GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 380 | 11q12.1 | APLNR | apelin receptor | 39 |
| Mouse | 7 | 377 | 2 D | Aplnr | apelin receptor | 11 |
| Rat | 7 | 377 | 3q24 | Aplnr | apelin receptor | 17,38 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| angiotensin receptor-like 1 | AGTRL1 | APJ | APJR | angiotensin II receptor-like 1 | B78 | GPCR34 | G-protein coupled receptor APJ | msr/apj |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | apj_human (Hs), apj_mouse (Mm), apj_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P35414 (Hs), Q9WV08 (Mm), Q9JHG3 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1628481 (Hs), CHEMBL4879524 (Mm), CHEMBL2398 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000134817 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000044338 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000009227 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 187 (Hs), 23796 (Mm), 83518 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000134817 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:187 (Hs), mmu:23796 (Mm), rno:83518 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600052 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P35414 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_005161 (Hs), NM_011784 (Mm), NM_031349 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_005152 (Hs), NP_035914 (Mm), NP_112639 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P35414 (Hs), Q9WV08 (Mm), Q9JHG3 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | APLNR (Hs) |
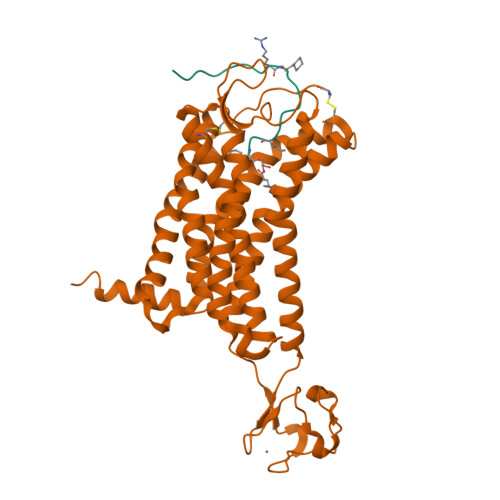
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| apelin-36 {Sp: Human} |
| apelin-13 {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| apelin-17 {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| apelin-36 {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| apelin receptor early endogenous ligand {Sp: Human} , apelin receptor early endogenous ligand {Sp: Mouse} |
| Elabela/Toddler-32 {Sp: Human} |
| Elabela/Toddler-21 {Sp: Human} |
| Elabela/Toddler-11 {Sp: Human} |
| [Pyr1]apelin-13 {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| [Pyr1]apelin-13 (APLN, Q9ULZ1) ≥ apelin-13 (APLN, Q9ULZ1) > apelin-36 (APLN, Q9ULZ1) [13,48] |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affinity/potency values for APT-101 are not available. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALX40-4C is also an antagonist of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and binds to the second extracellular loop of this receptor. (Ala13)-apelin-13 is the first reported functional antagonist that blocks the hypotensive actions of apelin in a dose dependent manner. However, pIC50 values were not reported in this study [26]. Binding data for antagonist ML221 are not available [29]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| The apelin receptor gene (APLNR) has been identified as one of a number of genes necessary to confer suceptibility of cancer cells to immunotherapy (i.e. T cell recognition and cytolysis) [40]. This effect is likely mediated by apelin receptor/JAK1 upregulation of the IFN-γ response that appears to promote antigen processing and presentation by tumours, and which improves the ability of T cells to recognize and attack the cancer cells. Defects in IFN-γ signalling is a recognised mechanism underlying resistance to immunotherapy [30]. The authors of [40] show that functional loss of APLNR in mouse models reduces the efficacy of immunotherapies (both adoptive cell transfer and checkpoint blockade) and is indicative of poor prognosis. |
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family | Adenylyl cyclase inhibition |
| Comments: Downstream of Gi activation apelin triggers a sharp increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels and activates ERKs via a PKC dependent pathway. Apelin dependent activation of ERK and PI3Kinase leads to activation of p70S6 kinase in endothelial cells. | |
| References: 8,15,17,32-33 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| The biology of the apelin receptor system has recently been comprehensively reviewed in the works of Kleinz et al. (2005) and Masri et al. (2005) [23,31]. |
References
1. Ashley EA, Powers J, Chen M, Kundu R, Finsterbach T, Caffarelli A, Deng A, Eichhorn J, Mahajan R, Agrawal R et al.. (2005) The endogenous peptide apelin potently improves cardiac contractility and reduces cardiac loading in vivo. Cardiovasc Res, 65 (1): 73-82. [PMID:15621035]
2. Ason B, Chen Y, Guo Q, Hoagland KM, Chui RW, Fielden M, Sutherland W, Chen R, Zhang Y, Mihardja S et al.. (2020) Cardiovascular response to small-molecule APJ activation. JCI Insight, 5 (8). [PMID:32208384]
3. Berry MF, Pirolli TJ, Jayasankar V, Burdick J, Morine KJ, Gardner TJ, Woo YJ. (2004) Apelin has in vivo inotropic effects on normal and failing hearts. Circulation, 110 (11 Suppl 1): II187-93. [PMID:15364861]
4. Brame AL, Maguire JJ, Yang P, Dyson A, Torella R, Cheriyan J, Singer M, Glen RC, Wilkinson IB, Davenport AP. (2015) Design, characterization, and first-in-human study of the vascular actions of a novel biased apelin receptor agonist. Hypertension, 65 (4): 834-40. [PMID:25712721]
5. Cayabyab M, Hinuma S, Farzan M, Choe H, Fukusumi S, Kitada C, Nishizawa N, Hosoya M, Nishimura O, Messele T et al.. (2000) Apelin, the natural ligand of the orphan seven-transmembrane receptor APJ, inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 entry. J Virol, 74 (24): 11972-6. [PMID:11090199]
6. Chen N, Chen X, Chen Y, Cheng AC, Connors RV, Deignan J, Dransfield PJ, Du X, Fu Z, Heath JA et al.. (2016) Triazole agonists of the apj receptor. Patent number: WO2016187308A1. Assignee: Amgen Inc.. Priority date: 20/05/2015. Publication date: 24/11/2016.
7. Cheng X, Cheng XS, Pang CC. (2003) Venous dilator effect of apelin, an endogenous peptide ligand for the orphan APJ receptor, in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol, 470 (3): 171-5. [PMID:12798955]
8. Choe W, Albright A, Sulcove J, Jaffer S, Hesselgesser J, Lavi E, Crino P, Kolson DL. (2000) Functional expression of the seven-transmembrane HIV-1 co-receptor APJ in neural cells. J Neurovirol, 6 Suppl 1: S61-9. [PMID:10871767]
9. De Mota N, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, El Messari S, Chartrel N, Roesch D, Dujardin C, Kordon C, Vaudry H, Moos F, Llorens-Cortes C. (2004) Apelin, a potent diuretic neuropeptide counteracting vasopressin actions through inhibition of vasopressin neuron activity and vasopressin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101 (28): 10464-9. [PMID:15231996]
10. Deng C, Chen H, Yang N, Feng Y, Hsueh AJ. (2015) Apela Regulates Fluid Homeostasis by Binding to the APJ Receptor to Activate Gi Signaling. J Biol Chem, 290 (30): 18261-8. [PMID:25995451]
11. Devic E, Rizzoti K, Bodin S, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. (1999) Amino acid sequence and embryonic expression of msr/apj, the mouse homolog of Xenopus X-msr and human APJ. Mech Dev, 84 (1-2): 199-203. [PMID:10473142]
12. El Messari S, Iturrioz X, Fassot C, De Mota N, Roesch D, Llorens-Cortes C. (2004) Functional dissociation of apelin receptor signaling and endocytosis: implications for the effects of apelin on arterial blood pressure. J Neurochem, 90 (6): 1290-301. [PMID:15341513]
13. Fan X, Zhou N, Zhang X, Mukhtar M, Lu Z, Fang J, DuBois GC, Pomerantz RJ. (2003) Structural and functional study of the apelin-13 peptide, an endogenous ligand of the HIV-1 coreceptor, APJ. Biochemistry, 42 (34): 10163-8. [PMID:12939143]
14. Gargalovic P, Wong P, Onorato J, Finlay H, Wang T, Yan M, Crain E, St-Onge S, Héroux M, Bouvier M et al.. (2021) In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Small-Molecule APJ (Apelin Receptor) Agonist, BMS-986224, as a Potential Treatment for Heart Failure. Circ Heart Fail, 14 (3): e007351. [PMID:33663236]
15. Habata Y, Fujii R, Hosoya M, Fukusumi S, Kawamata Y, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Nishizawa N, Murosaki S, Kurokawa T et al.. (1999) Apelin, the natural ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, is abundantly secreted in the colostrum. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1452 (1): 25-35. [PMID:10525157]
16. Hamada J, Kimura J, Ishida J, Kohda T, Morishita S, Ichihara S, Fukamizu A. (2008) Evaluation of novel cyclic analogues of apelin. Int J Mol Med, 22 (4): 547-52. [PMID:18813863]
17. Hosoya M, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Fujii R, Habata Y, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Honda S, Kurokawa T, Onda H et al.. (2000) Molecular and functional characteristics of APJ. Tissue distribution of mRNA and interaction with the endogenous ligand apelin. J Biol Chem, 275 (28): 21061-7. [PMID:10777510]
18. Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y, Nishiwaki S, Iguchi T, Harada S, Sugaya T, Matsuzaki H, Yamamoto R, Shiota N et al.. (2004) Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure in vivo. J Biol Chem, 279 (25): 26274-9. [PMID:15087458]
19. Iturrioz X, Alvear-Perez R, De Mota N, Franchet C, Guillier F, Leroux V, Dabire H, Le Jouan M, Chabane H, Gerbier R et al.. (2010) Identification and pharmacological properties of E339-3D6, the first nonpeptidic apelin receptor agonist. FASEB J, 24 (5): 1506-17. [PMID:20040517]
20. Katugampola SD, Maguire JJ, Matthewson SR, Davenport AP. (2001) [(125)I]-(Pyr(1))Apelin-13 is a novel radioligand for localizing the APJ orphan receptor in human and rat tissues with evidence for a vasoconstrictor role in man. Br J Pharmacol, 132 (6): 1255-60. [PMID:11250876]
21. Kawamata Y, Habata Y, Fukusumi S, Hosoya M, Fujii R, Hinuma S, Nishizawa N, Kitada C, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M. (2001) Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1538: 162-171. [PMID:11336787]
22. Khan P, Maloney PR, Hedrick M, Gosalia P, Milewski M, Li L, Roth GP, Sergienko E, Suyama E, Sugarman E et al.. (2011) Functional Agonists of the Apelin (APJ) Receptor. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program,. [PMID:22834038]
23. Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP. (2005) Emerging roles of apelin in biology and medicine. Pharmacol Ther, 107 (2): 198-211. [PMID:15907343]
24. Kleinz MJ, Skepper JN, Davenport AP. (2005) Immunocytochemical localisation of the apelin receptor, APJ, to human cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Regul Pept, 126 (3): 233-40. [PMID:15664671]
25. Lee DK, Cheng R, Nguyen T, Fan T, Kariyawasam AP, Liu Y, Osmond DH, George SR, O'Dowd BF. (2000) Characterization of apelin, the ligand for the APJ receptor. J Neurochem, 74 (1): 34-41. [PMID:10617103]
26. Lee DK, Saldivia VR, Nguyen T, Cheng R, George SR, O'Dowd BF. (2005) Modification of the terminal residue of apelin-13 antagonizes its hypotensive action. Endocrinology, 146 (1): 231-6. [PMID:15486224]
27. Ma Y, Yue Y, Ma Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Q, Song Y, Shen Y, Li X, Ma X, Li C et al.. (2017) Structural Basis for Apelin Control of the Human Apelin Receptor. Structure, 25 (6): 858-866.e4. [PMID:28528775]
28. Macaluso NJ, Pitkin SL, Maguire JJ, Davenport AP, Glen RC. (2011) Discovery of a competitive apelin receptor (APJ) antagonist. ChemMedChem, 6 (6): 1017-23. [PMID:21560248]
29. Maloney PR, Khan P, Hedrick M, Gosalia P, Milewski M, Li L, Roth GP, Sergienko E, Suyama E, Sugarman E et al.. (2012) Discovery of 4-oxo-6-((pyrimidin-2-ylthio)methyl)-4H-pyran-3-yl 4-nitrobenzoate (ML221) as a functional antagonist of the apelin (APJ) receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (21): 6656-60. [PMID:23010269]
30. Manguso RT, Pope HW, Zimmer MD, Brown FD, Yates KB, Miller BC, Collins NB, Bi K, LaFleur MW, Juneja VR et al.. (2017) In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target. Nature, 547 (7664): 413-418. [PMID:28723893]
31. Masri B, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. (2005) Apelin signalling: a promising pathway from cloning to pharmacology. Cell Signal, 17 (4): 415-26. [PMID:15601620]
32. Masri B, Lahlou H, Mazarguil H, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. (2002) Apelin (65-77) activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases via a PTX-sensitive G protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 290 (1): 539-45. [PMID:11779205]
33. Masri B, Morin N, Cornu M, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y. (2004) Apelin (65-77) activates p70 S6 kinase and is mitogenic for umbilical endothelial cells. FASEB J, 18 (15): 1909-11. [PMID:15385434]
34. McKeown SC, Zecri FJ, Fortier E, Taggart A, Sviridenko L, Adams CM, McAllister KH, Pin SS. (2014) The design and implementation of a generic lipopeptide scanning platform to enable the identification of 'locally acting' agonists for the apelin receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 24 (20): 4871-5. [PMID:25241924]
35. Medhurst AD, Jennings CA, Robbins MJ, Davis RP, Ellis C, Winborn KY, Lawrie KW, Hervieu G, Riley G, Bolaky JE, Herrity NC, Murdock P, Darker JG. (2003) Pharmacological and immunohistochemical characterization of the APJ receptor and its endogenous ligand apelin. J Neurochem, 84: 1162-1172. [PMID:12603839]
36. Meng W, Pi Z, Brigance R, Rossi KA, Schumacher WA, Bostwick JS, Gargalovic PS, Onorato JM, Luk CE, Generaux CN et al.. (2021) Identification of a Hydroxypyrimidinone Compound (21) as a Potent APJ Receptor Agonist for the Potential Treatment of Heart Failure. J Med Chem, 64 (24): 18102-18113. [PMID:34855405]
37. Narayanan S, Vasukuttan V, Laudermilk L, Snyder RW, Yueh YL, Gay EA, Runyon SP, Maitra R. (2025) Development of Central Nervous System-Penetrant Apelin Receptor Agonists. J Med Chem, 68 (21): 22312-22332. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c01176 [PMID:41114538]
38. O'Carroll AM, Selby TL, Palkovits M, Lolait SJ. (2000) Distribution of mRNA encoding B78/apj, the rat homologue of the human APJ receptor, and its endogenous ligand apelin in brain and peripheral tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1492 (1): 72-80. [PMID:11004481]
39. O'Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Kennedy JL, Shi X, Petronis A, George SR, Nguyen T. (1993) A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene, 136 (1-2): 355-60. [PMID:8294032]
40. Patel SJ, Sanjana NE, Kishton RJ, Eidizadeh A, Vodnala SK, Cam M, Gartner JJ, Jia L, Steinberg SM, Yamamoto TN et al.. (2017) Identification of essential genes for cancer immunotherapy. Nature, 548 (7669): 537-542. [PMID:28783722]
41. Pi Z, Johnson JA, Meng W, Phillips M, Schumacher WA, Bostwick JS, Gargalovic PS, Onorato JM, Generaux CN, Wang T et al.. (2021) Identification of 6-Hydroxypyrimidin-4(1H)-one-3-carboxamides as Potent and Orally Active APJ Receptor Agonists. ACS Med Chem Lett, 12 (11): 1766-1772. [PMID:34795866]
42. Read C, Fitzpatrick CM, Yang P, Kuc RE, Maguire JJ, Glen RC, Foster RE, Davenport AP. (2016) Cardiac action of the first G protein biased small molecule apelin agonist. Biochem Pharmacol, 116: 63-72. [PMID:27475715]
43. Reaux A, De Mota N, Skultetyova I, Lenkei Z, El Messari S, Gallatz K, Corvol P, Palkovits M, Llorens-Cortès C. (2001) Physiological role of a novel neuropeptide, apelin, and its receptor in the rat brain. J Neurochem, 77 (4): 1085-96. [PMID:11359874]
44. Runyon SP, Maitra R, Narayanan S, Thomas JB, Rehder KSm Olepu S. (2017) Improved apelin receptor (apj) agonists and uses thereof. Patent number: WO2017100558A1. Assignee: RTI International Inc. Priority date: 09/12/2016. Publication date: 15/06/2017.
45. Su S, Clarke A, Han Y, Chao HJ, Bostwick J, Schumacher W, Wang T, Yan M, Hsu MY, Simmons E et al.. (2019) Biphenyl Acid Derivatives as APJ Receptor Agonists. J Med Chem, 62 (22): 10456-10465. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01513 [PMID:31724863]
46. Szokodi I, Tavi P, Földes G, Voutilainen-Myllylä S, Ilves M, Tokola H, Pikkarainen S, Piuhola J, Rysä J, Tóth M et al.. (2002) Apelin, the novel endogenous ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, regulates cardiac contractility. Circ Res, 91 (5): 434-40. [PMID:12215493]
47. Taheri S, Murphy K, Cohen M, Sujkovic E, Kennedy A, Dhillo W, Dakin C, Sajedi A, Ghatei M, Bloom S. (2002) The effects of centrally administered apelin-13 on food intake, water intake and pituitary hormone release in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 291 (5): 1208-12. [PMID:11883945]
48. Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C et al.. (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 251 (2): 471-6. [PMID:9792798]
49. Tatemoto K, Takayama K, Zou MX, Kumaki I, Zhang W, Kumano K, Fujimiya M. (2001) The novel peptide apelin lowers blood pressure via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Regul Pept, 99 (2-3): 87-92. [PMID:11384769]
50. Tran K, Sainsily X, Côté J, Coquerel D, Couvineau P, Saibi S, Haroune L, Besserer-Offroy É, Flynn-Robitaille J, Resua Rojas M et al.. (2022) Size-Reduced Macrocyclic Analogues of [Pyr1]-apelin-13 Showing Negative Gα12 Bias Still Produce Prolonged Cardiac Effects. J Med Chem, 65 (1): 531-551. [PMID:34982553]
51. Yang P, Maguire JJ, Kuc RE, Siew K, Haris L, Torella R, Glen RC, Davenport AP. ELABELA/Toddler, a critical regulator of cardiac development, is expressed in the human cardiovascular system and binds the apelin receptor. Accessed on 07/07/2015. Modified on 07/07/2015. https://bit.ly/2RpvLqB
52. Zhou N, Fan X, Mukhtar M, Fang J, Patel CA, DuBois GC, Pomerantz RJ. (2003) Cell-cell fusion and internalization of the CNS-based, HIV-1 co-receptor, APJ. Virology, 307 (1): 22-36. [PMID:12667811]
53. Zou MX, Liu HY, Haraguchi Y, Soda Y, Tatemoto K, Hoshino H. (2000) Apelin peptides block the entry of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett, 473 (1): 15-8. [PMID:10802050]

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb