GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
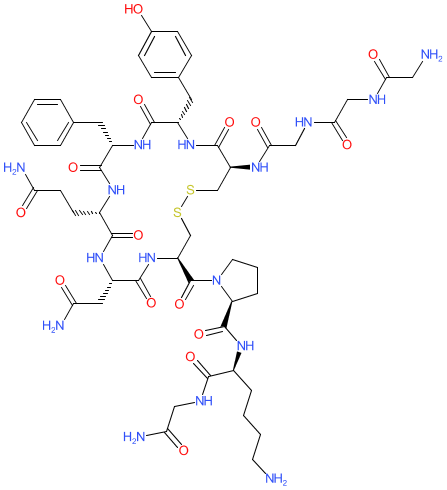
Synonyms: glycyl-glycyl-glycyl-L-cysteinyl-L-tyrosyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-glutaminyl-L-asparagyl-L-cysteinyl-L-prolyl-L-lysyl-glycinamide (4->9)-disulfide | Glypressin® | N-(N-(N-Glycylglycyl)glycyl)-8-L-lysinevasopressin | Terlivaz® | Variquel®
terlipressin is an approved drug (UK (2001), FDA (2022))
Compound class:
Peptide
Comment: Terlipressin is a clinically used vasopressin analogue. Terlipressin is biotransformed to its active moiety, lysine vasopressin (LVP). It has vasoconstrictive, antihemorrhagic, and antidiuretic properties.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Terlipressin is used as a vasoactive drug in the management of low blood pressure, principally when norepinephrine is ineffective. It also helps prevent urination. Indications for use include norepinephrine-resistant septic shock and hepatorenal syndrome. Terlipressin is approved for use in a number of countries, but not under EMA authorisation. Terlipressin was evaluated for efficacy in patients with hepatorenal syndrome type 1 (HRS-1) [1-2]. FDA approval for terlipressin (Terlivaz), as a treatment to improve kidney function in patients with hepatorenal syndrome, was granted in September 2022. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT01143246 | A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study to Confirm the Reversal of Hepatorenal Syndrome Type 1 With Terlipressin | Phase 3 Interventional | Mallinckrodt | Despite demonstrating an improvement in overall survival in patients with HRS-1, the FDA declined to approve terlipressin (in 2020) for this indication, stating that they would require more information to support a positive risk-benefit profile before reconsidering their decision. | 2 |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) |