GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
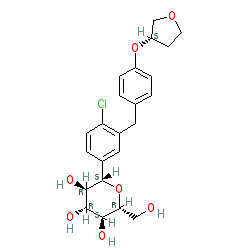
Synonyms: BI 10773 | Jardiance®
empagliflozin is an approved drug (FDA & EMA (2014))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Empagliflozin is a member of the 'gliflozin' class of drugs which inhibit reabsorption of glucose in the kidney to lower blood sugar.
It is the first glucose-lowering, antidiabetes therapy to be granted approval to reduce the risk of cardiovascular (CV) death in type 2 diabetes patients with CV disease. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: Empagliflozin was added to the RECOVERY trial (NCT04381936) in July 2021, to determine if using empagliflozin to correct metabolic dysregulation caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection can protect against organ damage and improve recovery in COVID-19 patients. This was predicated by results of a study exploring dapagliflozin-mediated organ protection, which found that the drug elicited a non-significant reduction in the risk of organ failure or death in COVID-19 patients [4]. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: empagliflozin |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Abdul-Ghani MA, DeFronzo RA. (2008)
Inhibition of renal glucose reabsorption: a novel strategy for achieving glucose control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract, 14 (6): 782-90. [PMID:18996802] |
|
2. Bays H. (2009)
From victim to ally: the kidney as an emerging target for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin, 25 (3): 671-81. [PMID:19232040] |
|
3. Grempler R, Thomas L, Eckhardt M, Himmelsbach F, Sauer A, Sharp DE, Bakker RA, Mark M, Klein T, Eickelmann P. (2012)
Empagliflozin, a novel selective sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor: characterisation and comparison with other SGLT-2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes Metab, 14 (1): 83-90. [PMID:21985634] |
|
4. Kosiborod MN, Esterline R, Furtado RHM, Oscarsson J, Gasparyan SB, Koch GG, Martinez F, Mukhtar O, Verma S, Chopra V et al.. (2021)
Dapagliflozin in patients with cardiometabolic risk factors hospitalised with COVID-19 (DARE-19): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 9 (9): 586-594. [PMID:34302745] |
|
5. Nair S, Wilding JP. (2010)
Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as a new treatment for diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 95 (1): 34-42. [PMID:19892839] |
|
6. RECOVERY Trial team.
Empagliflozin to be investigated as a possible treatment for COVID-19 in the RECOVERY trial. Accessed on 28/07/2021. Modified on 28/07/2021. recoverytrial.net, https://www.recoverytrial.net/news/empagliflozin-to-be-investigated-as-a-possible-treatment-for-covid-19-in-the-recovery-trial |
|
7. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ et al.. (2015)
Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med, 373 (22): 2117-28. [PMID:26378978] |