GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 382 | 1p21.2 | S1PR1 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 | |
| Mouse | 7 | 382 | 3 G1 | S1pr1 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 | |
| Rat | 7 | 383 | 2q41 | S1pr1 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| CD363 | EDG1 (Edg1) | endothelial differentiation G protein-coupled receptor 1 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | s1pr1_human (Hs), s1pr1_mouse (Mm), s1pr1_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P21453 (Hs), O08530 (Mm), P48303 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4333 (Hs), CHEMBL1914262 (Mm), CHEMBL1914263 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000170989 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000045092 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000013683 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 1901 (Hs), 13609 (Mm), 29733 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000170989 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:1901 (Hs), mmu:13609 (Mm), rno:29733 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 601974 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P21453 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001400 (Hs), NM_007901 (Mm), NM_017301 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_001391 (Hs), NP_031927 (Mm), NP_058997 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P21453 (Hs), O08530 (Mm), P48303 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | S1PR1 (Hs) |
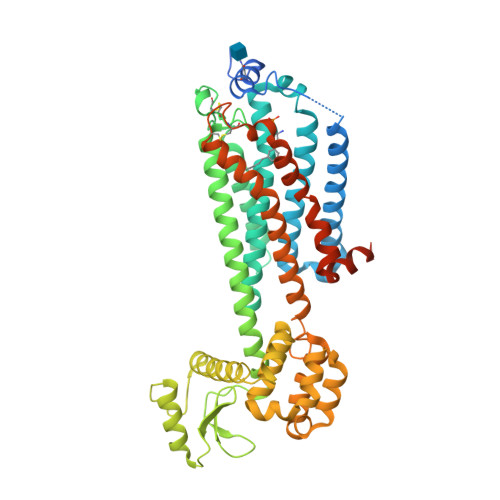
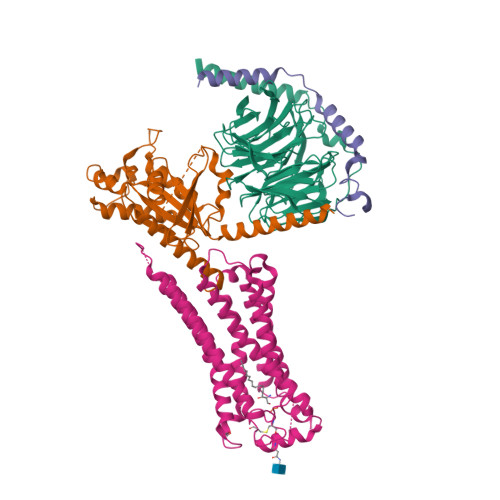
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
| Comments: Sphingosine 1-phosphate exhibits greater potency than sphingosylphosphorylcholine. LPA is a low potency agonist. |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate > dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate [5,47] |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| S1P1R activation by agonists downregulates allergic inflammation (i.e. it has an inhibitory effect) [31-32,61]. In human cord blood mast cells, S1P1R is required for migration but not for degranulation or cytokine and chemokine release [48,55]. S1P1R expression is elevated by allergen challenge in allergic rhinitis patients, but not in corticosteroid treated patients [43]. As a drug target selective S1P1R agonists are in development. |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation Calcium channel Phospholipase D stimulation Other - See Comments |
| Comments: Involved in ERK phosphorylation [49] and stimulation of the PI3K/PKB and MEK/ERK pathways [10], and activation of Rac [19]. | |
| References: 11,38,47 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
1. Allende ML, Dreier JL, Mandala S, Proia RL. (2004) Expression of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P1, on T-cells controls thymic emigration. J Biol Chem, 279 (15): 15396-401. [PMID:14732704]
2. Allende ML, Tuymetova G, Lee BG, Bonifacino E, Wu YP, Proia RL. (2010) S1P1 receptor directs the release of immature B cells from bone marrow into blood. J Exp Med, 207 (5): 1113-24. [PMID:20404103]
3. Allende ML, Yamashita T, Proia RL. (2003) G-protein-coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood, 102 (10): 3665-7. [PMID:12869509]
4. Allende ML, Zhou D, Kalkofen DN, Benhamed S, Tuymetova G, Borowski C, Bendelac A, Proia RL. (2008) S1P1 receptor expression regulates emergence of NKT cells in peripheral tissues. FASEB J, 22 (1): 307-15. [PMID:17785606]
5. Ancellin N, Hla T. (1999) Differential pharmacological properties and signal transduction of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors EDG-1, EDG-3, and EDG-5. J Biol Chem, 274 (27): 18997-9002. [PMID:10383399]
6. Baeyens AAL, Schwab SR. (2020) Finding a Way Out: S1P Signaling and Immune Cell Migration. Annu Rev Immunol, 38: 759-784. [PMID:32340572]
7. Blaho VA, Galvani S, Engelbrecht E, Liu C, Swendeman SL, Kono M, Proia RL, Steinman L, Han MH, Hla T. (2015) HDL-bound sphingosine-1-phosphate restrains lymphopoiesis and neuroinflammation. Nature, 523 (7560): 342-6. [PMID:26053123]
8. Bolli MH, Abele S, Binkert C, Bravo R, Buchmann S, Bur D, Gatfield J, Hess P, Kohl C, Mangold C et al.. (2010) 2-imino-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives as potent, orally active S1P1 receptor agonists. J Med Chem, 53 (10): 4198-211. [PMID:20446681]
9. Brinkmann V, Davis MD, Heise CE, Albert R, Cottens S, Hof R, Bruns C, Prieschl E, Baumruker T, Hiestand P et al.. (2002) The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem, 277 (24): 21453-7. [PMID:11967257]
10. Brizuela L, Rábano M, Gangoiti P, Narbona N, Macarulla JM, Trueba M, Gómez-Muñoz A. (2007) Sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulates aldosterone secretion through a mechanism involving the PI3K/PKB and MEK/ERK 1/2 pathways. J Lipid Res, 48 (10): 2264-74. [PMID:17609523]
11. Brizuela L, Rábano M, Peña A, Gangoiti P, Macarulla JM, Trueba M, Gómez-Muñoz A. (2006) Sphingosine 1-phosphate: a novel stimulator of aldosterone secretion. J Lipid Res, 47 (6): 1238-49. [PMID:16554657]
12. Buzard DJ, Kim SH, Lopez L, Kawasaki A, Zhu X, Moody J, Thoresen L, Calderon I, Ullman B, Han S et al.. (2014) Discovery of APD334: Design of a Clinical Stage Functional Antagonist of the Sphingosine-1-phosphate-1 Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett, 5 (12): 1313-7. [PMID:25516790]
13. Cahalan SM, Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, Sarkisyan G, Nguyen N, Schaeffer MT, Huang L, Yeager A, Clemons B, Scott F, Rosen H. (2011) Actions of a picomolar short-acting S1P₁ agonist in S1P₁-eGFP knock-in mice. Nat Chem Biol, 7 (5): 254-6. [PMID:21445057]
14. Choi JW, Gardell SE, Herr DR, Rivera R, Lee CW, Noguchi K, Teo ST, Yung YC, Lu M, Kennedy G et al.. (2011) FTY720 (fingolimod) efficacy in an animal model of multiple sclerosis requires astrocyte sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108 (2): 751-6. [PMID:21177428]
15. Davis MD, Clemens JJ, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2005) Sphingosine 1-phosphate analogs as receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem, 280 (11): 9833-41. [PMID:15590668]
16. Demont EH, Bailey JM, Bit RA, Brown JA, Campbell CA, Deeks N, Dowell SJ, Eldred C, Gaskin P, Gray JR et al.. (2016) Discovery of Tetrahydropyrazolopyridine as Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1P3)-Sparing S1P1 Agonists Active at Low Oral Doses. J Med Chem, 59 (3): 1003-20. [PMID:26751273]
17. Deng Q, Clemas JA, Chrebet G, Fischer P, Hale JJ, Li Z, Mills SG, Bergstrom J, Mandala S, Mosley R et al.. (2007) Identification of Leu276 of the S1P1 receptor and Phe263 of the S1P3 receptor in interaction with receptor specific agonists by molecular modeling, site-directed mutagenesis, and affinity studies. Mol Pharmacol, 71 (3): 724-35. [PMID:17170199]
18. Ding BS, Liu CH, Sun Y, Chen Y, Swendeman SL, Jung B, Chavez D, Cao Z, Christoffersen C, Nielsen LB et al.. (2016) HDL activation of endothelial sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1) promotes regeneration and suppresses fibrosis in the liver. JCI Insight, 1 (21): e87058. [PMID:28018969]
19. Faroudi M, Hons M, Zachacz A, Dumont C, Lyck R, Stein JV, Tybulewicz VL. (2010) Critical roles for Rac GTPases in T-cell migration to and within lymph nodes. Blood, 116 (25): 5536-47. [PMID:20870900]
20. Forrest M, Sun SY, Hajdu R, Bergstrom J, Card D, Doherty G, Hale J, Keohane C, Meyers C, Milligan J et al.. (2004) Immune cell regulation and cardiovascular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists in rodents are mediated via distinct receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 309 (2): 758-68. [PMID:14747617]
21. Foss FW, Snyder AH, Davis MD, Rouse M, Okusa MD, Lynch KR, Macdonald TL. (2007) Synthesis and biological evaluation of gamma-aminophosphonates as potent, subtype-selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists and antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem, 15 (2): 663-77. [PMID:17113298]
22. Fujishiro J, Kudou S, Iwai S, Takahashi M, Hakamata Y, Kinoshita M, Iwanami S, Izawa S, Yasue T, Hashizume K et al.. (2006) Use of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor agonist, KRP-203, in combination with a subtherapeutic dose of cyclosporine A for rat renal transplantation. Transplantation, 82 (6): 804-12. [PMID:17006328]
23. Galvani S, Sanson M, Blaho VA, Swendeman SL, Obinata H, Conger H, Dahlbäck B, Kono M, Proia RL, Smith JD et al.. (2015) HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P1 to limit vascular inflammation. Sci Signal, 8 (389): ra79. [PMID:26268607]
24. Gilmore JL, Xiao HY, Dhar TGM, Yang M, Xiao Z, Yang X, Taylor TL, McIntyre KW, Warrack BM, Shi H et al.. (2021) Bicyclic Ligand-Biased Agonists of S1P1: Exploring Side Chain Modifications to Modulate the PK, PD, and Safety Profiles. J Med Chem, 64 (3): 1454-1480. [PMID:33492963]
25. Gilmore JL, Xiao HY, Dhar TGM, Yang MG, Xiao Z, Xie J, Lehman-McKeeman LD, Gong L, Sun H, Lecureux L et al.. (2019) Identification and Preclinical Pharmacology of ((1 R,3 S)-1-Amino-3-(( S)-6-(2-methoxyphenethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)cyclopentyl)methanol (BMS-986166): A Differentiated Sphingosine-1-phosphate Receptor 1 (S1P1) Modulator Advanced into Clinical Trials. J Med Chem, 62 (5): 2265-2285. [PMID:30785748]
26. Glaenzel U, Jin Y, Nufer R, Li W, Schroer K, Adam-Stitah S, Peter van Marle S, Legangneux E, Borell H, James AD et al.. (2018) Metabolism and Disposition of Siponimod, a Novel Selective S1P1/S1P5 Agonist, in Healthy Volunteers and In Vitro Identification of Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes Involved in Its Oxidative Metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos, 46 (7): 1001-1013. [PMID:29735753]
27. Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, Jo E, Sanna MG, Brown S, Leaf N, Marsolais D, Schaeffer MT, Chapman J, Cameron M, Guerrero M et al.. (2008) Full pharmacological efficacy of a novel S1P1 agonist that does not require S1P-like headgroup interactions. Mol Pharmacol, 74 (5): 1308-18. [PMID:18708635]
28. Hale JJ, Lynch CL, Neway W, Mills SG, Hajdu R, Keohane CA, Rosenbach MJ, Milligan JA, Shei GJ, Parent SA et al.. (2004) A rational utilization of high-throughput screening affords selective, orally bioavailable 1-benzyl-3-carboxyazetidine sphingosine-1-phosphate-1 receptor agonists. J Med Chem, 47 (27): 6662-5. [PMID:15615513]
29. Hanson MA, Roth CB, Jo E, Griffith MT, Scott FL, Reinhart G, Desale H, Clemons B, Cahalan SM, Schuerer SC et al.. (2012) Crystal structure of a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Science, 335 (6070): 851-5. [PMID:22344443]
30. Hobson AD, Harris CM, van der Kam EL, Turner SC, Abibi A, Aguirre AL, Bousquet P, Kebede T, Konopacki DB, Gintant G et al.. (2015) Discovery of A-971432, An Orally Bioavailable Selective Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 5 (S1P5) Agonist for the Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Med Chem, 58 (23): 9154-70. [PMID:26509640]
31. Högenauer K, Billich A, Pally C, Streiff M, Wagner T, Welzenbach K, Nussbaumer P. (2008) Phosphorylation by sphingosine kinase 2 is essential for in vivo potency of FTY720 analogues. ChemMedChem, 3 (7): 1027-9. [PMID:18383466]
32. Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Kool M, Müller T, Soullié T, Willart MA, Hijdra D, Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN. (2006) Local application of FTY720 to the lung abrogates experimental asthma by altering dendritic cell function. J Clin Invest, 116 (11): 2935-44. [PMID:17080194]
33. Idzko M, Panther E, Corinti S, Morelli A, Ferrari D, Herouy Y, Dichmann S, Mockenhaupt M, Gebicke-Haerter P, Di Virgilio F et al.. (2002) Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces chemotaxis of immature and modulates cytokine-release in mature human dendritic cells for emergence of Th2 immune responses. FASEB J, 16 (6): 625-7. [PMID:11919175]
34. Im DS, Clemens J, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2001) Characterization of the human and mouse sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P5 (Edg-8): structure-activity relationship of sphingosine1-phosphate receptors. Biochemistry, 40 (46): 14053-60. [PMID:11705398]
35. Imeri F, Stepanovska Tanturovska B, Zivkovic A, Enzmann G, Schwalm S, Pfeilschifter J, Homann T, Kleuser B, Engelhardt B, Stark H et al.. (2021) Novel compounds with dual S1P receptor agonist and histamine H3 receptor antagonist activities act protective in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neuropharmacology, 186: 108464. [PMID:33460688]
36. Kabashima K, Haynes NM, Xu Y, Nutt SL, Allende ML, Proia RL, Cyster JG. (2006) Plasma cell S1P1 expression determines secondary lymphoid organ retention versus bone marrow tropism. J Exp Med, 203 (12): 2683-90. [PMID:17101733]
37. Kennedy PC, Zhu R, Huang T, Tomsig JL, Mathews TP, David M, Peyruchaud O, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2011) Characterization of a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor antagonist prodrug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 338 (3): 879-89. [PMID:21632869]
38. Kon J, Sato K, Watanabe T, Tomura H, Kuwabara A, Kimura T, Tamama K, Ishizuka T, Murata N, Kanda T et al.. (1999) Comparison of intrinsic activities of the putative sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtypes to regulate several signaling pathways in their cDNA-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem, 274 (34): 23940-7. [PMID:10446161]
39. Li Z, Chen W, Hale JJ, Lynch CL, Mills SG, Hajdu R, Keohane CA, Rosenbach MJ, Milligan JA, Shei GJ et al.. (2005) Discovery of potent 3,5-diphenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole sphingosine-1-phosphate-1 (S1P1) receptor agonists with exceptional selectivity against S1P2 and S1P3. J Med Chem, 48 (20): 6169-73. [PMID:16190743]
40. Liu G, Burns S, Huang G, Boyd K, Proia RL, Flavell RA, Chi H. (2009) The receptor S1P1 overrides regulatory T cell-mediated immune suppression through Akt-mTOR. Nat Immunol, 10 (7): 769-77. [PMID:19483717]
41. Liu S, Paknejad N, Zhu L, Kihara Y, Ray M, Chun J, Liu W, Hite RK, Huang XY. (2022) Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. Nat Commun, 13 (1): 731. [PMID:35136060]
42. Liu Y, Wada R, Yamashita T, Mi Y, Deng CX, Hobson JP, Rosenfeldt HM, Nava VE, Chae SS, Lee MJ et al.. (2000) Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J Clin Invest, 106 (8): 951-61. [PMID:11032855]
43. Mackle T, Gendy SS, Walsh M, McConn-Walsh R, Costello RW, Walsh MT. (2008) Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor expression in eosinophils of patients with allergic rhinitis, and effect of topical nasal steroid treatment on this receptor expression. J Laryngol Otol, 122 (12): 1309-17. [PMID:18808729]
44. Martinborough E, Boehm MF, Yeager AR, Tamiya J, Huang L, Brahmachary E, Moorjani M, Timony GA, Brooks JL, Peach R et al.. (2011) Selective sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor modulators and methods of chiral synthesis. Patent number: US20110172202 A1. Assignee: Martinborough E, Boehm MF, Yeager AR, Tamiya J, Huang L, Brahmachary E, Moorjani M, Timony GA, Brooks JL, Peach R et al.. Priority date: 13/11/2009. Publication date: 14/07/2011.
45. Matloubian M, Lo CG, Cinamon G, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Brinkmann V, Allende ML, Proia RL, Cyster JG. (2004) Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature, 427 (6972): 355-60. [PMID:14737169]
46. Niaudet C, Jung B, Kuo A, Swendeman S, Bull E, Seno T, Crocker R, Fu Z, Smith LEH, Hla T. (2023) Therapeutic activation of endothelial sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 by chaperone-bound S1P suppresses proliferative retinal neovascularization. EMBO Mol Med, 15 (5): e16645. [PMID:36912000]
47. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Gonda K, Okazaki H, Chang K, Yatomi Y, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. (1998) EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem, 273 (42): 27104-10. [PMID:9765227]
48. Olivera A. (2008) Unraveling the complexities of sphingosine-1-phosphate function: the mast cell model. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 86 (1-4): 1-11. [PMID:18403224]
49. Osinde M, Mullershausen F, Dev KK. (2007) Phosphorylated FTY720 stimulates ERK phosphorylation in astrocytes via S1P receptors. Neuropharmacology, 52 (5): 1210-8. [PMID:17379261]
50. Pan S, Gray NS, Gao W, Mi Y, Fan Y, Wang X, Tuntland T, Che J, Lefebvre S, Chen Y et al.. (2013) Discovery of BAF312 (Siponimod), a Potent and Selective S1P Receptor Modulator. ACS Med Chem Lett, 4 (3): 333-7. [PMID:24900670]
51. Pan S, Mi Y, Pally C, Beerli C, Chen A, Guerini D, Hinterding K, Nuesslein-Hildesheim B, Tuntland T, Lefebvre S et al.. (2006) A monoselective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist prevents allograft rejection in a stringent rat heart transplantation model. Chem Biol, 13 (11): 1227-34. [PMID:17114004]
52. Pereira JP, Xu Y, Cyster JG. (2010) A role for S1P and S1P1 in immature-B cell egress from mouse bone marrow. PLoS ONE, 5 (2): e9277. [PMID:20174580]
53. Piali L, Birker-Robaczewska M, Lescop C, Froidevaux S, Schmitz N, Morrison K, Kohl C, Rey M, Studer R, Vezzali E et al.. (2017) Cenerimod, a novel selective S1P1receptor modulator with unique signaling properties. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 5 (6). [PMID:29226621]
54. Poirier B, Briand V, Kadereit D, Schäfer M, Wohlfart P, Philippo MC, Caillaud D, Gouraud L, Grailhe P, Bidouard JP et al.. (2020) A G protein-biased S1P1 agonist, SAR247799, protects endothelial cells without affecting lymphocyte numbers. Sci Signal, 13 (634). [PMID:32487716]
55. Price MM, Oskeritzian CA, Milstien S, Spiegel S. (2008) Sphingosine-1-phosphate synthesis and functions in mast cells. Future Lipidol, 3 (6): 665-674. [PMID:19802381]
56. Quancard J, Bollbuck B, Janser P, Angst D, Berst F, Buehlmayer P, Streiff M, Beerli C, Brinkmann V, Guerini D et al.. (2012) A potent and selective S1P(1) antagonist with efficacy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Chem Biol, 19 (9): 1142-51. [PMID:22999882]
57. Sanna MG, Liao J, Jo E, Alfonso C, Ahn MY, Peterson MS, Webb B, Lefebvre S, Chun J, Gray N et al.. (2004) Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor subtypes S1P1 and S1P3, respectively, regulate lymphocyte recirculation and heart rate. J Biol Chem, 279 (14): 13839-48. [PMID:14732717]
58. Sanna MG, Vincent KP, Repetto E, Nguyen N, Brown SJ, Abgaryan L, Riley SW, Leaf NB, Cahalan SM, Kiosses WB et al.. (2016) Bitopic Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1P3) Antagonist Rescue from Complete Heart Block: Pharmacological and Genetic Evidence for Direct S1P3 Regulation of Mouse Cardiac Conduction. Mol Pharmacol, 89 (1): 176-86. [PMID:26494861]
59. Sanna MG, Wang SK, Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, Don A, Marsolais D, Matheu MP, Wei SH, Parker I, Jo E, Cheng WC et al.. (2006) Enhancement of capillary leakage and restoration of lymphocyte egress by a chiral S1P1 antagonist in vivo. Nat Chem Biol, 2 (8): 434-41. [PMID:16829954]
60. Sassoli C, Pierucci F, Tani A, Frati A, Chellini F, Matteini F, Vestri A, Anderloni G, Nosi D, Zecchi-Orlandini S et al.. (2018) Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Is Required for MMP-2 Function in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Cytoskeleton Assembly and Proliferation. Stem Cells Int, 2018: 5034679. [PMID:29713350]
61. Sawicka E, Zuany-Amorim C, Manlius C, Trifilieff A, Brinkmann V, Kemeny DM, Walker C. (2003) Inhibition of Th1- and Th2-mediated airway inflammation by the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist FTY720. J Immunol, 171 (11): 6206-14. [PMID:14634137]
62. Schwab SR, Cyster JG. (2007) Finding a way out: lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Nat Immunol, 8 (12): 1295-301. [PMID:18026082]
63. Scott FL, Clemons B, Brooks J, Brahmachary E, Powell R, Dedman H, Desale HG, Timony GA, Martinborough E, Rosen H et al.. (2016) Ozanimod (RPC1063) is a potent sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1 ) and receptor-5 (S1P5 ) agonist with autoimmune disease-modifying activity. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (11): 1778-92. [PMID:26990079]
64. Shimano K, Maeda Y, Kataoka H, Murase M, Mochizuki S, Utsumi H, Oshita K, Sugahara K. (2019) Amiselimod (MT-1303), a novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 functional antagonist, inhibits progress of chronic colitis induced by transfer of CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells. PLoS One, 14 (12): e0226154. [PMID:31805144]
65. Song J, Matsuda C, Kai Y, Nishida T, Nakajima K, Mizushima T, Kinoshita M, Yasue T, Sawa Y, Ito T. (2008) A novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist, 2-amino-2-propanediol hydrochloride (KRP-203), regulates chronic colitis in interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 324 (1): 276-83. [PMID:17898319]
66. Stepanovska Tanturovska B, Zivkovic A, Imeri F, Homann T, Kleuser B, Stark H, Huwiler A. (2021) ST-2191, an Anellated Bismorpholino Derivative of Oxy-Fingolimod, Shows Selective S1P1 Agonist and Functional Antagonist Potency In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules, 26 (17). [PMID:34500564]
67. Subei AM, Cohen JA. (2015) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators in multiple sclerosis. CNS Drugs, 29 (7): 565-75. [PMID:26239599]
68. Sugahara K, Maeda Y, Shimano K, Mogami A, Kataoka H, Ogawa K, Hikida K, Kumagai H, Asayama M, Yamamoto T et al.. (2017) Amiselimod, a novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 modulator, has potent therapeutic efficacy for autoimmune diseases, with low bradycardia risk. Br J Pharmacol, 174 (1): 15-27. [PMID:27714763]
69. Taylor Meadows KR, Steinberg MW, Clemons B, Stokes ME, Opiteck GJ, Peach R, Scott FL. (2018) Ozanimod (RPC1063), a selective S1PR1 and S1PR5 modulator, reduces chronic inflammation and alleviates kidney pathology in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE, 13 (4): e0193236. [PMID:29608575]
70. Tian Y, Jin J, Wang X, Han W, Li G, Zhou W, Xiao Q, Qi J, Chen X, Yin D. (2013) Design, synthesis and docking-based 3D-QSAR study of novel 2-substituted 2-aminopropane-1,3-diols as potent and selective agonists of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 (S1P1) receptor. Med Chem Comm, 4: 1267-1274. DOI: 10.1039/C3MD00079F
71. Velagapudi S, Rohrer L, Poti F, Feuerborn R, Perisa D, Wang D, Panteloglou G, Potapenko A, Yalcinkaya M, Hülsmeier AJ et al.. (2021) Apolipoprotein M and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Promote the Transendothelial Transport of High-Density Lipoprotein. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 41 (10): e468-e479. [PMID:34407633]
72. Wang W, Graeler MH, Goetzl EJ. (2004) Physiological sphingosine 1-phosphate requirement for optimal activity of mouse CD4+ regulatory T Cells. FASEB J, 18 (9): 1043-5. [PMID:15084513]
73. Xiao Q, Jin J, Wang X, Hu J, Xi M, Tian Y, Yin D. (2016) Synthesis, identification, and biological activity of metabolites of two novel selective S1P1 agonists. Bioorg Med Chem, 24 (10): 2273-9. [PMID:27068143]
74. Xu J, Gray F, Henderson A, Hicks K, Yang J, Thompson P, Oliver J. (2014) Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and bioavailability of GSK2018682, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev, 3 (3): 170-8. [PMID:27128606]
75. Yamamoto R, Okada Y, Hirose J, Koshika T, Kawato Y, Maeda M, Saito R, Hattori K, Harada H, Nagasaka Y et al.. (2014) ASP4058, a novel agonist for sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and 5, ameliorates rodent experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a favorable safety profile. PLoS ONE, 9 (10): e110819. [PMID:25347187]
76. Zhang G, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Fukushima N, Chun J. (1999) Comparative analysis of three murine G-protein coupled receptors activated by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Gene, 227 (1): 89-99. [PMID:9931453]
77. Zheng W, Pan W, Yang X. (2015) Immune adjustment compound, use thereof and pharmaceutical composition comprising same. Patent number: WO2015039587A1. Assignee: Suzhou Kangnaide Biopharmaceutical. Priority date: 22/09/2013. Publication date: 26/03/2015.

 Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb
Target has curated data in GtoImmuPdb