GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
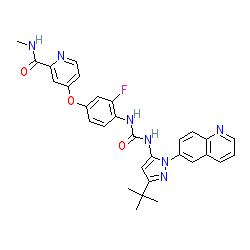
Synonyms: DCC 2036 | DCC-2036 | DP-1919
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Rebastinib (DCC-2036) is an investigational orally administered kinase inhibitor, with activity against FLT3-ITD, TIE2, KDR, LYN, BCR-ABL and TRKA kinases. Yes1 inhibition is reported in [6]. This compound has been termed a switch-control inhibitor as it binds to residues Arg386/Glu282 which ABL1 uses to switch between inactive and active conformations [1,3]. Rebastinib inhibits native and phosphphorylated ABL by inducing a type II inactive conformation [1].
It is one of the compounds claimed in patent WO2008046003 [7] and subsequent related patent applications. Rebastinib appears to be Example 1, whilst acknowledging the limitations and complexities applied in compound naming and structure provision in the patent document. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Rebastinib's inhibitory activity against the immunokinase TIE2 is being evaluated (in combinations with chemotherapeutics) in clinical trials in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumours. TIE2 is the receptor for angiopoietins and it is expressed by a subset of pro-tumoural M2 macrophages (TIE2 expressing macrophages, or TEMs). The TIE2/angiopoietin pathway plays an important role in regulating tumour angiogenesis, invasiveness, metastasis, and immunotolerance. Rebastinib blocks recruitment and function of these TIE2 +ve macrophages to tumours, and effects reductions in tumour growth and metastasis in in vivo models of metastatic cancer [4]. |