GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: Aureomycin®
chlortetracycline is an approved drug (FDA (1950))
Compound class:
Natural product
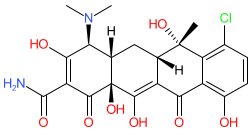
Comment: Chlortetracycline is a tetracycline antibacterial, originally isolated from Kitasatospora aureofaciens (formerly Streptomyces aureofaciens), and the first compound from this class to be discovered [3-5]. Note that the structure shown here matches the CAS-assigned structure. The PubChem link, provided in the table below, is to their standardized chemical structure (CID 54675777), although this is not an exact structural match.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| The World Health Organization's Model List of Essential Medicines lists chlortetracycline as a therapeutic alternative to tetracycline, under the category of ophthalmological preparations (anti-infective agents). Chlortetracycline hydrochloride was approved by the US FDA, as an ophthalmic ointment (under the trade name Aureomycin®), but has since been discontinued. There is no EU-wide EMA approval for use of this drug, although individual national approval agencies have granted marketing authorisation for ophthalmic and cutaneous use. Chlortetracycline is used widely in veterinary medicine. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Tetracyclines inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding reversibly to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit and preventing the aminoacyl tRNA from binding to the acceptor (A) site on the mRNA-ribosome complex (reviewed in [1-2]). |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Drugs.com |