Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Rank order lists
- Activators
- Inhibitors
- Gating Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Immuno Process Associations
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 2 | 0 | 390 | 11p15.1 | KCNJ11 | potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11 | 4 |
| Mouse | 2 | 0 | 390 | 7 29.66 cM | Kcnj11 | potassium inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11 | 4,15 |
| Rat | 2 | 0 | 390 | 1q22 | Kcnj11 | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11 | 6 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q14654 (Hs), Q61743 (Mm), P70673 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 2.60.40.1400 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1886 (Hs), CHEMBL3038487 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | Q14654 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000187486 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000096146 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000021128 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 3767 (Hs), 16514 (Mm), 83535 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000187486 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:3767 (Hs), mmu:16514 (Mm), rno:83535 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600937 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA122787 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q14654 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000525 (Hs), NM_010602 (Mm), NM_031358 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000516 (Hs), NP_034732 (Mm), NP_112648 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q14654 (Hs), Q61743 (Mm), P70673 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | KCNJ11 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
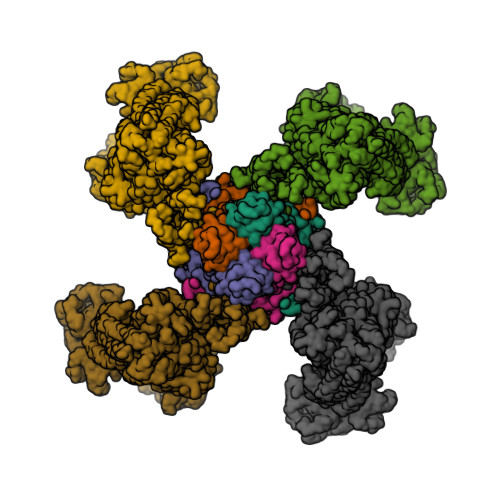
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Protein Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kir6.2 forms IK.ATP when in complex with SUR1 in pancreatic β cells [1,4], SUR2A in heart and skeletal muscle [5] and SUR2B in smooth muscle [6]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Functional Characteristics  |
|
| ATP-sensitive, inward-rectifier current | |
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
| Ion Selectivity and Conductance Comments | ||||||
| Conductance has been measured in heteromers of Kir6.2 coexpressed with either SUR1 (74.3-76.4pS, [2,4]) or SUR2A (79.3pS, [5]). |
| Associated subunits (Human) |
| SUR1, SUR2A, SUR2B |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| These studies were of Kir6.2 coexpressed with a member of the sulfonylurea receptor family (SUR1 [4], SUR2A [5] or SUR2B [6]). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gating inhibitors 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The pIC50 for Kir6.2 coexpressed with SUR1 and SUR2A are 5.0 and 4.0 respectively [4-5]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| These studies were of Kir6.2 coexpressed with a member of the sulfonylurea receptor family (SUR1 [4], SUR2A [5] or SUR2B [6]). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | ||
|
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| The sulfonyurea drugs (acetohexamide, tolbutamide and glibenclamide) inhibit sufonylurea receptors. The functional sulfonylurea receptor has been characterised as a hetero-octamer formed by four SUR (ATP binding cassette transporter, ABCC8 or ABCC9) and four Kir6.2 (inwardly rectifying potassium channel) subunits, with the Kir6.2 subunits forming the core ion pore and the SUR subunits providing the regulatory properties [10]. Co-expression of Kir6.2 with SUR1, reconstitutes the ATP-dependent K+ conductivity inhibited by the sulfonyureas [4]. |
References
1. Aguilar-Bryan L, Nichols CG, Wechsler SW, Clement 4th JP, Boyd 3rd AE, González G, Herrera-Sosa H, Nguy K, Bryan J, Nelson DA. (1995) Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science, 268 (5209): 423-6. [PMID:7716547]
2. Béguin P, Nagashima K, Nishimura M, Gonoi T, Seino S. (1999) PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the human K(ATP) channel: separate roles of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunit phosphorylation. EMBO J, 18 (17): 4722-32. [PMID:10469651]
3. Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, Howard N, Srinivasan S, Silva JM, Molnes J et al.. (2004) Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med, 350 (18): 1838-49. [PMID:15115830]
4. Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement 4th JP, Namba N, Inazawa J, Gonzalez G, Aguilar-Bryan L, Seino S, Bryan J. (1995) Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science, 270 (5239): 1166-70. [PMID:7502040]
5. Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement JP, Wang CZ, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Seino S. (1996) A family of sulfonylurea receptors determines the pharmacological properties of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Neuron, 16 (5): 1011-7. [PMID:8630239]
6. Isomoto S, Kondo C, Yamada M, Matsumoto S, Higashiguchi O, Horio Y, Matsuzawa Y, Kurachi Y. (1996) A novel sulfonylurea receptor forms with BIR (Kir6.2) a smooth muscle type ATP-sensitive K+ channel. J Biol Chem, 271 (40): 24321-4. [PMID:8798681]
7. Li N, Wu JX, Ding D, Cheng J, Gao N, Chen L. (2017) Structure of a Pancreatic ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel. Cell, 168 (1-2): 101-110.e10. [PMID:28086082]
8. Liss B, Haeckel O, Wildmann J, Miki T, Seino S, Roeper J. (2005) K-ATP channels promote the differential degeneration of dopaminergic midbrain neurons. Nat Neurosci, 8 (12): 1742-51. [PMID:16299504]
9. Miki T, Liss B, Minami K, Shiuchi T, Saraya A, Kashima Y, Horiuchi M, Ashcroft F, Minokoshi Y, Roeper J et al.. (2001) ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Nat Neurosci, 4 (5): 507-12. [PMID:11319559]
10. Miki T, Nagashima K, Seino S. (1999) The structure and function of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in insulin-secreting pancreatic beta-cells. J Mol Endocrinol, 22 (2): 113-23. [PMID:10194514]
11. Miki T, Nagashima K, Tashiro F, Kotake K, Yoshitomi H, Tamamoto A, Gonoi T, Iwanaga T, Miyazaki J, Seino S. (1998) Defective insulin secretion and enhanced insulin action in KATP channel-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95 (18): 10402-6. [PMID:9724715]
12. Miki T, Tashiro F, Iwanaga T, Nagashima K, Yoshitomi H, Aihara H, Nitta Y, Gonoi T, Inagaki N, Miyazaki Ji et al.. (1997) Abnormalities of pancreatic islets by targeted expression of a dominant-negative KATP channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (22): 11969-73. [PMID:9342346]
13. Nestorowicz A, Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Schoor KP, Wilson BA, Glaser B, Landau H, Stanley CA, Thornton PS, Seino S et al.. (1997) A nonsense mutation in the inward rectifier potassium channel gene, Kir6.2, is associated with familial hyperinsulinism. Diabetes, 46 (11): 1743-8. [PMID:9356020]
14. Pearson ER, Flechtner I, Njølstad PR, Malecki MT, Flanagan SE, Larkin B, Ashcroft FM, Klimes I, Codner E, Iotova V et al.. (2006) Switching from insulin to oral sulfonylureas in patients with diabetes due to Kir6.2 mutations. N Engl J Med, 355 (5): 467-77. [PMID:16885550]
15. Sakura H, Bond C, Warren-Perry M, Horsley S, Kearney L, Tucker S, Adelman J, Turner R, Ashcroft FM. (1995) Characterization and variation of a human inwardly-rectifying-K-channel gene (KCNJ6): a putative ATP-sensitive K-channel subunit. FEBS Lett, 367 (2): 193-7. [PMID:7796919]
16. Suzuki M, Sasaki N, Miki T, Sakamoto N, Ohmoto-Sekine Y, Tamagawa M, Seino S, Marbán E, Nakaya H. (2002) Role of sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels in cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J Clin Invest, 109 (4): 509-16. [PMID:11854323]
17. Yamada K, Ji JJ, Yuan H, Miki T, Sato S, Horimoto N, Shimizu T, Seino S, Inagaki N. (2001) Protective role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in hypoxia-induced generalized seizure. Science, 292 (5521): 1543-6. [PMID:11375491]
18. Zingman LV, Hodgson DM, Bast PH, Kane GC, Perez-Terzic C, Gumina RJ, Pucar D, Bienengraeber M, Dzeja PP, Miki T et al.. (2002) Kir6.2 is required for adaptation to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99 (20): 13278-83. [PMID:12271142]












