GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Voltage Dependence
- Gating Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Gene Expression and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 24 | 1 | 2377 | 17q21.33 | CACNA1G | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 G | 30 |
| Mouse | 24 | 1 | 2295 | 11 D | Cacna1g | calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit | 22 |
| Rat | 24 | 1 | 2254 | 10q26 | Cacna1g | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 G | 33 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| NBR13 | alpha-1G | calcium channel |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | O43497 (Hs), O54898 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4641 (Hs), CHEMBL4257 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | O43497 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000006283 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000020866 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000060528 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 8913 (Hs), 12291 (Mm), 29717 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000006283 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:8913 (Hs), mmu:12291 (Mm), rno:29717 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 604065 (Hs) |
| Pharos | O43497 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_198379 (Hs), NM_198387 (Hs), NM_198376 (Hs), NM_198378 (Hs), NM_009783 (Mm), NM_031601 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_938190 (Hs), NP_061496 (Hs), NP_938193 (Hs), NP_938201 (Hs), NP_938192 (Hs), NP_033913 (Mm), NP_113789 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | O43497 (Hs), O54898 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | CACNA1G (Hs) |
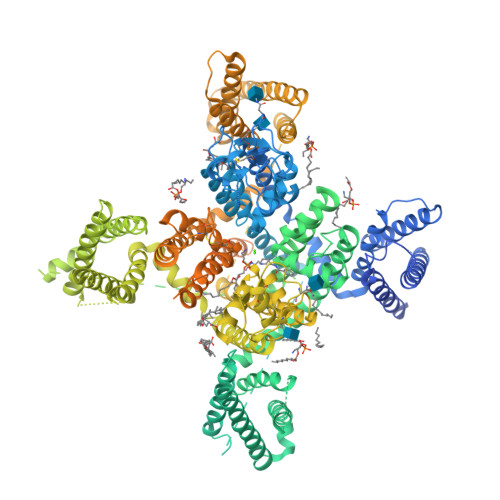
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Functional Characteristics  |
|
| T-type calcium current: Low voltage-activated, fast voltage-dependent inactivation | |
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
|
Voltage Dependence  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
Gating inhibitors 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kurtoxin was selective for recombinant channels expressed in oocytes, but not for native T-currents in thalamocortical cells [6,39]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block by Ni2+ is voltage dependent [23]. ML218 was developed by NIH’s Molecular Libraries Production Center and is freely available without intellectual property restrictions [45]. Like many compounds listed, its potency on Cav3.1 has not been reported, but is expected to be similar to its block of Cav3.2 and Cav3.3. For reviews of all known blockers see references [15,18,28]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Low-voltage-activated Cav3.1 calcium channels are involved in shaping the autoimmune response elicited by T cells by modulating their cytokine production profile [44]. |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||
|
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Physiological Functions Comments | ||||||||
| The above references are examples for each function. For further references see [32]. | ||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Expression and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
References
1. Bezençon O, Heidmann B, Siegrist R, Stamm S, Richard S, Pozzi D, Corminboeuf O, Roch C, Kessler M, Ertel EA et al.. (2017) Discovery of a Potent, Selective T-type Calcium Channel Blocker as a Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Generalized Epilepsies. J Med Chem, 60 (23): 9769-9789. [PMID:29116786]
2. Chemin J, Monteil A, Bourinet E, Nargeot J, Lory P. (2001) Alternatively spliced alpha(1G) (Ca(V)3.1) intracellular loops promote specific T-type Ca(2+) channel gating properties. Biophys J, 80 (3): 1238-50. [PMID:11222288]
3. Chemin J, Monteil A, Perez-Reyes E, Nargeot J, Lory P. (2001) Direct inhibition of T-type calcium channels by the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide. EMBO J, 20 (24): 7033-40. [PMID:11742980]
4. Chemin J, Siquier-Pernet K, Nicouleau M, Barcia G, Ahmad A, Medina-Cano D, Hanein S, Altin N, Hubert L, Bole-Feysot C et al.. (2018) De novo mutation screening in childhood-onset cerebellar atrophy identifies gain-of-function mutations in the CACNA1G calcium channel gene. Brain, 141 (7): 1998-2013. [PMID:29878067]
5. Choe W, Messinger RB, Leach E, Eckle VS, Obradovic A, Salajegheh R, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM. (2011) TTA-P2 is a potent and selective blocker of T-type calcium channels in rat sensory neurons and a novel antinociceptive agent. Mol Pharmacol, 80 (5): 900-10. [PMID:21821734]
6. Chuang RS, Jaffe H, Cribbs L, Perez-Reyes E, Swartz KJ. (1998) Inhibition of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels by a new scorpion toxin. Nat Neurosci, 1 (8): 668-74. [PMID:10196582]
7. Coulter DA, Huguenard JR, Prince DA. (1989) Calcium currents in rat thalamocortical relay neurones: kinetic properties of the transient, low-threshold current. J Physiol (Lond.), 414: 587-604. [PMID:2607443]
8. Coulter DA, Huguenard JR, Prince DA. (1989) Characterization of ethosuximide reduction of low-threshold calcium current in thalamic neurons. Ann Neurol, 25 (6): 582-93. [PMID:2545161]
9. Coutelier M, Blesneac I, Monteil A, Monin ML, Ando K, Mundwiller E, Brusco A, Le Ber I, Anheim M, Castrioto A et al.. (2015) A Recurrent Mutation in CACNA1G Alters Cav3.1 T-Type Calcium-Channel Conduction and Causes Autosomal-Dominant Cerebellar Ataxia. Am J Hum Genet, 97 (5): 726-37. [PMID:26456284]
10. Craig PJ, Beattie RE, Folly EA, Banerjee MD, Reeves MB, Priestley JV, Carney SL, Sher E, Perez-Reyes E, Volsen SG. (1999) Distribution of the voltage-dependent calcium channel alpha1G subunit mRNA and protein throughout the mature rat brain. Eur J Neurosci, 11 (8): 2949-64. [PMID:10457190]
11. Du Nguyen H, Okada T, Kitamura S, Yamaoka S, Horaguchi Y, Kasanami Y, Sekiguchi F, Tsubota M, Yoshida S, Nishikawa H et al.. (2018) Design and synthesis of novel anti-hyperalgesic agents based on 6-prenylnaringenin as the T-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem, 26 (15): 4410-4427. [PMID:30031654]
12. Emerick MC, Stein R, Kunze R, McNulty MM, Regan MR, Hanck DA, Agnew WS. (2006) Profiling the array of Ca(v)3.1 variants from the human T-type calcium channel gene CACNA1G: alternative structures, developmental expression, and biophysical variations. Proteins, 64 (2): 320-42. [PMID:16671074]
13. Francois A, Kerckhove N, Meleine M, Alloui A, Barrere C, Gelot A, Uebele VN, Renger JJ, Eschalier A, Ardid D et al.. (2013) State-dependent properties of a new T-type calcium channel blocker enhance Ca(V)3.2 selectivity and support analgesic effects. Pain, 154 (2): 283-93. [PMID:23257507]
14. Furukawa T, Miura R, Honda M, Kamiya N, Mori Y, Takeshita S, Isshiki T, Nukada T. (2004) Identification of R(-)-isomer of efonidipine as a selective blocker of T-type Ca2+ channels. Br J Pharmacol, 143 (8): 1050-7. [PMID:15545287]
15. Giordanetto F, Knerr L, Wållberg A. (2011) T-type calcium channels inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 21 (1): 85-101. [PMID:21087200]
16. Gomora JC, Daud AN, Weiergräber M, Perez-Reyes E. (2001) Block of cloned human T-type calcium channels by succinimide antiepileptic drugs. Mol Pharmacol, 60 (5): 1121-32. [PMID:11641441]
17. Gomora JC, Murbartián J, Arias JM, Lee JH, Perez-Reyes E. (2002) Cloning and expression of the human T-type channel Ca(v)3.3: insights into prepulse facilitation. Biophys J, 83 (1): 229-41. [PMID:12080115]
18. Heady TN, Gomora JC, Macdonald TL, Perez-Reyes E. (2001) Molecular pharmacology of T-type Ca2+ channels. Jpn J Pharmacol, 85 (4): 339-50. [PMID:11388636]
19. Jarvis MF, Scott VE, McGaraughty S, Chu KL, Xu J, Niforatos W, Milicic I, Joshi S, Zhang Q, Xia Z. (2014) A peripherally acting, selective T-type calcium channel blocker, ABT-639, effectively reduces nociceptive and neuropathic pain in rats. Biochem Pharmacol, 89 (4): 536-44. [PMID:24726441]
20. Kim D, Song I, Keum S, Lee T, Jeong MJ, Kim SS, McEnery MW, Shin HS. (2001) Lack of the burst firing of thalamocortical relay neurons and resistance to absence seizures in mice lacking alpha(1G) T-type Ca(2+) channels. Neuron, 31 (1): 35-45. [PMID:11498049]
21. Klassen T, Davis C, Goldman A, Burgess D, Chen T, Wheeler D, McPherson J, Bourquin T, Lewis L, Villasana D et al.. (2011) Exome sequencing of ion channel genes reveals complex profiles confounding personal risk assessment in epilepsy. Cell, 145 (7): 1036-48. [PMID:21703448]
22. Klugbauer N, Marais E, Lacinová L, Hofmann F. (1999) A T-type calcium channel from mouse brain. Pflugers Arch, 437 (5): 710-5. [PMID:10087148]
23. Lee JH, Gomora JC, Cribbs LL, Perez-Reyes E. (1999) Nickel block of three cloned T-type calcium channels: low concentrations selectively block alpha1H. Biophys J, 77 (6): 3034-42. [PMID:10585925]
24. Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ et al.. (2007) Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature, 445 (7124): 168-76. [PMID:17151600]
25. Mangoni ME, Traboulsie A, Leoni AL, Couette B, Marger L, Le Quang K, Kupfer E, Cohen-Solal A, Vilar J, Shin HS et al.. (2006) Bradycardia and slowing of the atrioventricular conduction in mice lacking CaV3.1/alpha1G T-type calcium channels. Circ Res, 98 (11): 1422-30. [PMID:16690884]
26. Marionneau C, Couette B, Liu J, Li H, Mangoni ME, Nargeot J, Lei M, Escande D, Demolombe S. (2005) Specific pattern of ionic channel gene expression associated with pacemaker activity in the mouse heart. J Physiol, 562 (Pt 1): 223-34. [PMID:15498808]
27. Martin RL, Lee JH, Cribbs LL, Perez-Reyes E, Hanck DA. (2000) Mibefradil block of cloned T-type calcium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 295 (1): 302-8. [PMID:10991994]
28. McGivern JG. (2006) Pharmacology and drug discovery for T-type calcium channels. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 5 (6): 587-603. [PMID:17168744]
29. McKay BE, McRory JE, Molineux ML, Hamid J, Snutch TP, Zamponi GW, Turner RW. (2006) Ca(V)3 T-type calcium channel isoforms differentially distribute to somatic and dendritic compartments in rat central neurons. Eur J Neurosci, 24 (9): 2581-94. [PMID:17100846]
30. Monteil A, Chemin J, Bourinet E, Mennessier G, Lory P, Nargeot J. (2000) Molecular and functional properties of the human alpha(1G) subunit that forms T-type calcium channels. J Biol Chem, 275 (9): 6090-100. [PMID:10692398]
31. Morino H, Matsuda Y, Muguruma K, Miyamoto R, Ohsawa R, Ohtake T, Otobe R, Watanabe M, Maruyama H, Hashimoto K et al.. (2015) A mutation in the low voltage-gated calcium channel CACNA1G alters the physiological properties of the channel, causing spinocerebellar ataxia. Mol Brain, 8: 89. [PMID:26715324]
32. Perez-Reyes E. (2003) Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol Rev, 83 (1): 117-61. [PMID:12506128]
33. Perez-Reyes E, Cribbs LL, Daud A, Lacerda AE, Barclay J, Williamson MP, Fox M, Rees M, Lee JH. (1998) Molecular characterization of a neuronal low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channel. Nature, 391 (6670): 896-900. [PMID:9495342]
34. Remen L, Bezençon O, Simons L, Gaston R, Downing D, Gatfield J, Roch C, Kessler M, Mosbacher J, Pfeifer T et al.. (2016) Preparation, Antiepileptic Activity, and Cardiovascular Safety of Dihydropyrazoles as Brain-Penetrant T-Type Calcium Channel Blockers. J Med Chem, 59 (18): 8398-411. [PMID:27579577]
35. Santi CM, Cayabyab FS, Sutton KG, McRory JE, Mezeyova J, Hamming KS, Parker D, Stea A, Snutch TP. (2002) Differential inhibition of T-type calcium channels by neuroleptics. J Neurosci, 22 (2): 396-403. [PMID:11784784]
36. Shcheglovitov AK, Boldyrev AI, Lyubanova OP, Shuba YM,. (2005) Peculiarities of selectivity of three subtypes of low-threshold T-type calcium channels. Neurophysiology, 37 (4): 277-286.
37. Shcheglovitov AK, Boldyrev AI, Lyubanova OP, Shuba YM,. (2005) Peculiarities of selectivity of three subtypes of low-threshold T-type calcium channels. Neurophysiology, 37 (4): 277-286.
38. Shcheglovitov AK, Boldyrev AI, Lyubanova OP, Shuba YM,. (2005) Peculiarities of selectivity of three subtypes of low-threshold T-type calcium channels. Neurophysiology, 37 (4): 277-286.
39. Sidach SS, Mintz IM. (2002) Kurtoxin, a gating modifier of neuronal high- and low-threshold ca channels. J Neurosci, 22 (6): 2023-34. [PMID:11896142]
40. Talley EM, Cribbs LL, Lee JH, Daud A, Perez-Reyes E, Bayliss DA. (1999) Differential distribution of three members of a gene family encoding low voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels. J Neurosci, 19 (6): 1895-911. [PMID:10066243]
41. Talley EM, Solórzano G, Depaulis A, Perez-Reyes E, Bayliss DA. (2000) Low-voltage-activated calcium channel subunit expression in a genetic model of absence epilepsy in the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 75 (1): 159-65. [PMID:10648900]
42. Tringham E, Powell KL, Cain SM, Kuplast K, Mezeyova J, Weerapura M, Eduljee C, Jiang X, Smith P, Morrison JL et al.. (2012) T-type calcium channel blockers that attenuate thalamic burst firing and suppress absence seizures. Sci Transl Med, 4 (121): 121ra19. [PMID:22344687]
43. Wallace SJ. (1986) Use of ethosuximide and valproate in the treatment of epilepsy. Neurologic clinics, 4 (3): 601-16. [PMID:3092003]
44. Wang H, Zhang X, Xue L, Xing J, Jouvin MH, Putney JW, Anderson MP, Trebak M, Kinet JP. (2016) Low-Voltage-Activated CaV3.1 Calcium Channels Shape T Helper Cell Cytokine Profiles. Immunity, 44 (4): 782-94. [PMID:27037192]
45. Xiang Z, Thompson AD, Brogan JT, Schulte ML, Melancon BJ, Mi D, Lewis LM, Zou B, Yang L, Morrison R et al.. (2011) The Discovery and Characterization of ML218: A Novel, Centrally Active T-Type Calcium Channel Inhibitor with Robust Effects in STN Neurons and in a Rodent Model of Parkinson's Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2 (12): 730-742. [PMID:22368764]
46. Xie X, Van Deusen AL, Vitko I, Babu DA, Davies LA, Huynh N, Cheng H, Yang N, Barrett PQ, Perez-Reyes E. (2007) Validation of high throughput screening assays against three subtypes of Ca(v)3 T-type channels using molecular and pharmacologic approaches. Assay Drug Dev Technol, 5 (2): 191-203. [PMID:17477828]
47. Zhang Y, Mori M, Burgess DL, Noebels JL. (2002) Mutations in high-voltage-activated calcium channel genes stimulate low-voltage-activated currents in mouse thalamic relay neurons. J Neurosci, 22 (15): 6362-71. [PMID:12151514]
48. Zhao Y, Huang G, Wu Q, Wu K, Li R, Lei J, Pan X, Yan N. (2019) Cryo-EM structures of apo and antagonist-bound human Cav3.1. Nature, 576 (7787): 492-497. [PMID:31766050]

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb