Contents:
| Quaternary Structure: Subunits |
| RAMP2 (Accessory protein) |
| calcitonin receptor-like receptor |
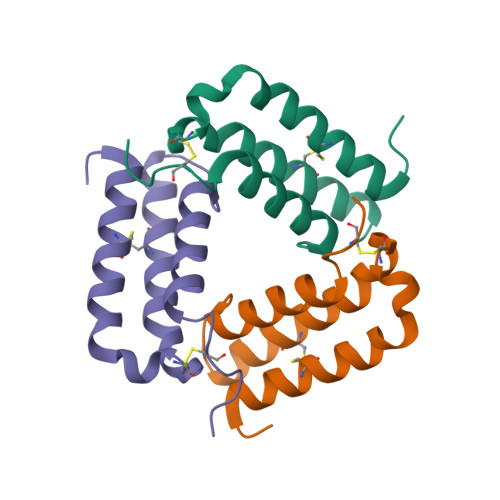
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
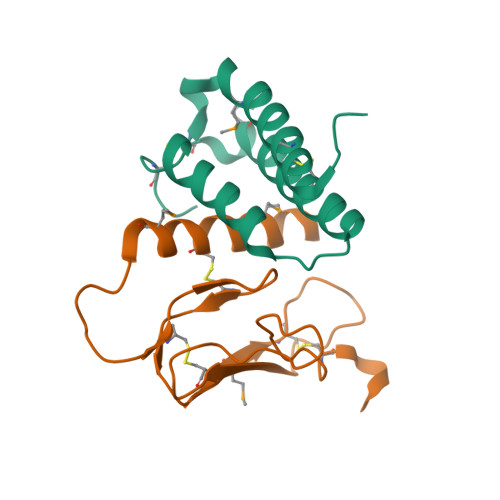
|
|
||||||||||
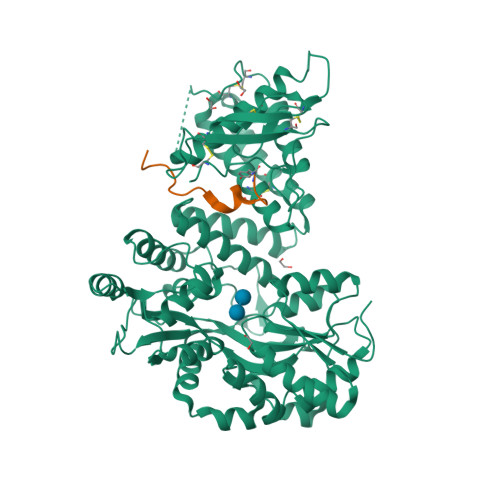
|
|
||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| adrenomedullin {Sp: Human} , adrenomedullin {Sp: Mouse} , adrenomedullin {Sp: Rat} |
| adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Human} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Mouse} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Rat} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Human} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Human} , β-CGRP {Sp: Mouse} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Rat} |
| Comments: Adrenomedullin and adrenomedullin 2/intermedin are the most likely physiological agonists. |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| adrenomedullin (ADM, P35318) > adrenomedullin 2/intermedin (ADM2, Q7Z4H4) > α-CGRP (CALCA, P06881), β-CGRP (CALCB, P10092), amylin (IAPP, P10997) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference [14] uses the rat calcitonin receptor-like receptor but mouse RAMP2. Reference [8] uses the rat calcitonin receptor-like receptor but human RAMP2. There is evidence that the actions of AM2/intermedin are likely to be system-dependent; there is one report that it is a partial agonist on AM1 receptors [28]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High concentrations of AM22-52 will also block CGRP receptors [6]. No antagonist satisfactorily discriminates between human AM1 and AM2 receptors, although in rats AM22-52 shows a tendency to preferentially block AM1 receptors. Even here the difference is small [12]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 1,20 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gi/Go family Gq/G11 family |
Guanylate cyclase stimulation Phospholipase C stimulation Other - See Comments |
| Comments: AM can also activate phosphatidylinositol 3-(OH) kinase [21]. | |
| References: 3,15 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
References
1. Aiyar N, Disa J, Pullen M, Nambi P. (2001) Receptor activity modifying proteins interaction with human and porcine calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) in HEK-293 cells. Mol Cell Biochem, 224 (1-2): 123-33. [PMID:11693189]
2. Aldecoa A, Gujer R, Fischer JA, Born W. (2000) Mammalian calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity modifying protein complexes define calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptors in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells. FEBS Lett, 471 (2-3): 156-60. [PMID:10767413]
3. Ali N, Yousufzai SY, Abdel-Latif AA. (2000) Activation of particulate guanylate cyclase by adrenomedullin in cultured SV-40 transformed cat iris sphincter smooth muscle (SV-CISM-2) cells. Cell Signal, 12: 491-498. [PMID:10989285]
4. Allen MA, Ferguson AV. (1996) In vitro recordings from area postrema neurons demonstrate responsiveness to adrenomedullin. Am J Physiol, 270 (4 Pt 2): R920-5. [PMID:8967423]
5. Andreis PG, Neri G, Prayer-Galetti T, Rossi GP, Gottardo G, Malendowicz LK, Nussdorfer GG. (1997) Effects of adrenomedullin on the human adrenal glands: an in vitro study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 82 (4): 1167-70. [PMID:9100590]
6. Bailey RJ, Hay DL. (2006) Pharmacology of the human CGRP1 receptor in Cos 7 cells. Peptides, 27 (6): 1367-75. [PMID:16375989]
7. Booe JM, Walker CS, Barwell J, Kuteyi G, Simms J, Jamaluddin MA, Warner ML, Bill RM, Harris PW, Brimble MA et al.. (2015) Structural Basis for Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein-Dependent Selective Peptide Recognition by a G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Mol Cell, 58 (6): 1040-52. [PMID:25982113]
8. Bühlmann N, Leuthäuser K, Muff R, Fischer JA, Born W. (1999) A receptor activity modifying protein (RAMP)2-dependent adrenomedullin receptor is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor when coexpressed with human RAMP1. Endocrinology, 140 (6): 2883-90. [PMID:10342881]
9. Dackor RT, Fritz-Six K, Dunworth WP, Gibbons CL, Smithies O, Caron KM. (2006) Hydrops fetalis, cardiovascular defects, and embryonic lethality in mice lacking the calcitonin receptor-like receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol, 26 (7): 2511-8. [PMID:16537897]
10. Fritz-Six KL, Dunworth WP, Li M, Caron KM. (2008) Adrenomedullin signaling is necessary for murine lymphatic vascular development. J Clin Invest, 118 (1): 40-50. [PMID:18097475]
11. Hay DL, Garelja ML, Poyner DR, Walker CS. (2018) Update on the pharmacology of calcitonin/CGRP family of peptides: IUPHAR Review 25. Br J Pharmacol, 175 (1): 3-17. [PMID:29059473]
12. Hay DL, Howitt SG, Conner AC, Schindler M, Smith DM, Poyner DR. (2003) CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 produce pharmacologically distinct adrenomedullin receptors: a comparison of effects of adrenomedullin22-52, CGRP8-37 and BIBN4096BS. Br J Pharmacol, 140 (3): 477-86. [PMID:12970090]
13. Husmann K, Born W, Fischer JA, Muff R. (2003) Three receptor-activity-modifying proteins define calcitonin gene-related peptide or adrenomedullin selectivity of the mouse calcitonin-like receptor in COS-7 cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 66 (11): 2107-15. [PMID:14609735]
14. Husmann K, Sexton PM, Fischer JA, Born W. (2000) Mouse receptor-activity-modifying proteins 1, -2 and -3: amino acid sequence, expression and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 162 (1-2): 35-43. [PMID:10854696]
15. Ichikawa I, Brenner BM. (1976) Of unglazed pottery and glomerular sieving. Kidney Int, 10 (3): 264-7. [PMID:787620]
16. Ichikawa-Shindo Y, Sakurai T, Kamiyoshi A, Kawate H, Iinuma N, Yoshizawa T, Koyama T, Fukuchi J, Iimuro S, Moriyama N et al.. (2008) The GPCR modulator protein RAMP2 is essential for angiogenesis and vascular integrity. J Clin Invest, 118 (1): 29-39. [PMID:18097473]
17. Igarashi K, Sakurai T, Kamiyoshi A, Ichikawa-Shindo Y, Kawate H, Yamauchi A, Toriyama Y, Tanaka M, Liu T, Xian X et al.. (2014) Pathophysiological roles of adrenomedullin-RAMP2 system in acute and chronic cerebral ischemia. Peptides, 62: 21-31. [PMID:25252154]
18. Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, Eto T. (1993) Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 192 (2): 553-60. [PMID:8387282]
19. Kusano S, Kukimoto-Niino M, Hino N, Ohsawa N, Okuda K, Sakamoto K, Shirouzu M, Shindo T, Yokoyama S. (2012) Structural basis for extracellular interactions between calcitonin receptor-like receptor and receptor activity-modifying protein 2 for adrenomedullin-specific binding. Protein Sci, 21 (2): 199-210. [PMID:22102369]
20. McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Wise A, Brown J, Thompson N, Solari R, Lee MG, Foord SM. (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature, 393 (6683): 333-9. [PMID:9620797]
21. Nishimatsu H, Suzuki E, Nagata D, Moriyama N, Satonaka H, Walsh K, Sata M, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Goto A et al.. (2001) Adrenomedullin induces endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway in rat aorta. Circ Res, 89 (1): 63-70. [PMID:11440979]
22. Oliver KR, Kane SA, Salvatore CA, Mallee JJ, Kinsey AM, Koblan KS, Keyvan-Fouladi N, Heavens RP, Wainwright A, Jacobson M et al.. (2001) Cloning, characterization and central nervous system distribution of receptor activity modifying proteins in the rat. Eur J Neurosci, 14 (4): 618-28. [PMID:11556887]
23. Owji AA, Smith DM, Coppock HA, Morgan DG, Bhogal R, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. (1995) An abundant and specific binding site for the novel vasodilator adrenomedullin in the rat. Endocrinology, 136 (5): 2127-34. [PMID:7720662]
24. Quigley A, Pike ACW, Burgess-Brown N, Krojer T, Shrestha L, Goubin S, Kim J, Das S, Muniz JRC, Canning P, Chaikuad A, Vollmar M, Von Delft F, Arrowsmith CH, Weigelt J, Edwards AM, Bountra C, Barr AJ, Carpenter EP. Structure of the Extracellular Domain of Human Ramp2. Accessed on 20/07/2012. Modified on 20/07/2012. PDB, http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?pdbId=2XVT
25. Tam CW, Husmann K, Clark NC, Clark JE, Lazar Z, Ittner LM, Götz J, Douglas G, Grant AD, Sugden D et al.. (2006) Enhanced vascular responses to adrenomedullin in mice overexpressing receptor-activity-modifying protein 2. Circ Res, 98 (2): 262-70. [PMID:16373602]
26. Uetake R, Sakurai T, Kamiyoshi A, Ichikawa-Shindo Y, Kawate H, Iesato Y, Yoshizawa T, Koyama T, Yang L, Toriyama Y et al.. (2014) Adrenomedullin-RAMP2 system suppresses ER stress-induced tubule cell death and is involved in kidney protection. PLoS ONE, 9 (2): e87667. [PMID:24505304]
27. Upton PD, Austin C, Taylor GM, Nandha KA, Clark AJ, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Smith DM. (1997) Expression of adrenomedullin (ADM) and its binding sites in the rat uterus: increased number of binding sites and ADM messenger ribonucleic acid in 20-day pregnant rats compared with nonpregnant rats. Endocrinology, 138 (6): 2508-14. [PMID:9165042]
28. Wunder F, Rebmann A, Geerts A, Kalthof B. (2008) Pharmacological and kinetic characterization of adrenomedullin 1 and calcitonin gene-related peptide 1 receptor reporter cell lines. Mol Pharmacol, 73 (4): 1235-43. [PMID:18174292]
29. Yoshizawa T, Sakurai T, Kamiyoshi A, Ichikawa-Shindo Y, Kawate H, Iesato Y, Koyama T, Uetake R, Yang L, Yamauchi A et al.. (2013) Novel regulation of cardiac metabolism and homeostasis by the adrenomedullin-receptor activity-modifying protein 2 system. Hypertension, 61 (2): 341-51. [PMID:23297372]