GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 359 | 3q24 | AGTR1 | angiotensin II receptor type 1 | 12,28,30,47,104 |
| Mouse | 7 | 359 | 13 16.0 cM | Agtr1a | angiotensin II receptor, type 1a | 141,183 |
| Mouse | 7 | 359 | 3 7.6 cM | Agtr1b | angiotensin II receptor, type 1b | 141,183 |
| Rat | 7 | 359 | 17q12 | Agtr1a | angiotensin II receptor, type 1a | 67-68,86,114 |
| Rat | 7 | 359 | 2q24 | Agtr1b | angiotensin II receptor, type 1b | 39,63,67,74,114,139,155,182 |
| Gene and Protein Information Comments | ||||||
| Both rat and mouse have a second gene that codes for the AT1 receptor. | ||||||
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | agtr1_human (Hs), agtra_mouse (Mm), agtrb_mouse (Mm), agtrb_rat (Rn), agtra_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P30556 (Hs), P29755 (Mm), P29754 (Mm), P29089 (Rn), P25095 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL227 (Hs), CHEMBL5741 (Mm), CHEMBL263 (Rn), CHEMBL329 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P30556 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000144891 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000054988 (Mm), ENSMUSG00000049115 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000010640 (Rn), ENSRNOG00000018346 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 185 (Hs), 11607 (Mm), 11608 (Mm), 24180 (Rn), 81638 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000144891 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:185 (Hs), mmu:11607 (Mm), mmu:11608 (Mm), rno:24180 (Rn), rno:81638 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 106165 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA138533 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P30556 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000685 (Hs), NM_175086 (Mm), NM_177322 (Mm), NM_030985 (Rn), NM_031009 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000676 (Hs), NP_796296 (Mm), NP_780295 (Mm), NP_112247 (Rn), NP_112271 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P30556 (Hs), P29755 (Mm), P29754 (Mm), P29089 (Rn), P25095 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | AGTR1 (Hs) |
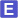
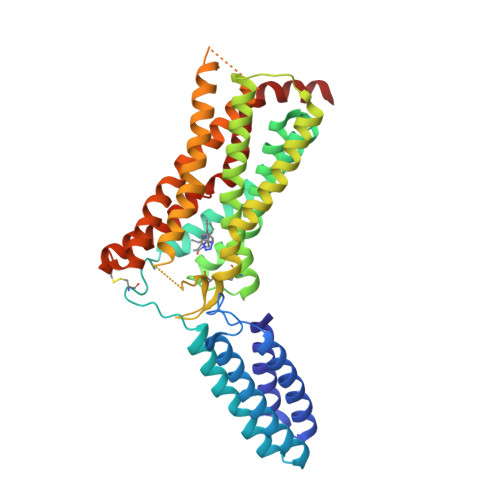
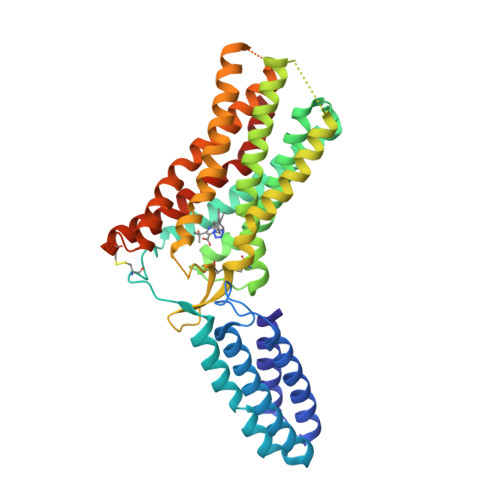
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| angiotensin A {Sp: Human} |
| angiotensin II {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| angiotensin III {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| angiotensin IV {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ind8-AngII, a modified version of AngII which was generated by the addition of a single connecting methylene group to the terminal phenyl moiety, produces an AT1R β-arrestin biased ligand (human receptor Ki 38 nM) [148], | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LY301875, LY303336, telmisartan, candesartan, irbesartan, valsartan, EXP3174, azilsartan medoxomil and saprisartan [152-153] are all classed as insurmountable antagonists. Partial agonist: Activate the receptor but have only partial efficacy (less than 50%) at the receptor relative to a full agonist. Insurmountable antagonists: When preincubated on cells/tissues these competitive antagonists cause a full or partial depression of the maximal response induced by an agonist (e.g. Angiotensin II) in a concentration-response curve. The degree of insurmountable inhibition is related to the formation of a slow dissociating receptor-antagonist complex [45,106,162,164-165]. Selective ligands ([Sar1,Ile4,Ile8]Ang II, [Sar1-Ala8]-Ang II, [Sar1-Ile8]-Ang II, [Sar1-Gly4,Gly8]-Ang II and TRV120027): Produce greater than 80% activation of G-protein-independent signal and less than 20% activation of G-protein-dependent signal. For an overview of AT1R antagonist binding properties see [108]. Two losartan derivatives have been developed for positron emission tomography (PET): [18F]FEtLos (Ki = 2000 nM) and [18F]AMBF3Los (Ki = 7.9 nM) [138]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Accumulating evidence suggests that regulation of the mutually antagonistic angiotensin receptors AT1 and AT2 is essential for maintaining control of inflammation and that an imbalance between these two receptors has pathophysiological potential [146]. |
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gi/Go family Gq/G11 family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation Calcium channel Phospholipase A2 stimulation Phospholipase D stimulation Other - See Comments |
|
Comments:
Other effectors and responses are inositol phosphate turnover, protein kinase C activation and RhoA activation. Other transducers are JAK2 resulting in STAT3 phosphorylation [100].; Src with effectors FAK, GIT1, CamK II, Cas [116,125]; pp60c-src with effector phospholipase C-gamma 1 [65,101]; β-arrestin resulting in MAPK phosphorylation in the cytoplasm; and CARMA3 with effector NF-κB [105]. Like many growth factors, activation of several tyrosine kinases (receptor (EGFR), non-receptor (JAK, Src, Pyk2)) and phosphorylation and activation of several downstream cascades such as mitogen activated protein (MAP kinase) cascade, the JAK-STAT pathway are observed. AT1R activation also lead to ROS production via activation of the NADH-NADPH oxidase pathways, modulation of ion channels, transactivation of EGFR [13,33,36,50,142-143,157,178]. G-protein dependent signalling leads to phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Elk-1 and MAPK whereas β-arrestin dependent signalling leads to MAPK phosphorylation in the cytoplasm [5,156] but not nuclear translocation. |
|
| References: 33 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression Comments | ||||||||||
| Mice lacking the AT1a receptor have a marked reduction of systolic blood pressure [180]. There is no impairment of development and no major abnormalities of the heart and vascular system in AT1A KO mice but there are mild signs of mesangial expansion and juxtaglomerular cell hypertrophy. The tubuloglomerular feedback loop is undetectable. The lack of AT1a signaling causes structural abnormalities in the renal vascular system and transforms the phenotype of VSMCs into cell proliferation, induces the escape of VSMCs from the circular mechanical integrity, and results in increased synthesis of extracellular matrices [64]. AT1a receptor knockout mice display less left ventricular remodeling and improved survival after myocardial infarction [53]. Deficiency of angiotensin type 1a receptors in adipocytes reduces differentiation and promotes hypertrophy of adipocytes in lean mice [129]. AngII can elicit renal vasoconstriction, albeit attenuated, in AT1A knockout mice [136]. Ischemia-induced angiogenesis was also impaired in in AT1a receptor knockout mice suggesting that AT1 receptor pathway promotes early angiogenesis by supporting inflammatory cell infiltration and angiogenic cytokine expression [140]. Genetic disruption of AT1a receptor improves long-term survival of mice with chronic severe aortic regurgitation (AR). In cases of chronic severe AR, blockade of AT1 receptor attenuates the progression of LV dilatation, hypertrophy and fibrosis, thereby mitigating heart failure and improving long-term survival [115]. AT1a receptor knockout in mice causes polyuria and urine concentration defects by reducing basal vasopressin levels and its receptor signaling proteins in the inner medulla [95]. AT1a receptor deficient mice exhibited reduced angiogenesis and delay in wound healing in angiotensin II type 1a receptor- [84]. AT1a receptor plays an important role in skin wound healing by accelerating keratinocyte and fibroblast migration via heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor-mediated EGF receptor transactivation [176]. Expression of AT1a receptors in C1 neurons restores the sympathoexcitation to angiotensin in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of AT1a knockout mice [21]. Mice lacking the AT1B receptor do not differ from wild-type. The AT1B receptor has a minor role but may compensate for much of the regulatory action in AT1A deleted rodent. For example, AT1B receptor mediates calcium signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells of AT1A receptor-deficient mice [190]. Animals with both AT1A and AT1B gene deletion have an impaired growth, hypotension and marked abnormalities in renal structures. There is a complete absence of pressor responses to Ang II. Transgenic mice overexpressing the AT1 receptor exhibit a drastic cardiac hypertrophy and die within several days of age. The transgenic rats however appear normal unless there is pressure or volume overload, which elicit a more pronounced hypertrophy than in normal rats. Overexpression of angiotensin II type I receptor in cardiomyocytes induces cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling with increased expression of ventricular atrial natriuretic factor and interstitial collagen deposition and died prematurely of heart failure. Neither the systolic blood pressure nor the heart rate were changed [126]. AT1R overexpression in the mouse myocardium produces a lethal phenotype associated with myocyte hyperplasia and heart block [54]. Increased expression of cardiac AT1a receptors decreases myocardial microvessel density after experimental myocardial infarction and this is amenable to AT(1) receptor blockade, suggesting that efficacy of AT1 receptor blockers post-myocardial infarction may be due to a stimulatory effect on angiogenesis [32]. Overexpression of AT1a receptors impairs excitation-contraction coupling in the mouse heart before the development of cardiac hypertrophy [135]. Overexpression of AT(1) receptor under the control of alpha-myosin heavy chain promoter in angiotensinogen-knockout background mice showed spontaneous systolic dysfunction and chamber dilatation, accompanied by severe interstitial fibrosis. Progression of cardiac remodeling in this model was prevented by treatment with candesartan, an inverse agonist for the AT(1) receptor demonstrating that constitutive activity of the AT(1) receptor under basal conditions contributes to the cardiac remodeling even in the absence of Ang II, when the AT(1) receptor is upregulated in the heart [181]. Transgenic rat model that exhibits an upregulated myocardial AT1 receptor density demonstrates augmented cardiac hypertrophy and contractile response to angiotensin II after volume and pressure overload, but not under baseline conditions [58]. Brain-selective overexpression of AT1a receptors resulted in enhanced cardiovascular responsiveness to intracerebroventricular (ICV) Ang II injection with no change in baseline blood. However, blockade of central AT1 receptors with ICV losartan reduced basal blood pressure suggesting an enhanced contribution of central AT1 receptors to the maintenance of baseline blood pressure in this model [88]. Renovascular hypertension in mice with brain-selective overexpression of AT1a receptors is buffered by increased nitric oxide production in the periphery suggesting that activation of endogenous NO systems plays an important role in buffering the maintenance of hypertension caused by overexpression of AT(1a) receptors in the brain [89]. Brain-selective overexpression of AT(1A) receptors results in enhanced salt appetite and altered water intake [90]. AT1 receptor overexpression in podocytes induces protein leakage and structural podocyte damage progressing to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in transgenic rats [59]. Mice with overexpression of a constitutively active AT1a receptor transgene in renal proximal tubule caused increased baseline blood pressure. Depletion of endogenous AT1a receptors in the proximal tubule reduced blood pressure. In contrast to the changes observed at baseline, there was no difference in the blood pressure response to a pressor dose of Ang II in either experimental model suggesting that Ang II signaling via the AT1a receptor in the renal proximal tubule is a regulator of systemic blood pressure under baseline conditions [94]. | ||||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology Comments | ||||||||||||
| Other pathophysiological actions of AT1 receptor include induction of cardiac fibrosis, renal fibrosis, perivascular fibrosis, induction of cell and tissue senescence, induction of insulin resistance, induction of endothelial dysfunction, induction of skeletal muscle wasting, reduction of exercise tolerance, induction of tissue ER stress, induction of aortic aneurysm, acceleration of atherosclerosis. Preeclampsia is associated with the presence of autoantibodies capable of activating the AT1R [168,175]. AT(1)-B(2)-receptor heterodimerization is also reported to be correlated to preeclampsia [1]. | ||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
| General Comments |
|
For information on miRNAs predicted to target AGTR1 3'-UTR please see TargetScan [46,93]. Crystallography has confirmed the different conformations that AT1R adopts in Gq-biased and β-arrestin-biased ligand-bound states [148]. AT1R cross talk with TRPV4 has been observed. Internalization of both the receptors is inhibited by antagonists that independently target either partner in the interaction pair [185]. |
References
1. AbdAlla S, Lother H, el Massiery A, Quitterer U. (2001) Increased AT(1) receptor heterodimers in preeclampsia mediate enhanced angiotensin II responsiveness. Nat Med, 7 (9): 1003-9. [PMID:11533702]
2. AbdAlla S, Lother H, Quitterer U. (2000) AT1-receptor heterodimers show enhanced G-protein activation and altered receptor sequestration. Nature, 407 (6800): 94-8. [PMID:10993080]
3. Agelis G, Resvani A, Durdagi S, Spyridaki K, Tůmová T, Slaninová J, Giannopoulos P, Vlahakos D, Liapakis G, Mavromoustakos T et al.. (2012) The discovery of new potent non-peptide Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockers: a concise synthesis, molecular docking studies and biological evaluation of N-substituted 5-butylimidazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem, 55: 358-74. [PMID:22889560]
4. Agelis G, Resvani A, Koukoulitsa C, Tůmová T, Slaninová J, Kalavrizioti D, Spyridaki K, Afantitis A, Melagraki G, Siafaka A et al.. (2013) Rational design, efficient syntheses and biological evaluation of N,N'-symmetrically bis-substituted butylimidazole analogs as a new class of potent Angiotensin II receptor blockers. Eur J Med Chem, 62: 352-70. [PMID:23376252]
5. Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Wei H, Lefkowitz RJ. (2004) Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J Biol Chem, 279 (34): 35518-25. [PMID:15205453]
6. Aiyar N, Griffin E, Shu A, Heys R, Bergsma DJ, Weinstock J, Edwards R. (1993) Characterization of [3H]SK&F 108566 as a radioligand for angiotensin type-1 receptor. J Recept Res, 13 (5): 849-61. [PMID:8463997]
7. Allen AM, Moeller I, Jenkins TA, Zhuo J, Aldred GP, Chai SY, Mendelsohn FA. (1998) Angiotensin receptors in the nervous system. Brain Res Bull, 47 (1): 17-28. [PMID:9766385]
8. Asico LD, Ladines C, Fuchs S, Accili D, Carey RM, Semeraro C, Pocchiari F, Felder RA, Eisner GM, Jose PA. (1998) Disruption of the dopamine D3 receptor gene produces renin-dependent hypertension. J Clin Invest, 102 (3): 493-8. [PMID:9691085]
9. Baiardi G, Macova M, Armando I, Ando H, Tyurmin D, Saavedra JM. (2005) Estrogen upregulates renal angiotensin II AT1 and AT2 receptors in the rat. Regul Pept, 124 (1-3): 7-17. [PMID:15544836]
10. Baker KM, Chernin MI, Wixson SK, Aceto JF. (1990) Renin-angiotensin system involvement in pressure-overload cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Am J Physiol, 259 (2 Pt 2): H324-32. [PMID:2143633]
11. Batenburg WW, Garrelds IM, Bernasconi CC, Juillerat-Jeanneret L, van Kats JP, Saxena PR, Danser AH. (2004) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor-mediated vasodilation in human coronary microarteries. Circulation, 109 (19): 2296-301. [PMID:15117835]
12. Bergsma DJ, Ellis C, Kumar C, Nuthulaganti P, Kersten H, Elshourbagy N, Griffin E, Stadel JM, Aiyar N. (1992) Cloning and characterization of a human angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 183 (3): 989-95. [PMID:1567413]
13. Berk BC, Corson MA. (1997) Angiotensin II signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: role of tyrosine kinases. Circ Res, 80 (5): 607-16. [PMID:9130441]
14. Bhatnagar A, Unal H, Jagannathan R, Kaveti S, Duan ZH, Yong S, Vasanji A, Kinter M, Desnoyer R, Karnik SS. (2013) Interaction of G-protein βγ complex with chromatin modulates GPCR-dependent gene regulation. PLoS ONE, 8 (1): e52689. [PMID:23326349]
15. Bonnardeaux A, Davies E, Jeunemaitre X, Féry I, Charru A, Clauser E, Tiret L, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F. (1994) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms in human essential hypertension. Hypertension, 24 (1): 63-9. [PMID:8021009]
16. Bullock GR, Steyaert I, Bilbe G, Carey RM, Kips J, De Paepe B, Pauwels R, Praet M, Siragy HM, de Gasparo M. (2001) Distribution of type-1 and type-2 angiotensin receptors in the normal human lung and in lungs from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Histochem Cell Biol, 115 (2): 117-24. [PMID:11444146]
17. Burns KD, Li N. (2003) The role of angiotensin II-stimulated renal tubular transport in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep, 5 (2): 165-71. [PMID:12642017]
18. Catt KJ, Mendelsohn FA, Millan MA, Aguilera G. (1984) The role of angiotensin II receptors in vascular regulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 6 Suppl 4: S575-86. [PMID:6083400]
19. Chansel D, Vandermeersch S, Pham P, Ardaillou R. (1993) Characterization of [3H]losartan receptors in isolated rat glomeruli. Eur J Pharmacol, 247 (2): 193-8. [PMID:8282008]
20. Chaves FJ, Corella D, Sorli JV, Marin-Garcia P, Guillen M, Redon J. (2004) Polymorphisms of the renin-angiotensin system influence height in normotensive women in a Spanish population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 89 (5): 2301-5. [PMID:15126556]
21. Chen D, Bassi JK, Walther T, Thomas WG, Allen AM. (2010) Expression of angiotensin type 1A receptors in C1 neurons restores the sympathoexcitation to angiotensin in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of angiotensin type 1A knockout mice. Hypertension, 56 (1): 143-50. [PMID:20458002]
22. Chen J, Guo L, Peiffer DA, Zhou L, Chan OT, Bibikova M, Wickham-Garcia E, Lu SH, Zhan Q, Wang-Rodriguez J et al.. (2008) Genomic profiling of 766 cancer-related genes in archived esophageal normal and carcinoma tissues. Int J Cancer, 122 (10): 2249-54. [PMID:18241037]
23. Chen TB, Lotti VJ, Chang RS. (1992) Characterization of the binding of [3H]L-158,809: a new potent and selective nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor (AT1) antagonist radioligand. Mol Pharmacol, 42 (6): 1077-82. [PMID:1480133]
24. Chiu AT, McCall DE, Roscoe WA. (1992) [125I]EXP985: a highly potent and specific nonpeptide radioligand antagonist for the AT1 angiotensin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 188 (3): 1030-9. [PMID:1445340]
25. Criscione L, de Gasparo M, Bühlmayer P, Whitebread S, Ramjoué HP, Wood J. (1993) Pharmacological profile of valsartan: a potent, orally active, nonpeptide antagonist of the angiotensin II AT1-receptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol, 110 (2): 761-71. [PMID:8242249]
26. Cullinane AB, Leung PS, Ortego J, Coca-Prados M, Harvey BJ. (2002) Renin-angiotensin system expression and secretory function in cultured human ciliary body non-pigmented epithelium. Br J Ophthalmol, 86 (6): 676-83. [PMID:12034692]
27. Curnow KM, Pascoe L, Davies E, White PC, Corvol P, Clauser E. (1995) Alternatively spliced human type 1 angiotensin II receptor mRNAs are translated at different efficiencies and encode two receptor isoforms. Mol Endocrinol, 9 (9): 1250-62. [PMID:7491117]
28. Curnow KM, Pascoe L, White PC. (1992) Genetic analysis of the human type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Mol Endocrinol, 6 (7): 1113-8. [PMID:1508224]
29. da Silva OG, Rossignoli Pde S, Carrillo-Sepúlveda MA, Barreto-Chaves ML, Chies AB. (2011) Involvement of the AT1 receptor in the venoconstriction induced by angiotensin II in both the inferior vena cava and femoral vein. Peptides, 32 (1): 112-7. [PMID:20955746]
30. Davies E, Bonnardeaux A, Lathrop GM, Corvol P, Clauser E, Soubrier F. (1994) Angiotensin II (type-1) receptor locus: CA repeat polymorphism and genetic mapping. Hum Mol Genet, 3 (5): 838. [PMID:8081376]
31. Davisson RL, Oliverio MI, Coffman TM, Sigmund CD. (2000) Divergent functions of angiotensin II receptor isoforms in the brain. J Clin Invest, 106 (1): 103-6. [PMID:10880053]
32. de Boer RA, Pinto YM, Suurmeijer AJ, Pokharel S, Scholtens E, Humler M, Saavedra JM, Boomsma F, van Gilst WH, van Veldhuisen DJ. (2003) Increased expression of cardiac angiotensin II type 1 (AT(1)) receptors decreases myocardial microvessel density after experimental myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res, 57 (2): 434-42. [PMID:12566116]
33. de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev, 52 (3): 415-72. [PMID:10977869]
34. de Gasparo M, Whitebread S. (1995) Binding of valsartan to mammalian angiotensin AT1 receptors. Regul Pept, 59 (3): 303-11. [PMID:8577935]
35. de Gasparo M, Whitebread S, Bottari SP, Levens NR. (1994) Heterogeneity of angiotensin receptor subtypes. In Medicinal Chemistry of the Renin-Angiotensin System.. Edited by Timmermanns PBMWM, Wexler RR (Elsevier) 269-294. [ISBN:0444820531]
36. Doan TN, Ali MS, Bernstein KE. (2001) Tyrosine kinase activation by the angiotensin II receptor in the absence of calcium signaling. J Biol Chem, 276 (24): 20954-8. [PMID:11319216]
37. Díez J, Laviades C, Orbe J, Zalba G, López B, González A, Mayor G, Páramo JA, Beloqui O. (2003) The A1166C polymorphism of the AT1 receptor gene is associated with collagen type I synthesis and myocardial stiffness in hypertensives. J Hypertens, 21 (11): 2085-92. [PMID:14597852]
38. Edwards RM, Aiyar N, Ohlstein EH, Weidley EF, Griffin E, Ezekiel M, Keenan RM, Ruffolo RR, Weinstock J. (1992) Pharmacological characterization of the nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, SK&F 108566. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 260 (1): 175-81. [PMID:1309870]
39. Elton TS, Stephan CC, Taylor GR, Kimball MG, Martin MM, Durand JN, Oparil S. (1992) Isolation of two distinct type I angiotensin II receptor genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 184 (2): 1067-73. [PMID:1575725]
40. Esteban V, Heringer-Walther S, Sterner-Kock A, de Bruin R, van den Engel S, Wang Y, Mezzano S, Egido J, Schultheiss HP, Ruiz-Ortega M et al.. (2009) Angiotensin-(1-7) and the g protein-coupled receptor MAS are key players in renal inflammation. PLoS ONE, 4 (4): e5406. [PMID:19404405]
41. Eto H, Biro S, Miyata M, Kaieda H, Obata H, Kihara T, Orihara K, Tei C. (2003) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor participates in extracellular matrix production in the late stage of remodeling after vascular injury. Cardiovasc Res, 59 (1): 200-11. [PMID:12829191]
42. Feng YH, Noda K, Saad Y, Liu XP, Husain A, Karnik SS. (1995) The docking of Arg2 of angiotensin II with Asp281 of AT1 receptor is essential for full agonism. J Biol Chem, 270 (21): 12846-50. [PMID:7759541]
43. Ferri C, Desideri G, Baldoncini R, Bellini C, Valenti M, Santucci A, De Mattia G. (1999) Angiotensin II increases the release of endothelin-1 from human cultured endothelial cells but does not regulate its circulating levels. Clin Sci, 96 (3): 261-70. [PMID:10029562]
44. Fierens F, Vanderheyden PM, De Backer JP, Vauquelin G. (1999) Binding of the antagonist [3H]candesartan to angiotensin II AT1 receptor-transfected [correction of tranfected] Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Pharmacol, 367 (2-3): 413-22. [PMID:10079018]
45. Fierens FL, Vanderheyden PM, De Backer JP, Vauquelin G. (1999) Insurmountable angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonists: the role of tight antagonist binding. Eur J Pharmacol, 372 (2): 199-206. [PMID:10395100]
46. Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP. (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res, 19 (1): 92-105. [PMID:18955434]
47. Furuta H, Guo DF, Inagami T. (1992) Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding human angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 183 (1): 8-13. [PMID:1543512]
48. Gasc JM, Shanmugam S, Sibony M, Corvol P. (1994) Tissue-specific expression of type 1 angiotensin II receptor subtypes. An in situ hybridization study. Hypertension, 24: 531-537. [PMID:7960011]
49. Gribouval O, Gonzales M, Neuhaus T, Aziza J, Bieth E, Laurent N, Bouton JM, Feuillet F, Makni S, Ben Amar H et al.. (2005) Mutations in genes in the renin-angiotensin system are associated with autosomal recessive renal tubular dysgenesis. Nat Genet, 37 (9): 964-8. [PMID:16116425]
50. Griendling KK, Ushio-Fukai M. (2000) Reactive oxygen species as mediators of angiotensin II signaling. Regul Pept, 91 (1-3): 21-7. [PMID:10967199]
51. Hancock AA, Surber BW, Rotert G, Thomas S, Tasker AS, Sorensen BK, Vodenlich AD, Opgenorth TJ, Kerkman DJ, DeBernardis JF. (1994) [3H]A-81988, a potent, selective, competitive antagonist radioligand for angiotensin AT1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 267 (1): 49-54. [PMID:8206129]
52. Handa RK, Krebs LT, Harding JW, Handa SE. (1998) Angiotensin IV AT4-receptor system in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol, 274 (2 Pt 2): F290-9. [PMID:9486224]
53. Harada K, Sugaya T, Murakami K, Yazaki Y, Komuro I. (1999) Angiotensin II type 1A receptor knockout mice display less left ventricular remodeling and improved survival after myocardial infarction. Circulation, 100 (20): 2093-9. [PMID:10562266]
54. Hein L, Stevens ME, Barsh GS, Pratt RE, Kobilka BK, Dzau VJ. (1997) Overexpression of angiotensin AT1 receptor transgene in the mouse myocardium produces a lethal phenotype associated with myocyte hyperplasia and heart block. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (12): 6391-6. [PMID:9177228]
55. Hernandez Schulman I, Zhou MS, Raij L. (2007) Cross-talk between angiotensin II receptor types 1 and 2: potential role in vascular remodeling in humans. Hypertension, 49 (2): 270-1. [PMID:17159080]
56. Herzig TC, Jobe SM, Aoki H, Molkentin JD, Cowley Jr AW, Izumo S, Markham BE. (1997) Angiotensin II type1a receptor gene expression in the heart: AP-1 and GATA-4 participate in the response to pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (14): 7543-8. [PMID:9207128]
57. Hilditch A, Hunt AA, Travers A, Polley J, Drew GM, Middlemiss D, Judd DB, Ross BC, Robertson MJ. (1995) Pharmacological effects of GR138950, a novel angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 272 (2): 750-7. [PMID:7853190]
58. Hoffmann S, Krause T, van Geel PP, Willenbrock R, Pagel I, Pinto YM, Buikema H, van Gilst WH, Lindschau C, Paul M et al.. (2001) Overexpression of the human angiotensin II type 1 receptor in the rat heart augments load induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Med, 79 (10): 601-8. [PMID:11692158]
59. Hoffmann S, Podlich D, Hähnel B, Kriz W, Gretz N. (2004) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor overexpression in podocytes induces glomerulosclerosis in transgenic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol, 15 (6): 1475-87. [PMID:15153558]
60. Hollon TR, Bek MJ, Lachowicz JE, Ariano MA, Mezey E, Ramachandran R, Wersinger SR, Soares-da-Silva P, Liu ZF, Grinberg A et al.. (2002) Mice lacking D5 dopamine receptors have increased sympathetic tone and are hypertensive. J Neurosci, 22 (24): 10801-10. [PMID:12486173]
61. Holloway AC, Qian H, Pipolo L, Ziogas J, Miura S, Karnik S, Southwell BR, Lew MJ, Thomas WG. (2002) Side-chain substitutions within angiotensin II reveal different requirements for signaling, internalization, and phosphorylation of type 1A angiotensin receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 61 (4): 768-77. [PMID:11901215]
62. Holycross BJ, Peach MJ, Owens GK. (1993) Angiotensin II stimulates increased protein synthesis, not increased DNA synthesis, in intact rat aortic segments, in vitro. J Vasc Res, 30 (2): 80-6. [PMID:8504199]
63. Inagami T, Iwai N, Sasaki K, Yamano Y, Bardhan S, Chaki S, Guo DF, Furuta H, Ohyama K, Kambayashi Y et al.. (1994) Cloning, expression and regulation of angiotensin II receptors. Eur Heart J, 15 Suppl D: 104-7. [PMID:7713098]
64. Inokuchi S, Kimura K, Sugaya T, Inokuchi K, Murakami K, Sakai T. (2001) Hyperplastic vascular smooth muscle cells of the intrarenal arteries in angiotensin II type 1a receptor null mutant mice. Kidney Int, 60 (2): 722-31. [PMID:11473655]
65. Ishida M, Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Ishida T, Bernstein KE, Berk BC. (1995) Angiotensin II activates pp60c-src in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res, 77 (6): 1053-9. [PMID:7586216]
66. Itoh S, Ding B, Shishido T, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Wang N, Maekawa N, Berk BC, Takeishi Y, Yan C, Blaxall BC et al.. (2006) Role of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase-mediated prorenin-converting enzyme in ischemic and diabetic myocardium. Circulation, 113 (14): 1787-98. [PMID:16585392]
67. Iwai N, Inagami T. (1992) Identification of two subtypes in the rat type I angiotensin II receptor. FEBS Lett, 298 (2-3): 257-60. [PMID:1544458]
68. Iwai N, Yamano Y, Chaki S, Konishi F, Bardhan S, Tibbetts C, Sasaki K, Hasegawa M, Matsuda Y, Inagami T. (1991) Rat angiotensin II receptor: cDNA sequence and regulation of the gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 177 (1): 299-304. [PMID:2043116]
69. Jaffré F, Bonnin P, Callebert J, Debbabi H, Setola V, Doly S, Monassier L, Mettauer B, Blaxall BC, Launay JM et al.. (2009) Serotonin and angiotensin receptors in cardiac fibroblasts coregulate adrenergic-dependent cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res, 104 (1): 113-23. [PMID:19023134]
70. Jagannathan R, Kaveti S, Desnoyer RW, Willard B, Kinter M, Karnik SS. (2010) AT1 receptor induced alterations in histone H2A reveal novel insights into GPCR control of chromatin remodeling. PLoS ONE, 5 (9): e12552. [PMID:20838438]
71. Jankowski V, Vanholder R, van der Giet M, Tölle M, Karadogan S, Gobom J, Furkert J, Oksche A, Krause E, Tran TN et al.. (2007) Mass-spectrometric identification of a novel angiotensin peptide in human plasma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 27 (2): 297-302. [PMID:17138938]
72. Jin W, Liu Y, Sheng HH, Jin L, Shen YY, Hua Q, Lu L, Yu JD, Huang W. (2003) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in promoter of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene associated with essential hypertension and coronary heart disease in Chinese population. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 24 (11): 1083-8. [PMID:14627489]
73. Jones A, Dhamrait SS, Payne JR, Hawe E, Li P, Toor IS, Luong L, Wootton PT, Miller GJ, Humphries SE et al.. (2003) Genetic variants of angiotensin II receptors and cardiovascular risk in hypertension. Hypertension, 42 (4): 500-6. [PMID:12925562]
74. Kakar SS, Sellers JC, Devor DC, Musgrove LC, Neill JD. (1992) Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs: differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 183 (3): 1090-6. [PMID:1567388]
75. Kanome T, Watanabe T, Nishio K, Takahashi K, Hongo S, Miyazaki A. (2008) Angiotensin II upregulates acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 via the angiotensin II Type 1 receptor in human monocyte-macrophages. Hypertens Res, 31 (9): 1801-10. [PMID:18971559]
76. Karnik SS, Unal H, Kemp JR, Tirupula KC, Eguchi S, Vanderheyden PM, Thomas WG. (2015) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIX. Angiotensin Receptors: Interpreters of Pathophysiological Angiotensinergic Stimuli [corrected]. Pharmacol Rev, 67 (4): 754-819. [PMID:26315714]
77. Kim JM, Heo HS, Ha YM, Ye BH, Lee EK, Choi YJ, Yu BP, Chung HY. (2012) Mechanism of Ang II involvement in activation of NF-κB through phosphorylation of p65 during aging. Age (Dordr), 34 (1): 11-25. [PMID:21318332]
78. Kobashi G, Hata A, Ohta K, Yamada H, Kato EH, Minakami H, Fujimoto S, Kondo K. (2004) A1166C variant of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene is associated with severe hypertension in pregnancy independently of T235 variant of angiotensinogen gene. J Hum Genet, 49 (4): 182-6. [PMID:15042429]
79. Koerten HK, de Bruijn JD, Daems WT. (1990) The formation of asbestos bodies by mouse peritoneal macrophages. An in vitro study. Am J Pathol, 137 (1): 121-34. [PMID:2372038]
80. Koike H, Sada T, Mizuno M. (2001) In vitro and in vivo pharmacology of olmesartan medoxomil, an angiotensin II type AT1 receptor antagonist. J Hypertens Suppl, 19 (1): S3-14. [PMID:11451212]
81. Konishi H, Kuroda S, Inada Y, Fujisawa Y. (1994) Novel subtype of human angiotensin II type 1 receptor: cDNA cloning and expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 199 (2): 467-74. [PMID:8135787]
82. Kurland L, Melhus H, Karlsson J, Kahan T, Malmqvist K, Ohman P, Nyström F, Hägg A, Lind L. (2002) Polymorphisms in the angiotensinogen and angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene are related to change in left ventricular mass during antihypertensive treatment: results from the Swedish Irbesartan Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Investigation versus Atenolol (SILVHIA) trial. J Hypertens, 20 (4): 657-63. [PMID:11910301]
83. Kuroda S, Konishi H, Okishio M, Fujisawa Y. (1994) Novel subtype of human angiotensin II type 1 receptor: analysis of signal transduction mechanism in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 199: 475-481. [PMID:8135788]
84. Kurosaka M, Suzuki T, Hosono K, Kamata Y, Fukamizu A, Kitasato H, Fujita Y, Majima M. (2009) Reduced angiogenesis and delay in wound healing in angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice. Biomed Pharmacother, 63 (9): 627-34. [PMID:19464844]
85. Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Kim YH, Knepper MA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. (2003) Regulation of sodium transporters in the thick ascending limb of rat kidney: response to angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 285: F152-F165. [PMID:12657563]
86. Langford K, Frenzel K, Martin BM, Bernstein KE. (1992) The genomic organization of the rat AT1 angiotensin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 183 (3): 1025-32. [PMID:1533121]
87. Lawnicka H, Ptasinska-Wnuk D, Mucha S, Kunert-Radek J, Pawlikowski M, Stepien H. (2012) The involvement of angiotensin type 1 and type 2 receptors in estrogen-induced cell proliferation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the rat anterior pituitary. ScientificWorldJournal, 2012: 358102. [PMID:22645419]
88. Lazartigues E, Dunlay SM, Loihl AK, Sinnayah P, Lang JA, Espelund JJ, Sigmund CD, Davisson RL. (2002) Brain-selective overexpression of angiotensin (AT1) receptors causes enhanced cardiovascular sensitivity in transgenic mice. Circ Res, 90 (5): 617-24. [PMID:11909827]
89. Lazartigues E, Lawrence AJ, Lamb FS, Davisson RL. (2004) Renovascular hypertension in mice with brain-selective overexpression of AT1a receptors is buffered by increased nitric oxide production in the periphery. Circ Res, 95 (5): 523-31. [PMID:15284190]
90. Lazartigues E, Sinnayah P, Augoyard G, Gharib C, Johnson AK, Davisson RL. (2008) Enhanced water and salt intake in transgenic mice with brain-restricted overexpression of angiotensin (AT1) receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 295 (5): R1539-45. [PMID:18753266]
91. Le MT, Vanderheyden PM, Szaszák M, Hunyady L, Vauquelin G. (2002) Angiotensin IV is a potent agonist for constitutive active human AT1 receptors. Distinct roles of the N-and C-terminal residues of angiotensin II during AT1 receptor activation. J Biol Chem, 277 (26): 23107-10. [PMID:12006574]
92. Lee HB, Yu MR, Yang Y, Jiang Z, Ha H. (2003) Reactive oxygen species-regulated signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol, 14 (8 Suppl 3): S241-5. [PMID:12874439]
93. Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell, 120 (1): 15-20. [PMID:15652477]
94. Li H, Weatherford ET, Davis DR, Keen HL, Grobe JL, Daugherty A, Cassis LA, Allen AM, Sigmund CD. (2011) Renal proximal tubule angiotensin AT1A receptors regulate blood pressure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 301 (4): R1067-77. [PMID:21753145]
95. Li XC, Shao Y, Zhuo JL. (2009) AT1a receptor knockout in mice impairs urine concentration by reducing basal vasopressin levels and its receptor signaling proteins in the inner medulla. Kidney Int, 76 (2): 169-77. [PMID:19387470]
96. Luchtefeld M, Bandlow N, Tietge UJ, Grote K, Pfeilschifter J, Kaszkin M, Beck S, Drexler H, Schieffer B. (2007) Angiotensin II type 1-receptor antagonism prevents type IIA secretory phospholipase A2-dependent lipid peroxidation. Atherosclerosis, 194 (1): 62-70. [PMID:17069818]
97. Madhur MS, Lob HE, McCann LA, Iwakura Y, Blinder Y, Guzik TJ, Harrison DG. (2010) Interleukin 17 promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension, 55 (2): 500-7. [PMID:20038749]
98. Maillard MP, Rossat J, Brunner HR, Burnier M. (2000) Tasosartan, enoltasosartan, and angiotensin II receptor blockade: the confounding role of protein binding. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 295 (2): 649-54. [PMID:11046101]
99. Mangrum AJ, Gomez RA, Norwood VF. (2002) Effects of AT(1A) receptor deletion on blood pressure and sodium excretion during altered dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 283 (3): F447-53. [PMID:12167595]
100. Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Paxton WG, Heerdt L, Berk BC, Delafontaine P, Bernstein KE. (1995) Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature, 375 (6528): 247-50. [PMID:7746328]
101. Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Paxton WG, Schieffer E, Bernstein KE. (1995) Electroporation of pp60c-src antibodies inhibits the angiotensin II activation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem, 270 (26): 15734-8. [PMID:7541047]
102. Martin MM, Willardson BM, Burton GF, White CR, McLaughlin JN, Bray SM, Ogilvie JW Jr, Elton TS. (2001) Human angiotensin II type 1 receptor isoforms encoded by messenger RNA splice variants are functionally distinct. Mol Endocrinol, 15: 281-293. [PMID:11158334]
103. Matsusaka T, Ichikawa I. (1997) Biological functions of angiotensin and its receptors. Annu Rev Physiol, 59: 395-412. [PMID:9074770]
104. Mauzy CA, Hwang O, Egloff AM, Wu LH, Chung FZ. (1992) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a gene encoding the human angiotensin II type 1A receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 186 (1): 277-84. [PMID:1378723]
105. McAllister-Lucas LM, Ruland J, Siu K, Jin X, Gu S, Kim DS, Kuffa P, Kohrt D, Mak TW, Nuñez G et al.. (2007) CARMA3/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation mediates angiotensin II-responsive inflammatory signaling in nonimmune cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (1): 139-44. [PMID:17101977]
106. McClellan KJ, Markham A. (1998) Telmisartan. Drugs, 56 (6): 1039-44; discussion 1045-6. [PMID:9878991]
107. Mertens B, Vanderheyden P, Michotte Y, Sarre S. (2010) Direct angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation decreases dopamine synthesis in the rat striatum. Neuropharmacology, 58 (7): 1038-44. [PMID:20097214]
108. Michel MC, Foster C, Brunner HR, Liu L. (2013) A systematic comparison of the properties of clinically used angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Rev, 65 (2): 809-48. [PMID:23487168]
109. Mii S, Ware JA, Mallette SA, Kent KC. (1994) Effect of angiotensin II on human vascular smooth muscle cell growth. J Surg Res, 57 (1): 174-8. [PMID:8041134]
110. Miura S, Feng YH, Husain A, Karnik SS. (1999) Role of aromaticity of agonist switches of angiotensin II in the activation of the AT1 receptor. J Biol Chem, 274 (11): 7103-10. [PMID:10066768]
111. Morphy R, Rankovic Z. (2005) Designed multiple ligands. An emerging drug discovery paradigm. J Med Chem, 48 (21): 6523-43. [PMID:16220969]
112. Mueller CF, Berger A, Zimmer S, Tiyerili V, Nickenig G. (2009) The heterogenous nuclear riboprotein S1-1 regulates AT1 receptor gene expression via transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys, 488 (1): 76-82. [PMID:19508861]
113. Mukohda M, Yamawaki H, Okada M, Hara Y. (2010) Methylglyoxal augments angiotensin II-induced contraction in rat isolated carotid artery. J Pharmacol Sci, 114 (4): 390-8. [PMID:21076237]
114. Murphy TJ, Alexander RW, Griendling KK, Runge MS, Bernstein KE. (1991) Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature, 351 (6323): 233-6. [PMID:2041570]
115. Nakanishi M, Harada M, Kishimoto I, Kuwahara K, Kawakami R, Nakagawa Y, Yasuno S, Usami S, Kinoshita H, Adachi Y et al.. (2007) Genetic disruption of angiotensin II type 1a receptor improves long-term survival of mice with chronic severe aortic regurgitation. Circ J, 71 (8): 1310-6. [PMID:17652901]
116. Natarajan K, Yin G, Berk BC. (2004) Scaffolds direct Src-specific signaling in response to angiotensin II: new roles for Cas and GIT1. Mol Pharmacol, 65 (4): 822-5. [PMID:15044610]
117. Navar LG, Kobori H, Prieto-Carrasquero M. (2003) Intrarenal angiotensin II and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep, 5 (2): 135-43. [PMID:12642013]
118. Nie YY, Da YJ, Zheng H, Yang XX, Jia L, Wen CH, Liang LS, Tian J, Chen ZL. (2012) Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel potent angiotensin II receptor antagonists with anti-hypertension effect. Bioorg Med Chem, 20 (8): 2747-61. [PMID:22410249]
119. Noda K, Saad Y, Karnik SS. (1995) Interaction of Phe8 of angiotensin II with Lys199 and His256 of AT1 receptor in agonist activation. J Biol Chem, 270 (48): 28511-4. [PMID:7499361]
120. Northcott CA, Watts S, Chen Y, Morris M, Chen A, Haywood JR. (2010) Adenoviral inhibition of AT1a receptors in the paraventricular nucleus inhibits acute increases in mean arterial blood pressure in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 299 (5): R1202-11. [PMID:20702798]
121. Ohlstein EH, Brooks DP, Feuerstein GZ, Ruffolo RR Jr. (1997) Inhibition of sympathetic outflow by the angiotensin II receptor antagonist, eprosartan, but not by losartan, valsartan or irbesartan: relationship to differences in prejunctional angiotensin II receptor blockade. Pharmacology, 55: 244-251. [PMID:9399334]
122. Ohyama K, Yamano Y, Sano T, Nakagomi Y, Wada M, Inagami T. (2002) Role of the conserved DRY motif on G protein activation of rat angiotensin II receptor type 1A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 292 (2): 362-7. [PMID:11906170]
123. Olins GM, Corpus VM, Chen ST, McMahon EG, Palomo MA, McGraw DE, Smits GJ, Null CL, Brown MA, Bittner SE et al.. (1993) Pharmacology of SC-52458, an orally active, nonpeptide angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 22 (4): 617-25. [PMID:7505365]
124. Oriji GK. (1999) Nitric oxide in cyclosporine A-induced hypertension: endothelin receptors gene expression. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 61 (1): 41-4. [PMID:10477041]
125. Pang J, Yan C, Natarajan K, Cavet ME, Massett MP, Yin G, Berk BC. (2008) GIT1 mediates HDAC5 activation by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 28 (5): 892-8. [PMID:18292392]
126. Paradis P, Dali-Youcef N, Paradis FW, Thibault G, Nemer M. (2000) Overexpression of angiotensin II type I receptor in cardiomyocytes induces cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97 (2): 931-6. [PMID:10639182]
127. Perlman S, Schambye HT, Rivero RA, Greenlee WJ, Hjorth SA, Schwartz TW. (1995) Non-peptide angiotensin agonist. Functional and molecular interaction with the AT1 receptor. J Biol Chem, 270 (4): 1493-6. [PMID:7829475]
128. Prescott MF, Webb RL, Reidy MA. (1991) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor versus angiotensin II, AT1 receptor antagonist. Effects on smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation after balloon catheter injury. Am J Pathol, 139 (6): 1291-6. [PMID:1750504]
129. Putnam K, Batifoulier-Yiannikouris F, Bharadwaj KG, Lewis E, Karounos M, Daugherty A, Cassis LA. (2012) Deficiency of angiotensin type 1a receptors in adipocytes reduces differentiation and promotes hypertrophy of adipocytes in lean mice. Endocrinology, 153 (10): 4677-86. [PMID:22919058]
130. Qadri F, Culman J, Veltmar A, Maas K, Rascher W, Unger T. (1993) Angiotensin II-induced vasopressin release is mediated through alpha-1 adrenoceptors and angiotensin II AT1 receptors in the supraoptic nucleus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 267 (2): 567-74. [PMID:8246129]
131. Rakugi H, Nakata E, Sasaki E, Kagawa T. (2014) Evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of fixed-dose combination therapy of azilsartan and amlodipine besylate in Japanese patients with grade I to II essential hypertension. Clin Ther, 36 (5): 711-21. [PMID:24742498]
132. Ramchandran R, Takezako T, Saad Y, Stull L, Fink B, Yamada H, Dikalov S, Harrison DG, Moravec C, Karnik SS. (2006) Angiotensinergic stimulation of vascular endothelium in mice causes hypotension, bradycardia, and attenuated angiotensin response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (50): 19087-92. [PMID:17148616]
133. Reaux A, Iturrioz X, Vazeux G, Fournie-Zaluski MC, David C, Roques BP, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C. (2000) Aminopeptidase A, which generates one of the main effector peptides of the brain renin-angiotensin system, angiotensin III, has a key role in central control of arterial blood pressure. Biochem Soc Trans, 28 (4): 435-40. [PMID:10961935]
134. Rhodes DR, Ateeq B, Cao Q, Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Laxman B, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Lonigro RJ, Helgeson BE, Bhojani MS et al.. (2009) AGTR1 overexpression defines a subset of breast cancer and confers sensitivity to losartan, an AGTR1 antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106 (25): 10284-9. [PMID:19487683]
135. Rivard K, Grandy SA, Douillette A, Paradis P, Nemer M, Allen BG, Fiset C. (2011) Overexpression of type 1 angiotensin II receptors impairs excitation-contraction coupling in the mouse heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 301 (5): H2018-27. [PMID:21856918]
136. Ruan X, Oliverio MI, Coffman TM, Arendshorst WJ. (1999) Renal vascular reactivity in mice: AngII-induced vasoconstriction in AT1A receptor null mice. J Am Soc Nephrol, 10 (12): 2620-30. [PMID:10589703]
137. Ruiz-Ortega M, Ruperez M, Esteban V, Egido J. (2003) Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II-induced vascular injury. Curr Hypertens Rep, 5 (1): 73-9. [PMID:12530939]
138. Sahylí Ortega Pijeira M, Sérgio Gonçalves Nunes P, Nascimento Dos Santos S, Zhang Z, Pérez Nario A, Araujo Perini E, Miguel Turato W, Rodríguez Riera Z, Chammas R, H Elsinga P et al.. (2020) Synthesis and Evaluation of [18F]FEtLos and [18F]AMBF3Los as Novel 18F-Labelled Losartan Derivatives for Molecular Imaging of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptors. Molecules, 25 (8). DOI: 10.3390/molecules25081872 [PMID:32325695]
139. Sandberg K, Ji H, Clark AJ, Shapira H, Catt KJ. (1992) Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem, 267 (14): 9455-8. [PMID:1374402]
140. Sasaki K, Murohara T, Ikeda H, Sugaya T, Shimada T, Shintani S, Imaizumi T. (2002) Evidence for the importance of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in ischemia-induced angiogenesis. J Clin Invest, 109 (5): 603-11. [PMID:11877468]
141. Sasamura H, Hein L, Krieger JE, Pratt RE, Kobilka BK, Dzau VJ. (1992) Cloning, characterization, and expression of two angiotensin receptor (AT-1) isoforms from the mouse genome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 185 (1): 253-9. [PMID:1599461]
142. Satoh K, Ichihara K, Landon EJ, Inagami T, Tang H. (2001) 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors block calcium-dependent tyrosine kinase Pyk2 activation by angiotensin II in vascular endothelial cells. involvement of geranylgeranylation of small G protein Rap1. J Biol Chem, 276 (19): 15761-7. [PMID:11278472]
143. Sayeski PP, Ali MS, Hawks K, Frank SJ, Bernstein KE. (1999) The angiotensin II-dependent association of Jak2 and c-Src requires the N-terminus of Jak2 and the SH2 domain of c-Src. Circ Res, 84 (11): 1332-8. [PMID:10364571]
144. Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM. (1998) Vascular biology of endothelin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 32 Suppl 3: S2-13. [PMID:9883741]
145. Shetty SS, DelGrande D. (2000) Differential inhibition of the prejunctional actions of angiotensin II in rat atria by valsartan, irbesartan, eprosartan, and losartan. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 294 (1): 179-86. [PMID:10871310]
146. Smith GR, Missailidis S. (2004) Cancer, inflammation and the AT1 and AT2 receptors. J Inflamm (Lond.), 1 (1): 3. [PMID:15813980]
147. Sung CP, Arleth AJ, Storer BL, Ohlstein EH. (1994) Angiotensin type 1 receptors mediate smooth muscle proliferation and endothelin biosynthesis in rat vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 271 (1): 429-37. [PMID:7965744]
148. Suomivuori CM, Latorraca NR, Wingler LM, Eismann S, King MC, Kleinhenz ALW, Skiba MA, Staus DP, Kruse AC, Lefkowitz RJ et al.. (2020) Molecular mechanism of biased signaling in a prototypical G protein-coupled receptor. Science, 367 (6480): 881-887. [PMID:32079767]
149. Syed YY. (2023) Sparsentan: First Approval. Drugs, 83 (6): 563-568. [PMID:37022667]
150. Takahara M, Shiraiwa T, Shindo M, Arai A, Kusuda Y, Katakami N, Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Shimomura I. (2014) Efficacy and safety of 10-mg azilsartan compared with 8-mg candesartan cilexetil in Japanese patients with hypertension: a randomized crossover non-inferiority trial. Hypertens Res, 37 (9): 852-7. [PMID:24739538]
151. Takayanagi R, Ohnaka K, Sakai Y, Nakao R, Yanase T, Haji M, Inagami T, Furuta H, Gou DF, Nakamuta M et al.. (1992) Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding human type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 183 (2): 910-6. [PMID:1550596]
152. Takezako T, Gogonea C, Saad Y, Noda K, Karnik SS. (2004) "Network leaning" as a mechanism of insurmountable antagonism of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor by non-peptide antagonists. J Biol Chem, 279 (15): 15248-57. [PMID:14754891]
153. Timmermans PB. (1999) Pharmacological properties of angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Can J Cardiol, 15 Suppl F: 26F-8F. [PMID:10579749]
154. Timmermans PB, Wong PC, Chiu AT, Herblin WF, Benfield P, Carini DJ, Lee RJ, Wexler RR, Saye JA, Smith RD. (1993) Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Rev, 45 (2): 205-51. [PMID:8372104]
155. Tissir F, Rivière M, Guo DF, Tsuzuki S, Inagami T, Levan G, Szpirer J, Szpirer C. (1995) Localization of the genes encoding the three rat angiotensin II receptors, Agtr1a, Agtr1b, Agtr2, and the human AGTR2 receptor respectively to rat chromosomes 17q12, 2q24 and Xq34, and the human Xq22. Cytogenet Cell Genet, 71 (1): 77-80. [PMID:7606933]
156. Tohgo A, Choy EW, Gesty-Palmer D, Pierce KL, Laporte S, Oakley RH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Luttrell LM. (2003) The stability of the G protein-coupled receptor-beta-arrestin interaction determines the mechanism and functional consequence of ERK activation. J Biol Chem, 278 (8): 6258-67. [PMID:12473660]
157. Touyz RM, He G, El Mabrouk M, Schiffrin EL. (2001) p38 Map kinase regulates vascular smooth muscle cell collagen synthesis by angiotensin II in SHR but not in WKY. Hypertension, 37 (2 Pt 2): 574-80. [PMID:11230337]
158. Tsuchida S, Matsusaka T, Chen X, Okubo S, Niimura F, Nishimura H, Fogo A, Utsunomiya H, Inagami T, Ichikawa I. (1998) Murine double nullizygotes of the angiotensin type 1A and 1B receptor genes duplicate severe abnormal phenotypes of angiotensinogen nullizygotes. J Clin Invest, 101 (4): 755-60. [PMID:9466969]
159. Unal H, Jagannathan R, Bhat MB, Karnik SS. (2010) Ligand-specific conformation of extracellular loop-2 in the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem, 285 (21): 16341-50. [PMID:20299456]
160. Unal H, Jagannathan R, Bhatnagar A, Tirupula K, Desnoyer R, Karnik SS. (2013) Long range effect of mutations on specific conformational changes in the extracellular loop 2 of angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem, 288 (1): 540-51. [PMID:23139413]
161. Underwood DJ, Strader CD, Rivero R, Patchett AA, Greenlee W, Prendergast K. (1994) Structural model of antagonist and agonist binding to the angiotensin II, AT1 subtype, G protein coupled receptor. Chem Biol, 1 (4): 211-21. [PMID:9383393]
162. Vanderheyden PM, Fierens FL, De Backer JP, Fraeyman N, Vauquelin G. (1999) Distinction between surmountable and insurmountable selective AT1 receptor antagonists by use of CHO-K1 cells expressing human angiotensin II AT1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol, 126 (4): 1057-65. [PMID:10193788]
163. Vanderheyden PM, Verheijen I, Fierens FL, Backer JP, Vauquelin G. (2000) Binding characteristics of [(3)H]-irbesartan to human recombinant angiotensin type 1 receptors. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, 1 (2): 159-65. [PMID:11967808]
164. Vanderheyden PM, Verheijen I, Fierens FL, DeBacker JP, Vauquelin G. (2000) Inhibition of angiotensin II-induced inositol phosphate production by triacid nonpeptide antagonists in CHO cells expressing human AT1 receptors. Pharm Res, 17 (12): 1482-8. [PMID:11303957]
165. Verheijen I, Fierens FL, Debacker JP, Vauquelin G, Vanderheyden PM. (2000) Interaction between the partially insurmountable antagonist valsartan and human recombinant angiotensin II type 1 receptors. Fundam Clin Pharmacol, 14: 577-585. [PMID:11206708]
166. Violin JD, DeWire SM, Yamashita D, Rominger DH, Nguyen L, Schiller K, Whalen EJ, Gowen M, Lark MW. (2010) Selectively engaging β-arrestins at the angiotensin II type 1 receptor reduces blood pressure and increases cardiac performance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 335 (3): 572-9. [PMID:20801892]
167. Vázquez J, Correa de Adjounian MF, Sumners C, González A, Diez-Freire C, Raizada MK. (2005) Selective silencing of angiotensin receptor subtype 1a (AT1aR) by RNA interference. Hypertension, 45 (1): 115-9. [PMID:15569855]
168. Wallukat G, Nissen E, Neichel D, Harris J. (2002) Spontaneously beating neonatal rat heart myocyte culture-a model to characterize angiotensin II at(1) receptor autoantibodies in patients with preeclampsia. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 38 (7): 376-7. [PMID:12534336]
169. Wang WY, Zee RY, Morris BJ. (1997) Association of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism with essential hypertension. Clin Genet, 51 (1): 31-4. [PMID:9084931]
170. Wei H, Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Karnik SS, Hunyady L, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ. (2003) Independent beta-arrestin 2 and G protein-mediated pathways for angiotensin II activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (19): 10782-7. [PMID:12949261]
171. Wexler RR, Greenlee WJ, Irvin JD, Goldberg MR, Prendergast K, Smith RD, Timmermans PB. (1996) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: the next generation in antihypertensive therapy. J Med Chem, 39 (3): 625-56. [PMID:8576904]
172. Wingler LM, Elgeti M, Hilger D, Latorraca NR, Lerch MT, Staus DP, Dror RO, Kobilka BK, Hubbell WL, Lefkowitz RJ. (2019) Angiotensin Analogs with Divergent Bias Stabilize Distinct Receptor Conformations. Cell, 176 (3): 468-478.e11. [PMID:30639099]
173. Wingler LM, Skiba MA, McMahon C, Staus DP, Kleinhenz ALW, Suomivuori CM, Latorraca NR, Dror RO, Lefkowitz RJ, Kruse AC. (2020) Angiotensin and biased analogs induce structurally distinct active conformations within a GPCR. Science, 367 (6480): 888-892. [PMID:32079768]
174. Wu Z, Maric C, Roesch DM, Zheng W, Verbalis JG, Sandberg K. (2003) Estrogen regulates adrenal angiotensin AT1 receptors by modulating AT1 receptor translation. Endocrinology, 144 (7): 3251-61. [PMID:12810582]
175. Xia Y, Wen H, Bobst S, Day MC, Kellems RE. (2003) Maternal autoantibodies from preeclamptic patients activate angiotensin receptors on human trophoblast cells. J Soc Gynecol Investig, 10 (2): 82-93. [PMID:12593997]
176. Yahata Y, Shirakata Y, Tokumaru S, Yang L, Dai X, Tohyama M, Tsuda T, Sayama K, Iwai M, Horiuchi M et al.. (2006) A novel function of angiotensin II in skin wound healing. Induction of fibroblast and keratinocyte migration by angiotensin II via heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor-mediated EGF receptor transactivation. J Biol Chem, 281 (19): 13209-16. [PMID:16543233]
177. Yamashita D, Chen XT. (2013) β-arrestin effectors and compositions and methods of use thereof. Patent number: US8486885B2. Assignee: Trevena Inc. Priority date: 29/12/2008. Publication date: 16/07/2013.
178. Yan C, Kim D, Aizawa T, Berk BC. (2003) Functional interplay between angiotensin II and nitric oxide: cyclic GMP as a key mediator. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 23 (1): 26-36. [PMID:12524221]
179. Yang R, Smolders I, Vanderheyden P, Demaegdt H, Van Eeckhaut A, Vauquelin G, Lukaszuk A, Tourwé D, Chai SY, Albiston AL et al.. (2011) Pressor and renal hemodynamic effects of the novel angiotensin A peptide are angiotensin II type 1A receptor dependent. Hypertension, 57 (5): 956-64. [PMID:21464395]
180. Yang R, Walther T, Gembardt F, Smolders I, Vanderheyden P, Albiston AL, Chai SY, Dupont AG. (2010) Renal vasoconstrictor and pressor responses to angiotensin IV in mice are AT1a-receptor mediated. J Hypertens, 28 (3): 487-94. [PMID:19907343]
181. Yasuda N, Akazawa H, Ito K, Shimizu I, Kudo-Sakamoto Y, Yabumoto C, Yano M, Yamamoto R, Ozasa Y, Minamino T et al.. (2012) Agonist-independent constitutive activity of angiotensin II receptor promotes cardiac remodeling in mice. Hypertension, 59 (3): 627-33. [PMID:22291447]
182. Ye MQ, Healy DP. (1992) Characterization of an angiotensin type-1 receptor partial cDNA from rat kidney: evidence for a novel AT1B receptor subtype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 185 (1): 204-10. [PMID:1599457]
183. Yoshida H, Kakuchi J, Guo DF, Furuta H, Iwai N, van der Meer-de Jong R, Inagami T, Ichikawa I. (1992) Analysis of the evolution of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene in mammals (mouse, rat, bovine and human). Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 186 (2): 1042-9. [PMID:1497638]
184. Yue H, Li W, Desnoyer R, Karnik SS. (2010) Role of nuclear unphosphorylated STAT3 in angiotensin II type 1 receptor-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res, 85 (1): 90-9. [PMID:19696070]
185. Zaccor NW, Sumner CJ, Snyder SH. (2020) The nonselective cation channel TRPV4 inhibits angiotensin II receptors. J Biol Chem, 295 (29): 9986-9997. [PMID:32493776]
186. Zahradka P, Werner JP, Buhay S, Litchie B, Helwer G, Thomas S. (2002) NF-kappaB activation is essential for angiotensin II-dependent proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 34 (12): 1609-21. [PMID:12505059]
187. Zhang H, Han GW, Batyuk A, Ishchenko A, White KL, Patel N, Sadybekov A, Zamlynny B, Rudd MT, Hollenstein K et al.. (2017) Structural basis for selectivity and diversity in angiotensin II receptors. Nature, 544 (7650): 327-332. [PMID:28379944]
188. Zhang H, Unal H, Desnoyer R, Han GW, Patel N, Katritch V, Karnik SS, Cherezov V, Stevens RC. (2015) Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor. J Biol Chem, 290 (49): 29127-39. [PMID:26420482]
189. Zhang H, Unal H, Gati C, Han GW, Liu W, Zatsepin NA, James D, Wang D, Nelson G, Weierstall U et al.. (2015) Structure of the Angiotensin receptor revealed by serial femtosecond crystallography. Cell, 161 (4): 833-44. [PMID:25913193]
190. Zhu Z, Zhang SH, Wagner C, Kurtz A, Maeda N, Coffman T, Arendshorst WJ. (1998) Angiotensin AT1B receptor mediates calcium signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells of AT1A receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension, 31 (5): 1171-7. [PMID:9576131]

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb