GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 353 | 19p13.2 | S1PR2 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 | |
| Mouse | 7 | 352 | 9 7.68 cM | S1pr2 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 | |
| Rat | 7 | 352 | 8q13 | S1pr2 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| edg5 | Gpcr13 | endothelial differentiation G protein-coupled receptor 5 | G protein-coupled receptor 13 | GPCR18 | S1P receptor 2 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | s1pr2_human (Hs), s1pr2_mouse (Mm), s1pr2_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | O95136 (Hs), P52592 (Mm), P47752 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL2955 (Hs), CHEMBL3616360 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000267534 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000043895 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000020653 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 9294 (Hs), 14739 (Mm), 29415 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000267534 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:9294 (Hs), mmu:14739 (Mm), rno:29415 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 605111 (Hs) |
| Pharos | O95136 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_004230 (Hs), NM_010333 (Mm), NM_017192 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_004221 (Hs), NP_034463 (Mm), NP_058888 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | O95136 (Hs), P52592 (Mm), P47752 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | S1PR2 (Hs) |
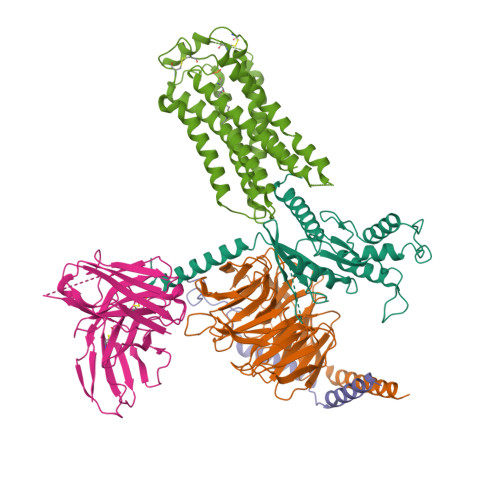
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
| Comments: Sphingosine 1-phosphate exhibits greater potency than sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate > dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate [2,29] |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S1P d20:1 is reported to inhibit S1P-inudced COX-2 expression via S1P2 in glioblastoma cell line LN299 [42]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Activation of S1P2R has pro-inflammatory effects (e.g. mast cell degranulation, regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and cytokine and chemokine release [22,32]. In human cord blood mast cells, S1P2R positively regulates allergen-induced degranulation and chemokine release [30,34]. |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gs family Gq/G11 family G12/G13 family |
Adenylyl cyclase stimulation Phospholipase C stimulation Calcium channel |
| Comments: Activation of Rho, MAPK, and phosphorylation of MLC [8]. | |
| References: 8,17 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| S1P2 receptor has been shown to be a specific receptor for the central nervous system membrane protein Nogo-A-Δ20 [18]. |
References
1. An S, Zheng Y, Bleu T. (2000) Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell proliferation, survival, and related signaling events mediated by G protein-coupled receptors Edg3 and Edg5. J Biol Chem, 275 (1): 288-96. [PMID:10617617]
2. Ancellin N, Hla T. (1999) Differential pharmacological properties and signal transduction of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors EDG-1, EDG-3, and EDG-5. J Biol Chem, 274 (27): 18997-9002. [PMID:10383399]
3. Arikawa K, Takuwa N, Yamaguchi H, Sugimoto N, Kitayama J, Nagawa H, Takehara K, Takuwa Y. (2003) Ligand-dependent inhibition of B16 melanoma cell migration and invasion via endogenous S1P2 G protein-coupled receptor. Requirement of inhibition of cellular RAC activity. J Biol Chem, 278 (35): 32841-51. [PMID:12810709]
4. Cattoretti G, Mandelbaum J, Lee N, Chaves AH, Mahler AM, Chadburn A, Dalla-Favera R, Pasqualucci L, MacLennan AJ. (2009) Targeted disruption of the S1P2 sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor gene leads to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma formation. Cancer Res, 69 (22): 8686-92. [PMID:19903857]
5. Chen H, Chen K, Huang W, Staudt LM, Cyster JG, Li X. (2022) Structure of S1PR2-heterotrimeric G13 signaling complex. Sci Adv, 8 (13): eabn0067. [PMID:35353559]
6. Demont EH, Bailey JM, Bit RA, Brown JA, Campbell CA, Deeks N, Dowell SJ, Eldred C, Gaskin P, Gray JR et al.. (2016) Discovery of Tetrahydropyrazolopyridine as Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1P3)-Sparing S1P1 Agonists Active at Low Oral Doses. J Med Chem, 59 (3): 1003-20. [PMID:26751273]
7. Drouillard A, Neyra A, Mathieu AL, Marçais A, Wencker M, Marvel J, Belot A, Walzer T. (2018) Human Naive and Memory T Cells Display Opposite Migratory Responses to Sphingosine-1 Phosphate. J Immunol, 200 (2): 551-557. [PMID:29237776]
8. Gonda K, Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Yatomi Y, Okazaki H, Sakurai T, Kimura S, Sillard R, Harii K, Takuwa Y. (1999) The novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor AGR16 is coupled via pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins to multiple signalling pathways. Biochem J, 337 ( Pt 1): 67-75. [PMID:9854026]
9. Green JA, Suzuki K, Cho B, Willison LD, Palmer D, Allen CD, Schmidt TH, Xu Y, Proia RL, Coughlin SR et al.. (2011) The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor S1P₂ maintains the homeostasis of germinal center B cells and promotes niche confinement. Nat Immunol, 12 (7): 672-80. [PMID:21642988]
10. Herr DR, Grillet N, Schwander M, Rivera R, Müller U, Chun J. (2007) Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) signaling is required for maintenance of hair cells mainly via activation of S1P2. J Neurosci, 27 (6): 1474-8. [PMID:17287522]
11. Herr DR, Lee CW, Wang W, Ware A, Rivera R, Chun J. (2013) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors are essential mediators of eyelid closure during embryonic development. J Biol Chem, 288 (41): 29882-9. [PMID:24003216]
12. Herr DR, Reolo MJ, Peh YX, Wang W, Lee CW, Rivera R, Paterson IC, Chun J. (2016) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1P2) attenuates reactive oxygen species formation and inhibits cell death: implications for otoprotective therapy. Sci Rep, 6: 24541. [PMID:27080739]
13. Ikeda H, Satoh H, Yanase M, Inoue Y, Tomiya T, Arai M, Tejima K, Nagashima K, Maekawa H, Yahagi N et al.. (2003) Antiproliferative property of sphingosine 1-phosphate in rat hepatocytes involves activation of Rho via Edg-5. Gastroenterology, 124 (2): 459-69. [PMID:12557151]
14. Im DS, Clemens J, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2001) Characterization of the human and mouse sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P5 (Edg-8): structure-activity relationship of sphingosine1-phosphate receptors. Biochemistry, 40 (46): 14053-60. [PMID:11705398]
15. Inoki I, Takuwa N, Sugimoto N, Yoshioka K, Takata S, Kaneko S, Takuwa Y. (2006) Negative regulation of endothelial morphogenesis and angiogenesis by S1P2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 346 (1): 293-300. [PMID:16756949]
16. Ishii I, Ye X, Friedman B, Kawamura S, Contos JJ, Kingsbury MA, Yang AH, Zhang G, Brown JH, Chun J. (2002) Marked perinatal lethality and cellular signaling deficits in mice null for the two sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors, S1P(2)/LP(B2)/EDG-5 and S1P(3)/LP(B3)/EDG-3. J Biol Chem, 277 (28): 25152-9. [PMID:12006579]
17. Jiang LI, Collins J, Davis R, Lin KM, DeCamp D, Roach T, Hsueh R, Rebres RA, Ross EM, Taussig R et al.. (2007) Use of a cAMP BRET sensor to characterize a novel regulation of cAMP by the sphingosine 1-phosphate/G13 pathway. J Biol Chem, 282 (14): 10576-84. [PMID:17283075]
18. Kempf A, Tews B, Arzt ME, Weinmann O, Obermair FJ, Pernet V, Zagrebelsky M, Delekate A, Iobbi C, Zemmar A et al.. (2014) The Sphingolipid Receptor S1PR2 Is a Receptor for Nogo-A Repressing Synaptic Plasticity. PLoS Biol, 12 (1): e1001763. [PMID:24453941]
19. Kon J, Sato K, Watanabe T, Tomura H, Kuwabara A, Kimura T, Tamama K, Ishizuka T, Murata N, Kanda T et al.. (1999) Comparison of intrinsic activities of the putative sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtypes to regulate several signaling pathways in their cDNA-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem, 274 (34): 23940-7. [PMID:10446161]
20. Kono M, Belyantseva IA, Skoura A, Frolenkov GI, Starost MF, Dreier JL, Lidington D, Bolz SS, Friedman TB, Hla T et al.. (2007) Deafness and stria vascularis defects in S1P2 receptor-null mice. J Biol Chem, 282 (14): 10690-6. [PMID:17284444]
21. Kono M, Mi Y, Liu Y, Sasaki T, Allende ML, Wu YP, Yamashita T, Proia RL. (2004) The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors S1P1, S1P2, and S1P3 function coordinately during embryonic angiogenesis. J Biol Chem, 279 (28): 29367-73. [PMID:15138255]
22. Kulinski JM, Muñoz-Cano R, Olivera A. (2016) Sphingosine-1-phosphate and other lipid mediators generated by mast cells as critical players in allergy and mast cell function. Eur J Pharmacol, 778: 56-67. [PMID:25941085]
23. Kusumi K, Shinozaki K, Yamaura Y, Hashimoto A, Kurata H, Naganawa A, Otsuki K, Matsushita T, Sekiguchi T, Kakuuchi A et al.. (2016) Discovery of novel S1P2 antagonists, part 3: Improving the oral bioavailability of a series of 1,3-bis(aryloxy)benzene derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 26 (4): 1209-13. [PMID:26794040]
24. Mackle T, Gendy SS, Walsh M, McConn-Walsh R, Costello RW, Walsh MT. (2008) Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor expression in eosinophils of patients with allergic rhinitis, and effect of topical nasal steroid treatment on this receptor expression. J Laryngol Otol, 122 (12): 1309-17. [PMID:18808729]
25. MacLennan AJ, Benner SJ, Andringa A, Chaves AH, Rosing JL, Vesey R, Karpman AM, Cronier SA, Lee N, Erway LC et al.. (2006) The S1P2 sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor is essential for auditory and vestibular function. Hear Res, 220 (1-2): 38-48. [PMID:16945494]
26. MacLennan AJ, Browe CS, Gaskin AA, Lado DC, Shaw G. (1994) Cloning and characterization of a putative G-protein coupled receptor potentially involved in development. Mol Cell Neurosci, 5 (3): 201-9. [PMID:8087418]
27. MacLennan AJ, Carney PR, Zhu WJ, Chaves AH, Garcia J, Grimes JR, Anderson KJ, Roper SN, Lee N. (2001) An essential role for the H218/AGR16/Edg-5/LP(B2) sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor in neuronal excitability. Eur J Neurosci, 14 (2): 203-9. [PMID:11553273]
28. McQuiston T, Luberto C, Del Poeta M. (2011) Role of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and S1P receptor 2 in the phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by alveolar macrophages. Microbiology (Reading, Engl.), 157 (Pt 5): 1416-27. [PMID:21292747]
29. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Gonda K, Okazaki H, Chang K, Yatomi Y, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. (1998) EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem, 273 (42): 27104-10. [PMID:9765227]
30. Olivera A. (2008) Unraveling the complexities of sphingosine-1-phosphate function: the mast cell model. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 86 (1-4): 1-11. [PMID:18403224]
31. Osada M, Yatomi Y, Ohmori T, Ikeda H, Ozaki Y. (2002) Enhancement of sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced migration of vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells by an EDG-5 antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 299 (3): 483-7. [PMID:12445827]
32. Oskeritzian CA, Price MM, Hait NC, Kapitonov D, Falanga YT, Morales JK, Ryan JJ, Milstien S, Spiegel S. (2010) Essential roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 in human mast cell activation, anaphylaxis, and pulmonary edema. J Exp Med, 207 (3): 465-74. [PMID:20194630]
33. Pan S, Mi Y, Pally C, Beerli C, Chen A, Guerini D, Hinterding K, Nuesslein-Hildesheim B, Tuntland T, Lefebvre S et al.. (2006) A monoselective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist prevents allograft rejection in a stringent rat heart transplantation model. Chem Biol, 13 (11): 1227-34. [PMID:17114004]
34. Price MM, Oskeritzian CA, Milstien S, Spiegel S. (2008) Sphingosine-1-phosphate synthesis and functions in mast cells. Future Lipidol, 3 (6): 665-674. [PMID:19802381]
35. Sanna MG, Liao J, Jo E, Alfonso C, Ahn MY, Peterson MS, Webb B, Lefebvre S, Chun J, Gray N et al.. (2004) Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor subtypes S1P1 and S1P3, respectively, regulate lymphocyte recirculation and heart rate. J Biol Chem, 279 (14): 13839-48. [PMID:14732717]
36. Satsu H, Schaeffer MT, Guerrero M, Saldana A, Eberhart C, Hodder P, Cayanan C, Schürer S, Bhhatarai B, Roberts E et al.. (2013) A sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 selective allosteric agonist. Bioorg Med Chem, 21 (17): 5373-82. [PMID:23849205]
37. Scott FL, Clemons B, Brooks J, Brahmachary E, Powell R, Dedman H, Desale HG, Timony GA, Martinborough E, Rosen H et al.. (2016) Ozanimod (RPC1063) is a potent sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1 ) and receptor-5 (S1P5 ) agonist with autoimmune disease-modifying activity. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (11): 1778-92. [PMID:26990079]
38. Skoura A, Sanchez T, Claffey K, Mandala SM, Proia RL, Hla T. (2007) Essential role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 in pathological angiogenesis of the mouse retina. J Clin Invest, 117 (9): 2506-16. [PMID:17710232]
39. Sobel K, Monnier L, Menyhart K, Bolinger M, Studer R, Nayler O, Gatfield J. (2015) FTY720 Phosphate Activates Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 and Selectively Couples to Gα12/13/Rho/ROCK to Induce Myofibroblast Contraction. Mol Pharmacol, 87 (6): 916-27. [PMID:25762025]
40. Szczepaniak WS, Pitt BR, McVerry BJ. (2010) S1P2 receptor-dependent Rho-kinase activation mediates vasoconstriction in the murine pulmonary circulation induced by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 299 (1): L137-45. [PMID:20435688]
41. Van Brocklyn JR, Tu Z, Edsall LC, Schmidt RR, Spiegel S. (1999) Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell rounding and neurite retraction are mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor H218. J Biol Chem, 274 (8): 4626-32. [PMID:9988698]
42. Vutukuri R, Koch A, Trautmann S, Schreiber Y, Thomas D, Mayser F, Meyer Zu Heringdorf D, Pfeilschifter J, Pfeilschifter W, Brunkhorst R. (2020) S1P d20:1, an endogenous modulator of S1P d18:1/S1P2 -dependent signaling. FASEB J, 34 (3): 3932-3942. [PMID:31944406]
43. Yang AH, Ishii I, Chun J. (2002) In vivo roles of lysophospholipid receptors revealed by gene targeting studies in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1582 (1-3): 197-203. [PMID:12069829]
44. Zhang G, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Fukushima N, Chun J. (1999) Comparative analysis of three murine G-protein coupled receptors activated by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Gene, 227 (1): 89-99. [PMID:9931453]

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb