GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
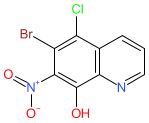
Synonyms: ASN-1733 | MET-102
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: APL-2301 is a nitroxoline derivative with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity [2]. It is being developed to target infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| APL-2301 has approval in Australia for a first-in-human Phase 1 trial (last update December 2023) [1]. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| APL-2301 has a dual mechanism of action [2]. It binds Ca2+ on the surface of bacteria, causing detachment of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and thus disrupting the integrity of the bacterial outer membrane, leading to broad-spectrum bactericidal activity. APL-2301 also demonstrates potent inhibition of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1), via a novel competitive mechanism. |