GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
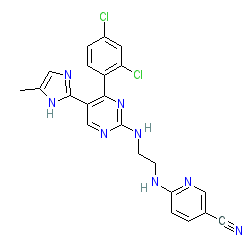
Synonyms: CHIR 99021 | CHIR-99021 | CHIR99021 | CT-99021 | CT99021
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3α and β (GSK-3α/β), equipotent at both isozymes [8]. The chemical structure of CHIR-99021 matches that submitted to the WHO for the INN laduviglusib. GSK-3β has been implicated in multiple human disorders, by influencing a number of significant cellular pathways (including insulin signalling and glycogen synthesis, neurotrophic factor signalling, Wnt signalling, neurotransmitter signalling and microtubule dynamics) [1]. CHIR-99021 acts as a functional Wnt pathway activator [2,10].
Zaki syndrome, a rare disorder of embryonic organ development in humans, can arise due to homozygous mutations in the Wnt ligand secretion mediator gene (WLS) [4]. CHIR-99021 has been used in a mouse model of Zaki syndrome to demonstrate that activation of Wnt pathway signalling can partially restore embryonic development [4]. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. An WF, Germain AR, Bishop JA, Nag PP, Metkar S, Ketterman J, Walk M, Weiwer M, Liu X, Patnaik D et al.. (2010)
Discovery of Potent and Highly Selective Inhibitors of GSK3b. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program,. [PMID:23658955] |
|
2. Badimon L, Casaní L, Camino-Lopez S, Juan-Babot O, Borrell-Pages M. (2019)
GSK3β inhibition and canonical Wnt signaling in mice hearts after myocardial ischemic damage. PLoS ONE, 14 (6): e0218098. [PMID:31220102] |
|
3. Cai Z, Zhao Y, Zhao B. (2012)
Roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res, 9 (7): 864-79. [PMID:22272620] |
|
4. Chai G, Szenker-Ravi E, Chung C, Li Z, Wang L, Khatoo M, Marshall T, Jiang N, Yang X, McEvoy-Venneri J et al.. (2021)
A Human Pleiotropic Multiorgan Condition Caused by Deficient Wnt Secretion. N Engl J Med, 385 (14): 1292-1301. [PMID:34587386] |
|
5. Eldar-Finkelman H, Schreyer SA, Shinohara MM, LeBoeuf RC, Krebs EG. (1999)
Increased glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity in diabetes- and obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes, 48 (8): 1662-6. [PMID:10426388] |
|
6. Hurtado DE, Molina-Porcel L, Carroll JC, Macdonald C, Aboagye AK, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. (2012)
Selectively silencing GSK-3 isoforms reduces plaques and tangles in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci, 32 (21): 7392-402. [PMID:22623685] |
|
7. Nikoulina SE, Ciaraldi TP, Mudaliar S, Mohideen P, Carter L, Henry RR. (2000)
Potential role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in skeletal muscle insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 49 (2): 263-71. [PMID:10868943] |
|
8. Ring DB, Johnson KW, Henriksen EJ, Nuss JM, Goff D, Kinnick TR, Ma ST, Reeder JW, Samuels I, Slabiak T et al.. (2003)
Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes, 52 (3): 588-95. [PMID:12606497] |
|
9. Takashima A, Noguchi K, Sato K, Hoshino T, Imahori K. (1993)
Tau protein kinase I is essential for amyloid beta-protein-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (16): 7789-93. [PMID:8356085] |
|
10. Yoshida Y, Soma T, Matsuzaki T, Kishimoto J. (2019)
Wnt activator CHIR99021-stimulated human dermal papilla spheroids contribute to hair follicle formation and production of reconstituted follicle-enriched human skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 516 (3): 599-605. [PMID:31221480] |