Contents:
- Quaternary Structure
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Antibodies
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
| Quaternary Structure: Subunits |
| RAMP1 (Accessory protein) |
| calcitonin receptor-like receptor |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| CGRP1 |
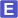
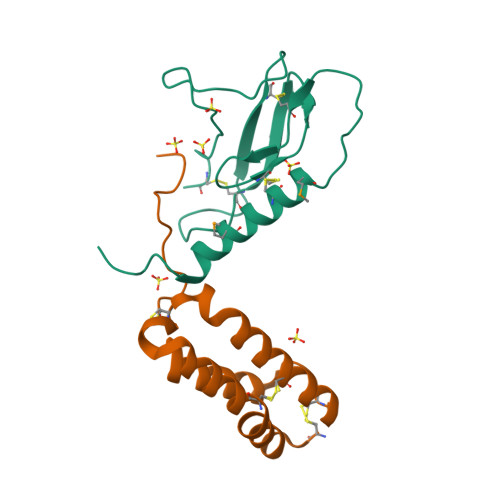
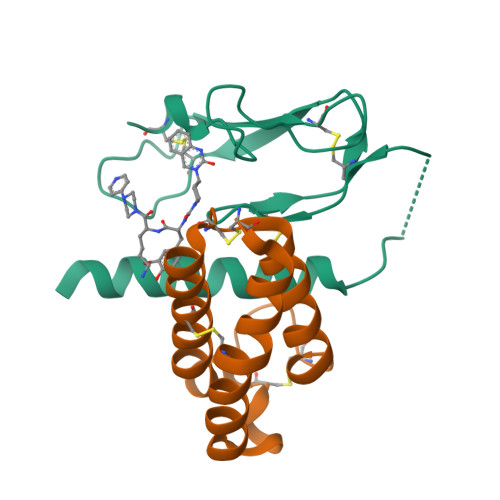
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
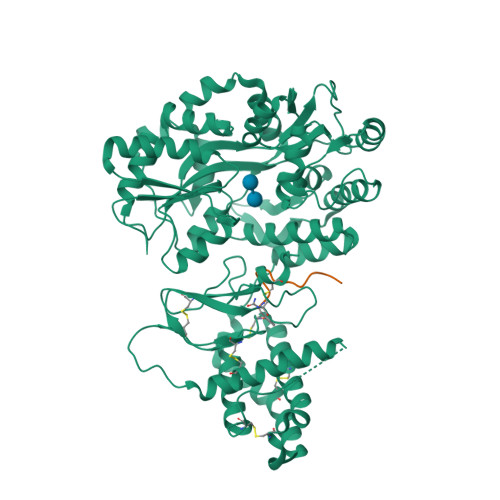
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| adrenomedullin {Sp: Human} , adrenomedullin {Sp: Mouse} , adrenomedullin {Sp: Rat} |
| adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Human} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Mouse} , adrenomedullin 2/intermedin {Sp: Rat} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Human} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Human} , β-CGRP {Sp: Mouse} |
| α-CGRP {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| β-CGRP {Sp: Rat} |
| α-CGRP-(8-37) (rat) |
| Comments: α-CGRP and β-CGRP are the principal endogenous agonists |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| α-CGRP (CALCA, P06881), β-CGRP (CALCB, P10092) > adrenomedullin (ADM, P35318) ≥ adrenomedullin 2/intermedin (ADM2, Q7Z4H4) > amylin (IAPP, P10997) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference [29] uses the rat calcitonin receptor-like receptor but mouse RAMP1. Reference [12] uses the rat calcitonin receptor-like receptor but human RAMP1. [Cys(ACM)2,7]-CGRP and [Cys(Et)2,7]-CGRP were introduced as selective CGRP2 agonists. This receptor phenotype is now considered to be a mixture of AM and AMY receptors [21]. [Cys(ACM)2,7]-CGRP is a partial agonist and the efficacy of [Cys(Et)2,7]-CGRP is very system dependent at CGRP and AMY receptors [6,22,44]. It is therefore recommended that these peptides are used with caution. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BIBN4096BS (and MK-0974) shows at least an order of magnitude selectivity for primate over non-primate receptors. The pharmacology of these compounds have recently been reviewed [42]. This affinity is conferred by a tryptophan at position 74 of human RAMP1 [35]. A variety of other non-peptide antagonists have been described, but their pharmacology has not been widely explored [35]. In functional assays the pA2 for CGRP 8-37 shows a wide spread of values from around 7 to nearly 9, depending on the system being analysed [19,24]. Thus it is difficult to use it to classify receptors. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibodies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 1,37 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gi/Go family Gq/G11 family |
Phospholipase C stimulation Potassium channel |
| Comments: CGRP can also activate a phosphatidylinositol 3-(OH) kinase dependent pathway and increase cGMP [47]. | |
| References: 2,34 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
References
1. Aiyar N, Disa J, Pullen M, Nambi P. (2001) Receptor activity modifying proteins interaction with human and porcine calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) in HEK-293 cells. Mol Cell Biochem, 224 (1-2): 123-33. [PMID:11693189]
2. Aiyar N, Disa J, Stadel JM, Lysko PG. (1999) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor independently stimulates 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate and Ca2+ signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biochem, 197 (1-2): 179-85. [PMID:10485337]
3. Aldecoa A, Gujer R, Fischer JA, Born W. (2000) Mammalian calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity modifying protein complexes define calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptors in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells. FEBS Lett, 471 (2-3): 156-60. [PMID:10767413]
4. Andreis PG, Mazzocchi G, Rebuffat P, Nussdorfer GG. (1997) Effects of adrenomedullin and proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide on rat zona glomerulosa cells. Life Sci, 60 (19): 1693-7. [PMID:9129124]
5. Avgoustou P. et al.. (2020) Discovery of a First-in-Class Potent Small Molecule Antagonist against the Adrenomedullin-2 Receptor. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00032
6. Bailey RJ, Hay DL. (2006) Pharmacology of the human CGRP1 receptor in Cos 7 cells. Peptides, 27 (6): 1367-75. [PMID:16375989]
7. Bell D, McDermott BJ. (1994) Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates a positive contractile response in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 23 (6): 1011-21. [PMID:7523774]
8. Bell IM, Fraley ME. (2012) Piperidinone carboxamide azaindane CGRP receptor antagonists. Patent number: US20120122911. Assignee: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.. Priority date: 12/11/2010. Publication date: 17/05/2012.
9. Booe JM, Walker CS, Barwell J, Kuteyi G, Simms J, Jamaluddin MA, Warner ML, Bill RM, Harris PW, Brimble MA et al.. (2015) Structural Basis for Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein-Dependent Selective Peptide Recognition by a G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Mol Cell, 58 (6): 1040-52. [PMID:25982113]
10. Bucknell SJ, Ator MA, Brown AJH, Brown J, Cansfield AD, Cansfield JE, Christopher JA, Congreve M, Cseke G, Deflorian F et al.. (2020) Structure-Based Drug Discovery of N-((R)-3-(7-Methyl-1H-indazol-5-yl)-1-oxo-1-(((S)-1-oxo-3-(piperidin-4-yl)-1-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl)propan-2-yl)amino)propan-2-yl)-2'-oxo-1',2'-dihydrospiro[piperidine-4,4'-pyrido[2,3-d][1,3]oxazine]-1-carboxamide (HTL22562): A Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor Antagonist for Acute Treatment of Migraine. J Med Chem, 63 (14): 7906-7920. [PMID:32558564]
11. Bullock CM, Wookey P, Bennett A, Mobasheri A, Dickerson I, Kelly S. (2014) Peripheral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor activation and mechanical sensitization of the joint in rat models of osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Rheumatol, 66 (8): 2188-200. [PMID:24719311]
12. Bühlmann N, Leuthäuser K, Muff R, Fischer JA, Born W. (1999) A receptor activity modifying protein (RAMP)2-dependent adrenomedullin receptor is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor when coexpressed with human RAMP1. Endocrinology, 140 (6): 2883-90. [PMID:10342881]
13. Champion HC, Bivalacqua TJ, Pierce RL, Murphy WA, Coy DH, Hyman AL, Kadowitz PJ. (2003) Responses to human CGRP, ADM, and PAMP in human thymic arteries. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 284 (2): R531-7. [PMID:12529288]
14. Chaturvedula PV, Mercer SE, Pin SS, Thalody G, Xu C, Conway CM, Keavy D, Signor L, Cantor GH, Mathias N et al.. (2013) Discovery of (R)-N-(3-(7-methyl-1H-indazol-5-yl)-1-(4-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-4-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)piperidine-1-carboxamide (BMS-742413): a potent human CGRP antagonist with superior safety profile for the treatment of migraine through intranasal delivery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 23 (11): 3157-61. [PMID:23632269]
15. Devesa I, Ferrándiz-Huertas C, Mathivanan S, Wolf C, Luján R, Changeux JP, Ferrer-Montiel A. (2014) αCGRP is essential for algesic exocytotic mobilization of TRPV1 channels in peptidergic nociceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111 (51): 18345-50. [PMID:25489075]
16. Doods H, Hallermayer G, Wu D, Entzeroth M, Rudolf K, Engel W, Eberlein W. (2000) Pharmacological profile of BIBN4096BS, the first selective small molecule CGRP antagonist. Br J Pharmacol, 129 (3): 420-3. [PMID:10711339]
17. Edvinsson L, Gulbenkian S, Barroso CP, Cunha e Sá M, Polak JM, Mortensen A, Jørgensen L, Jansen-Olesen I. (1998) Innervation of the human middle meningeal artery: immunohistochemistry, ultrastructure, and role of endothelium for vasomotility. Peptides, 19 (7): 1213-25. [PMID:9786171]
18. Edvinsson L, Sams A, Jansen-Olesen I, Tajti J, Kane SA, Rutledge RZ, Koblan KS, Hill RG, Longmore J. (2001) Characterisation of the effects of a non-peptide CGRP receptor antagonist in SK-N-MC cells and isolated human cerebral arteries. Eur J Pharmacol, 415 (1): 39-44. [PMID:11245850]
19. Evans BN, Rosenblatt MI, Mnayer LO, Oliver KR, Dickerson IM. (2000) CGRP-RCP, a novel protein required for signal transduction at calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptors. J Biol Chem, 275 (40): 31438-43. [PMID:10903324]
20. Han SP, Naes L, Westfall TC. (1990) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is the endogenous mediator of nonadrenergic-noncholinergic vasodilation in rat mesentery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 255 (2): 423-8. [PMID:2243334]
21. Hay DL. (2007) What makes a CGRP2 receptor?. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 34 (10): 963-71. [PMID:17714080]
22. Hay DL, Christopoulos G, Christopoulos A, Poyner DR, Sexton PM. (2005) Pharmacological discrimination of calcitonin receptor: receptor activity-modifying protein complexes. Mol Pharmacol, 67 (5): 1655-65. [PMID:15692146]
23. Hay DL, Christopoulos G, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM. (2006) Determinants of 1-piperidinecarboxamide, N-[2-[[5-amino-l-[[4-(4-pyridinyl)-l-piperazinyl]carbonyl]pentyl]amino]-1-[(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxoethyl]-4-(1,4-dihydro-2-oxo-3(2H)-quinazolinyl) (BIBN4096BS) affinity for calcitonin gene-related peptide and amylin receptors--the role of receptor activity modifying protein 1. Mol Pharmacol, 70: 1984-1991. [PMID:16959943]
24. Hay DL, Conner AC, Howitt SG, Takhshid MA, Simms J, Mahmoud K, Poyner DR. (2004) The pharmacology of CGRP-responsive receptors in cultured and transfected cells. Peptides, 25: 2019-2026. [PMID:15501536]
25. Hay DL, Howitt SG, Conner AC, Schindler M, Smith DM, Poyner DR. (2003) CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 produce pharmacologically distinct adrenomedullin receptors: a comparison of effects of adrenomedullin22-52, CGRP8-37 and BIBN4096BS. Br J Pharmacol, 140 (3): 477-86. [PMID:12970090]
26. Haynes JM, Cooper ME. (1995) Adrenomedullin and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat isolated kidney and in the anaesthetised rat: in vitro and in vivo effects. Eur J Pharmacol, 280 (1): 91-4. [PMID:7498258]
27. Hong Y, Hay DL, Quirion R, Poyner DR. (2012) The pharmacology of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin. Br J Pharmacol, 166 (1): 110-20. [PMID:21658025]
28. Husmann K, Born W, Fischer JA, Muff R. (2003) Three receptor-activity-modifying proteins define calcitonin gene-related peptide or adrenomedullin selectivity of the mouse calcitonin-like receptor in COS-7 cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 66 (11): 2107-15. [PMID:14609735]
29. Husmann K, Sexton PM, Fischer JA, Born W. (2000) Mouse receptor-activity-modifying proteins 1, -2 and -3: amino acid sequence, expression and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 162 (1-2): 35-43. [PMID:10854696]
30. Joshi P, Anderson C, Binch H, Hadida S, Yoo S, Bergeron D, Decker C, terHaar E, Moore J, Garcia-Guzman M et al.. (2014) Identification of potent CNS-penetrant thiazolidinones as novel CGRP receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 24 (3): 845-9. [PMID:24405707]
31. Jusek G, Reim D, Tsujikawa K, Holzmann B. (2012) Deficiency of the CGRP receptor component RAMP1 attenuates immunosuppression during the early phase of septic peritonitis. Immunobiology, 217 (8): 761-7. [PMID:22656887]
32. Kano H, Kohno M, Yasunari K, Yokokawa K, Horio T, Ikeda M, Minami M, Hanehira T, Takeda T, Yoshikawa J. (1996) Adrenomedullin as a novel antiproliferative factor of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens, 14 (2): 209-13. [PMID:8728298]
33. Kurashige C, Hosono K, Matsuda H, Tsujikawa K, Okamoto H, Majima M. (2014) Roles of receptor activity-modifying protein 1 in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis during skin wound healing in mice. FASEB J, 28 (3): 1237-47. [PMID:24308973]
34. Main MJ, Brown J, Brown S, Fraser NJ, Foord SM. (1998) The CGRP receptor can couple via pertussis toxin sensitive and insensitive G proteins. FEBS Lett, 441 (1): 6-10. [PMID:9877154]
35. Mallee JJ, Salvatore CA, LeBourdelles B, Oliver KR, Longmore J, Koblan KS, Kane SA. (2002) Receptor activity-modifying protein 1 determines the species selectivity of non-peptide CGRP receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem, 277 (16): 14294-8. [PMID:11847213]
36. Martínez V, Cuttitta F, Taché Y. (1997) Central action of adrenomedullin to inhibit gastric emptying in rats. Endocrinology, 138 (9): 3749-55. [PMID:9275061]
37. McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Wise A, Brown J, Thompson N, Solari R, Lee MG, Foord SM. (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature, 393 (6683): 333-9. [PMID:9620797]
38. Mercer SE, Chaturvedula PV, Conway CM, Cook DA, Davis CD, Pin SS, Macci R, Schartman R, Signor LJ, Widmann KA et al.. (2021) Azepino-indazoles as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 31: 127624. [PMID:33096162]
39. Mikami N, Watanabe K, Hashimoto N, Miyagi Y, Sueda K, Fukada S, Yamamoto H, Tsujikawa K. (2012) Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by promoting Th17-cell functions. Int Immunol, 24 (11): 681-91. [PMID:22843730]
40. Mogil JS, Miermeister F, Seifert F, Strasburg K, Zimmermann K, Reinold H, Austin JS, Bernardini N, Chesler EJ, Hofmann HA et al.. (2005) Variable sensitivity to noxious heat is mediated by differential expression of the CGRP gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102 (36): 12938-43. [PMID:16118273]
41. Moore E, Fraley ME, Bell IM, Burgey CS, White RB, Li CC, Regan CP, Danziger A, Stranieri Michener M, Hostetler E et al.. (2020) Characterization of Ubrogepant: A Potent and Selective Antagonist of the Human Calcitonin Gene‒Related Peptide Receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, [Epub ahead of print]. [PMID:31992609]
42. Moore EL, Salvatore CA. (2012) Targeting a family B GPCR/RAMP receptor complex: CGRP receptor antagonists and migraine. Br J Pharmacol, 166 (1): 66-78. [PMID:21871019]
43. Nakamuta H, Fukuda Y, Koida M, Fujii N, Otaka A, Funakoshi S, Yajima H, Mitsuyasu N, Orlowski RC. (1986) Binding sites of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP): abundant occurrence in visceral organs. Jpn J Pharmacol, 42 (2): 175-80. [PMID:3025489]
44. Nodin C, Vauquelin G, von Mentzer B. (2005) Cys2,7EtalphaCGRP is a potent agonist for CGRP1 receptors in SK-N-MC cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 69 (8): 1235-40. [PMID:15794944]
45. Oliver KR, Kane SA, Salvatore CA, Mallee JJ, Kinsey AM, Koblan KS, Keyvan-Fouladi N, Heavens RP, Wainwright A, Jacobson M et al.. (2001) Cloning, characterization and central nervous system distribution of receptor activity modifying proteins in the rat. Eur J Neurosci, 14 (4): 618-28. [PMID:11556887]
46. Pan KS, Siow A, Hay DL, Walker CS. (2020) Antagonism of CGRP Signaling by Rimegepant at Two Receptors. Front Pharmacol, 11: 1240. [PMID:32973499]
47. Parameswaran N, Disa J, Spielman WS, Brooks DP, Nambi P, Aiyar N. (2000) Activation of multiple mitogen-activated protein kinases by recombinant calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 389 (2-3): 125-30. [PMID:10688975]
48. Qing X, Keith IM. (2003) Targeted blocking of gene expression for CGRP receptors elevates pulmonary artery pressure in hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 285 (1): L86-96. [PMID:12626334]
49. Saetrum Opgaard O, Hasbak P, de Vries R, Saxena PR, Edvinsson L. (2000) Positive inotropy mediated via CGRP receptors in isolated human myocardial trabeculae. Eur J Pharmacol, 397 (2-3): 373-82. [PMID:10844137]
50. Salvatore CA, Hershey JC, Corcoran HA, Fay JF, Johnston VK, Moore EL, Mosser SD, Burgey CS, Paone DV, Shaw AW et al.. (2008) Pharmacological characterization of MK-0974 [N-[(3R,6S)-6-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)azepan-3-yl]-4-(2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carboxamide], a potent and orally active calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist for the treatment of migraine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 324 (2): 416-21. [PMID:18039958]
51. Shi L, Lehto SG, Zhu DX, Sun H, Zhang J, Smith BP, Immke DC, Wild KD, Xu C. (2016) Pharmacologic Characterization of AMG 334, a Potent and Selective Human Monoclonal Antibody against the Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 356 (1): 223-31. [PMID:26559125]
52. Taylor GM, Meeran K, O'Shea D, Smith DM, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. (1996) Adrenomedullin inhibits feeding in the rat by a mechanism involving calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors. Endocrinology, 137 (8): 3260-4. [PMID:8754748]
53. ter Haar E, Koth CM, Abdul-Manan N, Swenson L, Coll JT, Lippke JA, Lepre CA, Garcia-Guzman M, Moore JM. (2010) Crystal structure of the ectodomain complex of the CGRP receptor, a class-B GPCR, reveals the site of drug antagonism. Structure, 18 (9): 1083-93. [PMID:20826335]
54. Tsujikawa K, Yayama K, Hayashi T, Matsushita H, Yamaguchi T, Shigeno T, Ogitani Y, Hirayama M, Kato T, Fukada S et al.. (2007) Hypertension and dysregulated proinflammatory cytokine production in receptor activity-modifying protein 1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (42): 16702-7. [PMID:17923674]
55. Upton PD, Austin C, Taylor GM, Nandha KA, Clark AJ, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Smith DM. (1997) Expression of adrenomedullin (ADM) and its binding sites in the rat uterus: increased number of binding sites and ADM messenger ribonucleic acid in 20-day pregnant rats compared with nonpregnant rats. Endocrinology, 138 (6): 2508-14. [PMID:9165042]
56. Walker CS, Li X, Whiting L, Glyn-Jones S, Zhang S, Hickey AJ, Sewell MA, Ruggiero K, Phillips AR, Kraegen EW et al.. (2010) Mice lacking the neuropeptide alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide are protected against diet-induced obesity. Endocrinology, 151 (9): 4257-69. [PMID:20610563]
57. Wang Z, Martorell BC, Wälchli T, Vogel O, Fischer J, Born W, Vogel J. (2015) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptors are important to maintain cerebrovascular reactivity in chronic hypertension. PLoS ONE, 10 (4): e0123697. [PMID:25860809]
58. Zhang Z, Liu X, Morgan DA, Kuburas A, Thedens DR, Russo AF, Rahmouni K. (2011) Neuronal receptor activity-modifying protein 1 promotes energy expenditure in mice. Diabetes, 60 (4): 1063-71. [PMID:21357463]
59. Zhang Z, Winborn CS, Marquez de Prado B, Russo AF. (2007) Sensitization of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors by receptor activity-modifying protein-1 in the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosci, 27 (10): 2693-703. [PMID:17344407]