GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class B G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 593 | 3p21.31 | PTH1R | parathyroid hormone 1 receptor | 17,27,57,62 |
| Mouse | 7 | 591 | 9 60.56 cM | Pth1r | parathyroid hormone 1 receptor | 46 |
| Rat | 7 | 591 | 8q32 | Pth1r | parathyroid hormone 1 receptor | 1 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
|
| PPR [24] | PTHR | PTHR1 | |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | pth1r_human (Hs), pth1r_mouse (Mm), pth1r_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | Q03431 (Hs), P41593 (Mm), P25961 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 4.10.1240.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1793 (Hs), CHEMBL1075300 (Mm), CHEMBL6038 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000160801 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000032492 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000020948 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 5745 (Hs), 19228 (Mm), 56813 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000160801 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:5745 (Hs), mmu:19228 (Mm), rno:56813 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 168468 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA118140 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q03431 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000316 (Hs), NM_011199 (Mm), NM_020073 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000307 (Hs), NP_035329 (Mm), NP_064458 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q03431 (Hs), P41593 (Mm), P25961 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | PTH1R (Hs) |
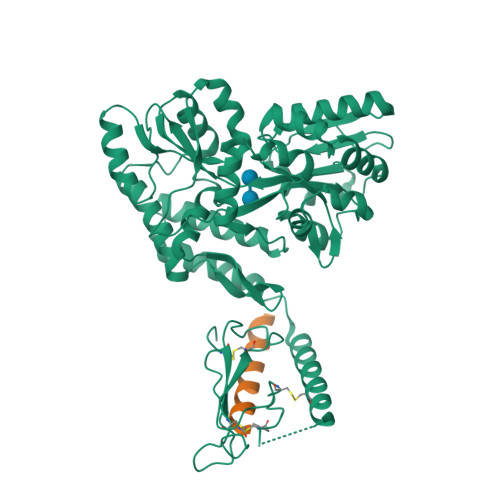
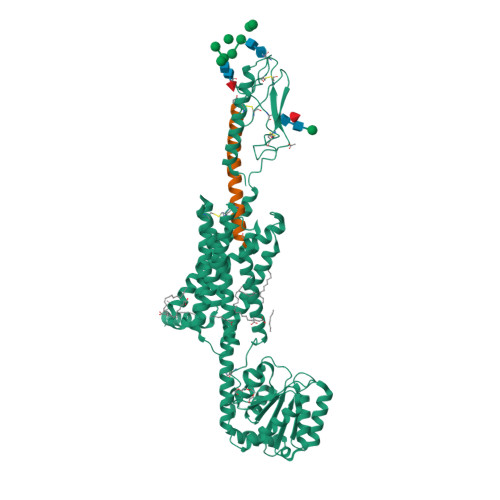
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| PTH {Sp: Human} , PTH {Sp: Mouse} , PTH {Sp: Rat} |
| PTHrP-(1-36) {Sp: Human} |
| PTHrP {Sp: Human} |
| TIP39 {Sp: Human, Bovine} |
| Comments: Other endogenous fragments of parathyroid hormone-related protein precursor are PTHrP-(107-139) (human)/PTHrP-(107-139) (mouse)/PTHrP-(107-139) (rat) and PTHrP-(38-94). |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| PTH (PTH, P01270) = PTHrP (PTHLH, P12272) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The species of peptide ligand is stated in parentheses. This can include synthetic peptides made based on the sequence of the stated species. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The species of peptide ligand is stated in parentheses. This can include synthetic peptides made based on the sequence of the stated species. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 49,53,61,63 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gq/G11 family | Phospholipase C stimulation |
| References: 20,35,49,63 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
| General Comments |
| See [55] for a study describing the molecular modelling of the interaction between PTH and the PTH1 and PTH2 receptors. |
References
1. Abou-Samra AB, Jüppner H, Force T, Freeman MW, Kong XF, Schipani E, Urena P, Richards J, Bonventre JV, Potts Jr JT et al.. (1992) Expression cloning of a common receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide from rat osteoblast-like cells: a single receptor stimulates intracellular accumulation of both cAMP and inositol trisphosphates and increases intracellular free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (7): 2732-6. [PMID:1313566]
2. Abou-Samra AB, Jüppner H, Khalifa A, Karga H, Kong XF, Schiffer-Alberts D, Xie LY, Segre GV. (1993) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates adrenocorticotropin release in AtT-20 cells stably expressing a common receptor for PTH and PTH-related peptide. Endocrinology, 132 (2): 801-5. [PMID:7678801]
3. Amizuka N, Henderson JE, White JH, Karaplis AC, Goltzman D, Sasaki T, Ozawa H. (2000) Recent studies on the biological action of parathyroid hormone (PTH)-related peptide (PTHrP) and PTH/PTHrP receptor in cartilage and bone. Histol Histopathol, 15 (3): 957-70. [PMID:10963138]
4. Arai Y, Kiyotsuka Y, Nagamochi M, Oyama K, Izumi M. (2022) Lead optimization of pyrido[2,3-d][1]benzazepin-6-one derivatives leading to the discovery of a potent, selective, and orally available human parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (hPTHR1) antagonist (DS69910557). Bioorg Med Chem, 64: 116763. [PMID:35487102]
5. Augustine M, Horwitz MJ. (2013) Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein analogs as therapies for osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 11 (4): 400-6. [PMID:24078470]
6. Barrett MG, Belinsky GS, Tashjian Jr AH. (1997) A new action of parathyroid hormone. receptor-mediated stimulation of extracellular acidification in human osteoblast-like SaOS-2 cells. J Biol Chem, 272 (42): 26346-53. [PMID:9334207]
7. Bastepe M, Raas-Rothschild A, Silver J, Weissman I, Wientroub S, Jüppner H, Gillis D. (2004) A form of Jansen's metaphyseal chondrodysplasia with limited metabolic and skeletal abnormalities is caused by a novel activating parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 89 (7): 3595-600. [PMID:15240651]
8. Behar V, Nakamoto C, Greenberg Z, Bisello A, Suva LJ, Rosenblatt M, Chorev M. (1996) Histidine at position 5 is the specificity "switch" between two parathyroid hormone receptor subtypes. Endocrinology, 137 (10): 4217-24. [PMID:8828480]
9. Bergwitz C, Jusseaume SA, Luck MD, Jüppner H, Gardella TJ. (1997) Residues in the membrane-spanning and extracellular loop regions of the parathyroid hormone (PTH)-2 receptor determine signaling selectivity for PTH and PTH-related peptide. J Biol Chem, 272 (46): 28861-8. [PMID:9360953]
10. Bounoutas GS, Tawfeek H, Fröhlich LF, Chung UI, Abou-Samra AB. (2006) Impact of impaired receptor internalization on calcium homeostasis in knock-in mice expressing a phosphorylation-deficient parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor. Endocrinology, 147 (10): 4674-9. [PMID:16840548]
11. Calvi LM, Sims NA, Hunzelman JL, Knight MC, Giovannetti A, Saxton JM, Kronenberg HM, Baron R, Schipani E. (2001) Activated parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor in osteoblastic cells differentially affects cortical and trabecular bone. J Clin Invest, 107 (3): 277-86. [PMID:11160151]
12. Carter PH, Jüppner H, Gardella TJ. (1999) Studies of the N-terminal region of a parathyroid hormone-related peptide (1-36) analog: receptor subtype-selective agonists, antagonists, and photochemical cross-linking agents. Endocrinology, 140 (11): 4972-81. [PMID:10537121]
13. Clark JA, Bonner TI, Kim AS, Usdin TB. (1998) Multiple regions of ligand discrimination revealed by analysis of chimeric parathyroid hormone 2 (PTH2) and PTH/PTH-related peptide (PTHrP) receptors. Mol Endocrinol, 12 (2): 193-206. [PMID:9482662]
14. Couvineau A, Wouters V, Bertrand G, Rouyer C, Gérard B, Boon LM, Grandchamp B, Vikkula M, Silve C. (2008) PTHR1 mutations associated with Ollier disease result in receptor loss of function. Hum Mol Genet, 17 (18): 2766-75. [PMID:18559376]
15. Diamond AG, Gonterman RM, Anderson AL, Menon K, Offutt CD, Weaver CH, Philbrick WM, Foley J. (2006) Parathyroid hormone hormone-related protein and the PTH receptor regulate angiogenesis of the skin. J Invest Dermatol, 126 (9): 2127-34. [PMID:16675960]
16. Duchatelet S, Ostergaard E, Cortes D, Lemainque A, Julier C. (2005) Recessive mutations in PTHR1 cause contrasting skeletal dysplasias in Eiken and Blomstrand syndromes. Hum Mol Genet, 14 (1): 1-5. [PMID:15525660]
17. Eggenberger M, Flühmann B, Muff R, Lauber M, Lichtensteiger W, Hunziker W, Fischer JA, Born W. (1996) Structure of a parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor of the human cerebellum and functional expression in human neuroblastoma SK-N-MC cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 36 (1): 127-36. [PMID:9011748]
18. Ehrenmann J, Schöppe J, Klenk C, Rappas M, Kummer L, Doré AS, Plückthun A. (2018) High-resolution crystal structure of parathyroid hormone 1 receptor in complex with a peptide agonist. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 25 (12): 1086-1092. [PMID:30455434]
19. Endlich N, Nobiling R, Kriz W, Endlich K. (2001) Expression and signaling of parathyroid hormone-related protein in cultured podocytes. Exp Nephrol, 9 (6): 436-43. [PMID:11702004]
20. Esbrit P, Benítez-Verguizas J, de Miguel F, Valín A, García-Ocaña A. (2000) Characterization of parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor and signaling in hypercalcemic Walker 256 tumor cells. J Endocrinol, 166 (1): 11-20. [PMID:10856878]
21. Fermor B, Skerry TM. (1995) PTH/PTHrP receptor expression on osteoblasts and osteocytes but not resorbing bone surfaces in growing rats. J Bone Miner Res, 10 (12): 1935-43. [PMID:8619374]
22. Frazier-Bowers SA, Simmons D, Wright JT, Proffit WR, Ackerman JL. (2010) Primary failure of eruption and PTH1R: the importance of a genetic diagnosis for orthodontic treatment planning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 137 (2): 160.e1-7; discussion 160-1. [PMID:20152661]
23. Gardella TJ, Jüppner H, Wilson AK, Keutmann HT, Abou-Samra AB, Segre GV, Bringhurst FR, Potts Jr JT, Nussbaum SR, Kronenberg HM. (1994) Determinants of [Arg2]PTH-(1-34) binding and signaling in the transmembrane region of the parathyroid hormone receptor. Endocrinology, 135 (3): 1186-94. [PMID:8070362]
24. Gardella TJ, Luck MD, Fan MH, Lee C. (1996) Transmembrane residues of the parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor that specifically affect binding and signaling by agonist ligands. J Biol Chem, 271 (22): 12820-5. [PMID:8662729]
25. Gardella TJ, Luck MD, Jensen GS, Usdin TB, Jüppner H. (1996) Converting parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) into a potent PTH-2 receptor agonist. J Biol Chem, 271 (33): 19888-93. [PMID:8702701]
26. Gardella TJ, Luck MD, Wilson AK, Keutmann HT, Nussbaum SR, Potts Jr JT, Kronenberg HM. (1995) Parathyroid hormone (PTH)-PTH-related peptide hybrid peptides reveal functional interactions between the 1-14 and 15-34 domains of the ligand. J Biol Chem, 270 (12): 6584-8. [PMID:7896796]
27. Gelbert L, Schipani E, Jüppner H, Abou-Samra AB, Segre GV, Naylor S, Drabkin H, Heath H. (1994) Chromosomal localization of the parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor gene to human chromosome 3p21.1-p24.2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 79: 1046-1048. [PMID:7962272]
28. Gessi M, Monego G, Lauriola L, Maggiano N, Ranelletti FO. (2005) Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (hPTHrP) and parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor type 1 (PTHR1) expression in human thymus. J Histochem Cytochem, 53 (8): 955-62. [PMID:15879577]
29. Gesty-Palmer D, Chen M, Reiter E, Ahn S, Nelson CD, Wang S, Eckhardt AE, Cowan CL, Spurney RF, Luttrell LM et al.. (2006) Distinct beta-arrestin- and G protein-dependent pathways for parathyroid hormone receptor-stimulated ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem, 281 (16): 10856-64. [PMID:16492667]
30. Guo J, Iida-Klein A, Huang X, Abou-Samra AB, Segre GV, Bringhurst FR. (1995) Parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor density modulates activation of phospholipase C and phosphate transport by PTH in LLC-PK1 cells. Endocrinology, 136 (9): 3884-91. [PMID:7649096]
31. Hoare SR, Clark JA, Usdin TB. (2000) Molecular determinants of tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues (TIP39) selectivity for the parathyroid hormone-2 (PTH2) receptor. N-terminal truncation of TIP39 reverses PTH2 receptor/PTH1 receptor binding selectivity. J Biol Chem, 275 (35): 27274-83. [PMID:10854439]
32. Hoare SR, Usdin TB. (2000) Tuberoinfundibular peptide (7-39) [TIP(7-39)], a novel, selective, high-affinity antagonist for the parathyroid hormone-1 receptor with no detectable agonist activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 295 (2): 761-70. [PMID:11046116]
33. Hoogendam J, Farih-Sips H, Wynaendts LC, Löwik CW, Wit JM, Karperien M. (2006) Novel mutations in the PTHR1 causing Blomstrand osteochondrodysplasia type I and II. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,: -. [PMID:17164305]
34. Hopyan S, Gokgoz N, Poon R, Gensure RC, Yu C, Cole WG, Bell RS, Jüppner H, Andrulis IL, Wunder JS et al.. (2002) A mutant PTH/PTHrP type I receptor in enchondromatosis. Nat Genet, 30 (3): 306-10. [PMID:11850620]
35. Iida-Klein A, Guo J, Takemura M, Drake MT, Potts Jr JT, Abou-Samra A, Bringhurst FR, Segre GV. (1997) Mutations in the second cytoplasmic loop of the rat parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related protein receptor result in selective loss of PTH-stimulated phospholipase C activity. J Biol Chem, 272 (11): 6882-9. [PMID:9054374]
36. Jobert AS, Leroy C, Butlen D, Silve C. (1997) Parathyroid hormone-induced calcium release from intracellular stores in a human kidney cell line in the absence of stimulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate production. Endocrinology, 138 (12): 5282-92. [PMID:9389512]
37. Jobert AS, Zhang P, Couvineau A, Bonaventure J, Roume J, Le Merrer M, Silve C. (1998) Absence of functional receptors for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide in Blomstrand chondrodysplasia. J Clin Invest, 102 (1): 34-40. [PMID:9649554]
38. Jonsson KB, John MR, Gensure RC, Gardella TJ, Jüppner H. (2001) Tuberoinfundibular peptide 39 binds to the parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor, but functions as an antagonist. Endocrinology, 142 (2): 704-9. [PMID:11159842]
39. Kanzawa M, Sugimoto T, Kobayashi T, Kobayashi A, Chihara K. (2000) Association between parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor gene polymorphism and the extent of bone mass reduction in primary hyperparathyroidism. Horm Metab Res, 32 (9): 355-8. [PMID:11014383]
40. Karaplis AC, He B, Nguyen MT, Young ID, Semeraro D, Ozawa H, Amizuka N. (1998) Inactivating mutation in the human parathyroid hormone receptor type 1 gene in Blomstrand chondrodysplasia. Endocrinology, 139 (12): 5255-8. [PMID:9832466]
41. Karperien M, van der Harten HJ, van Schooten R, Farih-Sips H, den Hollander NS, Kneppers SL, Nijweide P, Papapoulos SE, Löwik CW. (1999) A frame-shift mutation in the type I parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor causing Blomstrand lethal osteochondrodysplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 84: 3713-3720. [PMID:10523019]
42. Kronenberg HM, Lanske B, Kovacs CS, Chung UI, Lee K, Segre GV, Schipani E, Jüppner H. (1998) Functional analysis of the PTH/PTHrP network of ligands and receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res, 53: 283-301. [PMID:9769712]
43. Langub MC, Monier-Faugere MC, Qi Q, Geng Z, Koszewski NJ, Malluche HH. (2001) Parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide type 1 receptor in human bone. J Bone Miner Res, 16 (3): 448-56. [PMID:11277262]
44. Lanske B, Karaplis AC, Lee K, Luz A, Vortkamp A, Pirro A, Karperien M, Defize LH, Ho C, Mulligan RC et al.. (1996) PTH/PTHrP receptor in early development and Indian hedgehog-regulated bone growth. Science, 273 (5275): 663-6. [PMID:8662561]
45. Lossdörfer S, Götz W, Rath-Deschner B, Jäger A. (2006) Parathyroid hormone(1-34) mediates proliferative and apoptotic signaling in human periodontal ligament cells in vitro via protein kinase C-dependent and protein kinase A-dependent pathways. Cell Tissue Res, 325 (3): 469-79. [PMID:16670921]
46. McCuaig KA, Clarke JC, White JH. (1994) Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the mouse parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 91 (11): 5051-5. [PMID:8197183]
47. Minagawa M, Yasuda T, Watanabe T, Minamitani K, Takahashi Y, Goltzman D, White JH, Hendy GN, Kohno Y. (2002) Association between AAAG repeat polymorphism in the P3 promoter of the human parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor gene and adult height, urinary pyridinoline excretion, and promoter activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 87 (4): 1791-6. [PMID:11932319]
48. Nishimura Y, Esaki T, Isshiki Y, Furuta Y, Mizutani A, Kotake T, Emura T, Watanabe Y, Ohta M, Nakagawa T et al.. (2020) Lead Optimization and Avoidance of Reactive Metabolite Leading to PCO371, a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available Human Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 (hPTHR1) Agonist. J Med Chem, 63 (10): 5089-5099. [PMID:32022560]
49. Offermanns S, Iida-Klein A, Segre GV, Simon MI. (1996) G alpha q family members couple parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide and calcitonin receptors to phospholipase C in COS-7 cells. Mol Endocrinol, 10 (5): 566-74. [PMID:8732687]
50. Okazaki M, Ferrandon S, Vilardaga JP, Bouxsein ML, Potts JT, Gardella TJ. (2008) Prolonged signaling at the parathyroid hormone receptor by peptide ligands targeted to a specific receptor conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105 (43): 16525-30. [PMID:18946036]
51. Pines M, Fukayama S, Costas K, Meurer E, Goldsmith PK, Xu X, Muallem S, Behar V, Chorev M, Rosenblatt M et al.. (1996) Inositol 1-,4-,5-trisphosphate-dependent Ca2+ signaling by the recombinant human PTH/PTHrP receptor stably expressed in a human kidney cell line. Bone, 18 (4): 381-9. [PMID:8726398]
52. Pioszak AA, Xu HE. (2008) Molecular recognition of parathyroid hormone by its G protein-coupled receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105 (13): 5034-9. [PMID:18375760]
53. Plati J, Tsomaia N, Piserchio A, Mierke DF. (2007) Structural features of parathyroid hormone receptor coupled to Galpha(s)-protein. Biophys J, 92 (2): 535-40. [PMID:17040990]
54. Rozeman LB, Sangiorgi L, Briaire-de Bruijn IH, Mainil-Varlet P, Bertoni F, Cleton-Jansen AM, Hogendoorn PC, Bovée JV. (2004) Enchondromatosis (Ollier disease, Maffucci syndrome) is not caused by the PTHR1 mutation p.R150C. Hum Mutat, 24 (6): 466-73. [PMID:15523647]
55. Rölz C, Pellegrini M, Mierke DF. (1999) Molecular characterization of the receptor-ligand complex for parathyroid hormone. Biochemistry, 38 (20): 6397-405. [PMID:10350457]
56. Schipani E, Jensen GS, Pincus J, Nissenson RA, Gardella TJ, Jüppner H. (1997) Constitutive activation of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signaling pathway by parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptors mutated at the two loci for Jansen's metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. Mol Endocrinol, 11 (7): 851-8. [PMID:9178745]
57. Schipani E, Karga H, Karaplis AC, Potts Jr JT, Kronenberg HM, Segre GV, Abou-Samra AB, Jüppner H. (1993) Identical complementary deoxyribonucleic acids encode a human renal and bone parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor. Endocrinology, 132 (5): 2157-65. [PMID:8386612]
58. Schipani E, Kruse K, Jüppner H. (1995) A constitutively active mutant PTH-PTHrP receptor in Jansen-type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. Science, 268 (5207): 98-100. [PMID:7701349]
59. Schipani E, Langman C, Hunzelman J, Le Merrer M, Loke KY, Dillon MJ, Silve C, Jüppner H. (1999) A novel parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor mutation in Jansen's metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 84 (9): 3052-7. [PMID:10487664]
60. Schipani E, Langman CB, Parfitt AM, Jensen GS, Kikuchi S, Kooh SW, Cole WG, Jüppner H. (1996) Constitutively activated receptors for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide in Jansen's metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. N Engl J Med, 335 (10): 708-14. [PMID:8703170]
61. Schneider H, Feyen JH, Seuwen K. (1994) A C-terminally truncated human parathyroid hormone receptor is functional and activates multiple G proteins. FEBS Lett, 351 (2): 281-5. [PMID:8082781]
62. Schneider H, Feyen JH, Seuwen K, Movva NR. (1993) Cloning and functional expression of a human parathyroid hormone receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 246 (2): 149-55. [PMID:8397094]
63. Schwindinger WF, Fredericks J, Watkins L, Robinson H, Bathon JM, Pines M, Suva LJ, Levine MA. (1998) Coupling of the PTH/PTHrP receptor to multiple G-proteins. Direct demonstration of receptor activation of Gs, Gq/11, and Gi(1) by [alpha-32P]GTP-gamma-azidoanilide photoaffinity labeling. Endocrine, 8 (2): 201-9. [PMID:9704578]
64. Scillitani A, Jang C, Wong BY, Hendy GN, Cole DE. (2006) A functional polymorphism in the PTHR1 promoter region is associated with adult height and BMD measured at the femoral neck in a large cohort of young caucasian women. Hum Genet, 119 (4): 416-21. [PMID:16508749]
65. Seuwen K, Boddeke HG. (1995) Heparin-insensitive calcium release from intracellular stores triggered by the recombinant human parathyroid hormone receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 114: 1613-1620. [PMID:7599930]
66. Shimizu M, Joyashiki E, Noda H, Watanabe T, Okazaki M, Nagayasu M, Adachi K, Tamura T, Potts Jr JT, Gardella TJ et al.. (2016) Pharmacodynamic Actions of a Long-Acting PTH Analog (LA-PTH) in Thyroparathyroidectomized (TPTX) Rats and Normal Monkeys. J Bone Miner Res, 31 (7): 1405-12. [PMID:26865415]
67. Silve C, Jüppner H. (2006) Ollier disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 1: 37. [PMID:16995932]
68. Soegiarto DW, Kiachopoulos S, Schipani E, Jüppner H, Erben RG, Lanske B. (2001) Partial rescue of PTH/PTHrP receptor knockout mice by targeted expression of the Jansen transgene. Endocrinology, 142 (12): 5303-10. [PMID:11713230]
69. Takasu H, Bringhurst FR. (1998) Type-1 parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide (PTHrP) receptors activate phospholipase C in response to carboxyl-truncated analogs of PTH(1-34). Endocrinology, 139 (10): 4293-9. [PMID:9751512]
70. Takasu H, Gardella TJ, Luck MD, Potts Jr JT, Bringhurst FR. (1999) Amino-terminal modifications of human parathyroid hormone (PTH) selectively alter phospholipase C signaling via the type 1 PTH receptor: implications for design of signal-specific PTH ligands. Biochemistry, 38 (41): 13453-60. [PMID:10521252]
71. Takasu H, Guo J, Bringhurst FR. (1999) Dual signaling and ligand selectivity of the human PTH/PTHrP receptor. J Bone Miner Res, 14 (1): 11-20. [PMID:9893061]
72. Tian J, Smogorzewski M, Kedes L, Massry SG. (1993) Parathyroid hormone-parathyroid hormone related protein receptor messenger RNA is present in many tissues besides the kidney. Am J Nephrol, 13 (3): 210-3. [PMID:8213933]
73. Ureña P, Kong XF, Abou-Samra AB, Jüppner H, Kronenberg HM, Potts Jr JT, Segre GV. (1993) Parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor messenger ribonucleic acids are widely distributed in rat tissues. Endocrinology, 133 (2): 617-23. [PMID:8393771]
74. Watson PH, Fraher LJ, Hendy GN, Chung UI, Kisiel M, Natale BV, Hodsman AB. (2000) Nuclear localization of the type 1 PTH/PTHrP receptor in rat tissues. J Bone Miner Res, 15 (6): 1033-44. [PMID:10841172]
75. Watson PH, Fraher LJ, Kisiel M, DeSousa D, Hendy G, Hodsman AB. (1999) Enhanced osteoblast development after continuous infusion of hPTH(1-84) in the rat. Bone, 24 (2): 89-94. [PMID:9951775]
76. Yang T, Hassan S, Huang YG, Smart AM, Briggs JP, Schnermann JB. (1997) Expression of PTHrP, PTH/PTHrP receptor, and Ca(2+)-sensing receptor mRNAs along the rat nephron. Am J Physiol, 272 (6 Pt 2): F751-8. [PMID:9227636]
77. Zhang P, Jobert AS, Couvineau A, Silve C. (1998) A homozygous inactivating mutation in the parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor causing Blomstrand chondrodysplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 83 (9): 3365-8. [PMID:9745456]
78. Zhang YY, Liu PY, Lu Y, Xiao P, Liu YJ, Long JR, Shen H, Zhao LJ, Elze L, Recker RR et al.. (2006) Tests of linkage and association of PTH/PTHrP receptor type 1 gene with bone mineral density and height in Caucasians. J Bone Miner Metab, 24 (1): 36-41. [PMID:16369896]