GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
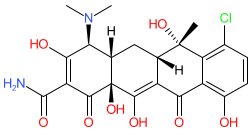
Synonyms: Aureomycin®
chlortetracycline is an approved drug (FDA (1950))
Compound class:
Natural product
Comment: Chlortetracycline is a tetracycline antibacterial, originally isolated from Kitasatospora aureofaciens (formerly Streptomyces aureofaciens), and the first compound from this class to be discovered [3-5]. Note that the structure shown here matches the CAS-assigned structure. The PubChem link, provided in the table below, is to their standardized chemical structure (CID 54675777), although this is not an exact structural match.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Chopra I, Hawkey PM, Hinton M. (1992)
Tetracyclines, molecular and clinical aspects. J Antimicrob Chemother, 29 (3): 245-77. [PMID:1592696] |
|
2. Chopra I, Roberts M. (2001)
Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 65 (2): 232-60 ; second page, table of contents. [PMID:11381101] |
|
3. DUGGAR BM. (1948)
Aureomycin; a product of the continuing search for new antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 51 (Art. 2): 177-81. [PMID:18112227] |
|
4. Paine Jr TF, Collins HS, Finland M. (1948)
Bacteriologic Studies on Aureomycin. J Bacteriol, 56 (4): 489-97. [PMID:16561597] |
|
5. PRICE CW, RANDALL WA, WELCH H. (1948)
Bacteriological studies of aureomycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 51 (Art. 2): 211-7. [PMID:18124196] |