilfiker MA, Lawhorn BG et al.. (2019) Discovery of GSK2798745: A Clinical Candidate for Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4). ACS Med Chem Lett, 10 (8): 1228-1233. [PMID:31413810]
10. Camacho N, Krakow D, Johnykutty S, Katzman PJ, Pepkowitz S, Vriens J, Nilius B, Boyce BF, Cohn DH. (2010) Dominant TRPV4 mutations in nonlethal and lethal metatropic dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A, 152A (5): 1169-77. [PMID:20425821]
11. Cuajungco MP, Grimm C, Oshima K, D'hoedt D, Nilius B, Mensenkamp AR, Bindels RJ, Plomann M, Heller S. (2006) PACSINs bind to the TRPV4 cation channel. PACSIN 3 modulates the subcellular localization of TRPV4. J Biol Chem, 281 (27): 18753-62. [PMID:16627472]
12. Delany NS, Hurle M, Facer P, Alnadaf T, Plumpton C, Kinghorn I, See CG, Costigan M, Anand P, Woolf CJ et al.. (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel human vanilloid receptor-like protein, VRL-2. Physiol Genomics, 4 (3): 165-74. [PMID:11160995]
13. Deng HX, Klein CJ, Yan J, Shi Y, Wu Y, Fecto F, Yau HJ, Yang Y, Zhai H, Siddique N et al.. (2010) Scapuloperoneal spinal muscular atrophy and CMT2C are allelic disorders caused by alterations in TRPV4. Nat Genet, 42 (2): 165-9. [PMID:20037587]
14. Deng Z, Paknejad N, Maksaev G, Sala-Rabanal M, Nichols CG, Hite RK, Yuan P. (2018) Cryo-EM and X-ray structures of TRPV4 reveal insight into ion permeation and gating mechanisms. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 25 (3): 252-260. [PMID:29483651]
15. Doñate-Macian P, Duarte Y, Rubio-Moscardo F, Pérez-Vilaró G, Canan J, Díez J, González-Nilo F, Valverde MA. (2022) Structural determinants of TRPV4 inhibition and identification of new antagonists with antiviral activity. Br J Pharmacol, 179 (14): 3576-3591. [PMID:32959389]
16. Dunn KM, Hill-Eubanks DC, Liedtke WB, Nelson MT. (2013) TRPV4 channels stimulate Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in astrocytic endfeet and amplify neurovascular coupling responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110 (15): 6157-62. [PMID:23530219]
17. Earley S, Pauyo T, Drapp R, Tavares MJ, Liedtke W, Brayden JE. (2009) TRPV4-dependent dilation of peripheral resistance arteries influences arterial pressure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 297 (3): H1096-102. [PMID:19617407]
18. Everaerts W, Vriens J, Owsianik G, Appendino G, Voets T, De Ridder D, Nilius B. (2010) Functional characterization of transient receptor potential channels in mouse urothelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 298 (3): F692-701. [PMID:20015940]
19. Everaerts W, Zhen X, Ghosh D, Vriens J, Gevaert T, Gilbert JP, Hayward NJ, McNamara CR, Xue F, Moran MM et al.. (2010) Inhibition of the cation channel TRPV4 improves bladder function in mice and rats with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107 (44): 19084-9. [PMID:20956320]
20. Galizia L, Pizzoni A, Fernandez J, Rivarola V, Capurro C, Ford P. (2012) Functional interaction between AQP2 and TRPV4 in renal cells. J Cell Biochem, 113 (2): 580-9. [PMID:21938744]
21. Gao P, Li L, Wei X, Wang M, Hong Y, Wu H, Shen Y, Ma T, Wei X, Zhang Q et al.. (2020) Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Channel Vanilloid 4 by DPP-4 (Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4) Inhibitor Vildagliptin Protects Against Diabetic Endothelial Dysfunction. Hypertension, 75 (1): 150-162. [PMID:31735085]
22. Gevaert T, Vriens J, Segal A, Everaerts W, Roskams T, Talavera K, Owsianik G, Liedtke W, Daelemans D, Dewachter I et al.. (2007) Deletion of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPV4 impairs murine bladder voiding. J Clin Invest, 117 (11): 3453-62. [PMID:17948126]
23. Gradilone SA, Masyuk AI, Splinter PL, Banales JM, Huang BQ, Tietz PS, Masyuk TV, Larusso NF. (2007) Cholangiocyte cilia express TRPV4 and detect changes in luminal tonicity inducing bicarbonate secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (48): 19138-43. [PMID:18024594]
24. Guler AD, Lee H, Iida T, Shimizu I, Tominaga M, Caterina M. (2002) Heat-evoked activation of the ion channel, TRPV4. J Neurosci, 22 (15): 6408-14. [PMID:12151520]
25. Hamanaka K, Jian MY, Weber DS, Alvarez DF, Townsley MI, Al-Mehdi AB, King JA, Liedtke W, Parker JC. (2007) TRPV4 initiates the acute calcium-dependent permeability increase during ventilator-induced lung injury in isolated mouse lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 293 (4): L923-32. [PMID:17660328]
26. Kittaka H, Yamanoi Y, Tominaga M. (2017) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channel as a target of crotamiton and its bimodal effects. Pflugers Arch, 469 (10): 1313-1323. [PMID:28612138]
27. Klausen TK, Pagani A, Minassi A, Ech-Chahad A, Prenen J, Owsianik G, Hoffmann EK, Pedersen SF, Appendino G, Nilius B. (2009) Modulation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid channel TRPV4 by 4alpha-phorbol esters: a structure-activity study. J Med Chem, 52 (9): 2933-9. [PMID:19361196]
28. Krakow D, Vriens J, Camacho N, Luong P, Deixler H, Funari TL, Bacino CA, Irons MB, Holm IA, Sadler L et al.. (2009) Mutations in the gene encoding the calcium-permeable ion channel TRPV4 produce spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, Kozlowski type and metatropic dysplasia. Am J Hum Genet, 84 (3): 307-15. [PMID:19232556]
29. Kusudo T, Wang Z, Mizuno A, Suzuki M, Yamashita H. (2012) TRPV4 deficiency increases skeletal muscle metabolic capacity and resistance against diet-induced obesity. J Appl Physiol, 112 (7): 1223-32. [PMID:22207724]
30. Lamandé SR, Yuan Y, Gresshoff IL, Rowley L, Belluoccio D, Kaluarachchi K, Little CB, Botzenhart E, Zerres K, Amor DJ et al.. (2011) Mutations in TRPV4 cause an inherited arthropathy of hands and feet. Nat Genet, 43 (11): 1142-6. [PMID:21964574]
31. Landouré G, Zdebik AA, Martinez TL, Burnett BG, Stanescu HC, Inada H, Shi Y, Taye AA, Kong L, Munns CH et al.. (2010) Mutations in TRPV4 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2C. Nat Genet, 42 (2): 170-4. [PMID:20037586]
32. Liedtke W, Choe Y, Martí-Renom MA, Bell AM, Denis CS, Sali A, Hudspeth AJ, Friedman JM, Heller S. (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell, 103 (3): 525-35. [PMID:11081638]
33. Liu X, Bandyopadhyay BC, Bandyopadhyay B, Nakamoto T, Singh B, Liedtke W, Melvin JE, Ambudkar I. (2006) A role for AQP5 in activation of TRPV4 by hypotonicity: concerted involvement of AQP5 and TRPV4 in regulation of cell volume recovery. J Biol Chem, 281 (22): 15485-95. [PMID:16571723]
34. Ma X, Nilius B, Wong JW, Huang Y, Yao X. (2011) Electrophysiological properties of heteromeric TRPV4-C1 channels. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1808 (12): 2789-97. [PMID:21871867]
35. Ma X, Qiu S, Luo J, Ma Y, Ngai CY, Shen B, Wong CO, Huang Y, Yao X. (2010) Functional role of vanilloid transient receptor potential 4-canonical transient receptor potential 1 complex in flow-induced Ca2+ influx. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 30 (4): 851-8. [PMID:20093626]
36. Masuyama R, Vriens J, Voets T, Karashima Y, Owsianik G, Vennekens R, Lieben L, Torrekens S, Moermans K, Vanden Bosch A et al.. (2008) TRPV4-mediated calcium influx regulates terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Cell Metab, 8 (3): 257-65. [PMID:18762026]
37. Mizoguchi F, Mizuno A, Hayata T, Nakashima K, Heller S, Ushida T, Sokabe M, Miyasaka N, Suzuki M, Ezura Y et al.. (2008) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 deficiency suppresses unloading-induced bone loss. J Cell Physiol, 216 (1): 47-53. [PMID:18264976]
38. Nakagawa F, Higashi S, Ando E, Ohsumi T, Watanabe S, Takeuchi H. (2020) Modification of TRPV4 activity by acetaminophen. Heliyon, 6 (1): e03301. [PMID:32051870]
39. Parenti A, De Logu F, Geppetti P, Benemei S. (2016) What is the evidence for the role of TRP channels in inflammatory and immune cells?. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (6): 953-69. [PMID:26603538]
40. Poole DP, Amadesi S, Veldhuis NA, Abogadie FC, Lieu T, Darby W, Liedtke W, Lew MJ, McIntyre P, Bunnett NW. (2013) Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) protein and transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) protein coupling is required for sustained inflammatory signaling. J Biol Chem, 288 (8): 5790-802. [PMID:23288842]
41. Rock MJ, Prenen J, Funari VA, Funari TL, Merriman B, Nelson SF, Lachman RS, Wilcox WR, Reyno S, Quadrelli R et al.. (2008) Gain-of-function mutations in TRPV4 cause autosomal dominant brachyolmia. Nat Genet, 40 (8): 999-1003. [PMID:18587396]
42. Ryskamp DA, Witkovsky P, Barabas P, Huang W, Koehler C, Akimov NP, Lee SH, Chauhan S, Xing W, Rentería RC et al.. (2011) The polymodal ion channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 modulates calcium flux, spiking rate, and apoptosis of mouse retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci, 31 (19): 7089-101. [PMID:21562271]
43. Shao J, Han J, Zhu Y, Mao A, Wang Z, Zhang K, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Tang C, Ma X. (2019) Curcumin Induces Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation by Activating Endothelial TRPV4 Channels. J Cardiovasc Transl Res, 12 (6): 600-607. [PMID:31664615]
44. Sidhaye VK, Güler AD, Schweitzer KS, D'Alessio F, Caterina MJ, King LS. (2006) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 regulates aquaporin-5 abundance under hypotonic conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (12): 4747-52. [PMID:16537379]
45. Smith PL, Maloney KN, Pothen RG, Clardy J, Clapham DE. (2006) Bisandrographolide from Andrographis paniculata activates TRPV4 channels. J Biol Chem, 281 (40): 29897-904. [PMID:16899456]
46. Sokabe T, Fukumi-Tominaga T, Yonemura S, Mizuno A, Tominaga M. (2010) The TRPV4 channel contributes to intercellular junction formation in keratinocytes. J Biol Chem, 285 (24): 18749-58. [PMID:20413591]
47. Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD. (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol, 2 (10): 695-702. [PMID:11025659]
48. Strotmann R, Schultz G, Plant TD. (2003) Ca2+-dependent potentiation of the nonselective cation channel TRPV4 is mediated by a C-terminal calmodulin binding site. J Biol Chem, 278 (29): 26541-9. [PMID:12724311]
49. Suzuki M, Hirao A, Mizuno A. (2003) Microtubule-associated [corrected] protein 7 increases the membrane expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4). J Biol Chem, 278 (51): 51448-53. [PMID:14517216]
50. Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Kodaira K, Imai M. (2003) Impaired pressure sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. J Biol Chem, 278 (25): 22664-8. [PMID:12692122]
51. Tabuchi K, Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Hara A. (2005) Hearing impairment in TRPV4 knockout mice. Neurosci Lett, 382 (3): 304-8. [PMID:15925108]
52. Thorneloe KS, Cheung M, Bao W, Alsaid H, Lenhard S, Jian MY, Costell M, Maniscalco-Hauk K, Krawiec JA, Olzinski A et al.. (2012) An orally active TRPV4 channel blocker prevents and resolves pulmonary edema induced by heart failure. Sci Transl Med, 4 (159): 159ra148. [PMID:23136043]
53. Thorneloe KS, Sulpizio AC, Lin Z, Figueroa DJ, Clouse AK, McCafferty GP, Chendrimada TP, Lashinger ES, Gordon E, Evans L et al.. (2008) N-((1S)-1-{[4-((2S)-2-{[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoyl)-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl}-3-methylbutyl)-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide (GSK1016790A), a novel and potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel agonist induces urinary bladder contraction and hyperactivity: Part I. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 326 (2): 432-42. [PMID:18499743]
54. Tian W, Fu Y, Garcia-Elias A, Fernández-Fernández JM, Vicente R, Kramer PL, Klein RF, Hitzemann R, Orwoll ES, Wilmot B et al.. (2009) A loss-of-function nonsynonymous polymorphism in the osmoregulatory TRPV4 gene is associated with human hyponatremia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106 (33): 14034-9. [PMID:19666518]
55. Todaka H, Taniguchi J, Satoh J, Mizuno A, Suzuki M. (2004) Warm temperature-sensitive transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) plays an essential role in thermal hyperalgesia. J Biol Chem, 279 (34): 35133-8. [PMID:15187078]
56. Vincent F, Acevedo A, Nguyen MT, Dourado M, DeFalco J, Gustafson A, Spiro P, Emerling DE, Kelly MG, Duncton MA. (2009) Identification and characterization of novel TRPV4 modulators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 389 (3): 490-4. [PMID:19737537]
57. Voets T, Prenen J, Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Wissenbach U, Bödding M, Droogmans G, Nilius B. (2002) Molecular determinants of permeation through the cation channel TRPV4. J Biol Chem, 277 (37): 33704-10. [PMID:12093812]
58. Wang B, Wu Q, Liao J, Zhang S, Liu H, Yang C, Dong Q, Zhao N, Huang Z, Guo K et al.. (2019) Propofol Induces Cardioprotection Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Suppression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Channel. Front Pharmacol, 10: 1150. [PMID:31636563]
59. Wang Y, Fu X, Gaiser S, Köttgen M, Kramer-Zucker A, Walz G, Wegierski T. (2007) OS-9 regulates the transit and polyubiquitination of TRPV4 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem, 282 (50): 36561-70. [PMID:17932042]
60. Watanabe H, Davis JB, Smart D, Jerman JC, Smith GD, Hayes P, Vriens J, Cairns W, Wissenbach U, Prenen J et al.. (2002) Activation of TRPV4 channels (hVRL-2/mTRP12) by phorbol derivatives. J Biol Chem, 277 (16): 13569-77. [PMID:11827975]
61. Watanabe H, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B. (2003) Anandamide and arachidonic acid use epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to activate TRPV4 channels. Nature, 424 (6947): 434-8. [PMID:12879072]
62. Watanabe H, Vriens J, Suh SH, Benham CD, Droogmans G, Nilius B. (2002) Heat-evoked activation of TRPV4 channels in a HEK293 cell expression system and in native mouse aorta endothelial cells. J Biol Chem, 277 (49): 47044-51. [PMID:12354759]
63. Wei ZL, Nguyen MT, O'Mahony DJ, Acevedo A, Zipfel S, Zhang Q, Liu L, Dourado M, Chi C, Yip V et al.. (2015) Identification of orally-bioavailable antagonists of the TRPV4 ion-channel. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 25 (18): 4011-5. [PMID:26235950]
64. Willette RN, Bao W, Nerurkar S, Yue TL, Doe CP, Stankus G, Turner GH, Ju H, Thomas H, Fishman CE et al.. (2008) Systemic activation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 4 channel causes endothelial failure and circulatory collapse: Part 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 326 (2): 443-52. [PMID:18499744]
65. Wu L, Gao X, Brown RC, Heller S, O'Neil RG. (2007) Dual role of the TRPV4 channel as a sensor of flow and osmolality in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 293 (5): F1699-713. [PMID:17699550]
66. Xu F, Satoh E, Iijima T. (2003) Protein kinase C-mediated Ca2+ entry in HEK 293 cells transiently expressing human TRPV4. Br J Pharmacol, 140 (2): 413-21. [PMID:12970074]
67. Xu H, Zhao H, Tian W, Yoshida K, Roullet JB, Cohen DM. (2003) Regulation of a transient receptor potential (TRP) channel by tyrosine phosphorylation. SRC family kinase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of TRPV4 on TYR-253 mediates its response to hypotonic stress. J Biol Chem, 278 (13): 11520-7. [PMID:12538589]
68. Yan J, Ye F, Ju Y, Wang D, Chen J, Zhang X, Yin Z, Wang C, Yang Y, Zhu C et al.. (2021) Cimifugin relieves pruritus in psoriasis by inhibiting TRPV4. Cell Calcium, 97: 102429. [PMID:34087722]
69. Ye L, Kleiner S, Wu J, Sah R, Gupta RK, Banks AS, Cohen P, Khandekar MJ, Boström P, Mepani RJ et al.. (2012) TRPV4 is a regulator of adipose oxidative metabolism, inflammation, and energy homeostasis. Cell, 151 (1): 96-110. [PMID:23021218]
70. Zaika O, Mamenko M, Berrout J, Boukelmoune N, O'Neil RG, Pochynyuk O. (2013) TRPV4 dysfunction promotes renal cystogenesis in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol, 24 (4): 604-16. [PMID:23411787]
71. Zhang DX, Mendoza SA, Bubolz AH, Mizuno A, Ge ZD, Li R, Warltier DC, Suzuki M, Gutterman DD. (2009) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4-deficient mice exhibit impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in vitro and in vivo. Hypertension, 53 (3): 532-8. [PMID:19188524]
72. Zhou T, Wang Z, Guo M, Zhang K, Geng L, Mao A, Yang Y, Yu F. (2020) Puerarin induces mouse mesenteric vasodilation and ameliorates hypertension involving endothelial TRPV4 channels. Food Funct, 11 (11): 10137-10148. [PMID:33155599]

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb