Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Allosteric Modulators
- Other Binding Ligands
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 380 | 8q11.23 | OPRK1 | opioid receptor kappa 1 | 65,103,135 |
| Mouse | 7 | 380 | 1 1.89 cM | Oprk1 | opioid receptor, kappa 1 | 8,47,61,77,128 |
| Rat | 7 | 380 | 5q12 | Oprk1 | opioid receptor, kappa 1 | 16,59,67-68,76 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| KOR-1 | Kappa receptor | OP2 | KOP | KOPr |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | oprk_human (Hs), oprk_mouse (Mm), oprk_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P41145 (Hs), P33534 (Mm), P34975 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL237 (Hs), CHEMBL4329 (Mm), CHEMBL3614 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P41145 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000082556 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000025905 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000007647 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 4986 (Hs), 18387 (Mm), 29335 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000082556 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:4986 (Hs), mmu:18387 (Mm), rno:29335 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 165196 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P41145 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000912 (Hs), NM_011011 (Mm), NM_017167 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000903 (Hs), NP_035141 (Mm), NP_058863 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
83653 (in complex with JDTic) 83652 (in complex with JDTic) |
| UniProtKB | P41145 (Hs), P33534 (Mm), P34975 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | OPRK1 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
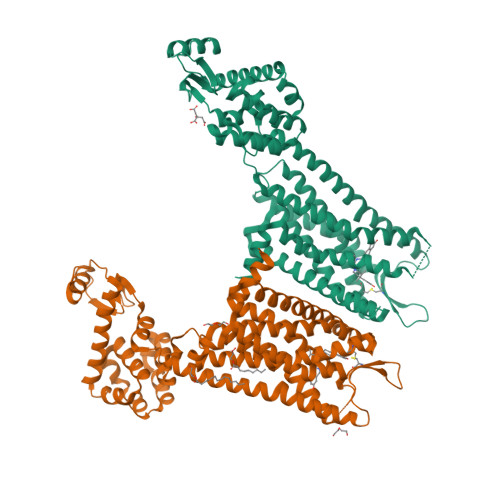
|
|
||||||||||||
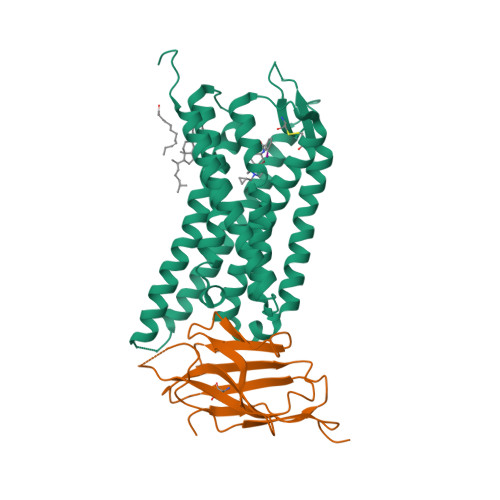
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| big dynorphin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin A-(1-13) {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin A {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin A-(1-8) {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin B {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| β-endorphin {Sp: Human} , β-endorphin {Sp: Mouse} , β-endorphin {Sp: Rat} |
| [Leu]enkephalin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| [Met]enkephalin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| α-neoendorphin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| β-neoendorphin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| Comments: Dynorphin A and big dynorphin are the highest potency endogenous ligands |
| Principal endogenous agonists (Human) |
| big dynorphin (PDYN, P01213), dynorphin A (PDYN, P01213) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ki values were determined in the absence of Na+ and GDP, except TRK820. Discrimination of full or partial agonism is very dependent on the level of receptor expression and on the assay used to monitor agonist effects. Many agents may behave as full agonists or potent partial agonists in cell lines expressing cloned receptors in high concentration, but in other environments they may show only weak agonist activity. The identification of agonist activity in the table is largely based on the ability to stimulate GTPγS binding in cell lines expressing cloned human kappa receptors. Agents giving 85% or greater stimulation than that given by U69593 have been characterized as Full Agonists [116]. κ opioid receptors have been divided into several different subtypes, mainly on the basis of [3H]agonist binding assays. Generally 2 subtypes are recognised: κ1 and κ2. The benzeneacetamides and peptides are considered κ1 agonists and the benzomorphans bind to κ1 and κ2. However, there is only one gene product and the subtypes are considered putative. Selective κ agonists are of several structural types. All have high affinity for the κ receptor and are full agonists. We have tagged the μ receptor as the primary drug target for hydrocodone based on this drug having the highest affinity at this receptor compared to the κ and δ receptors [75]. Similarly, we have tagged the μ receptor as the primary target of the drug hydromorphone [125]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulator Comments | ||
| Although no small molecules are considered direct allosteric regulators of κ opioid receptors, a number of proteins such as G protein-coupled receptor kinases, β-arrestins and G proteins clearly regulate receptor affinities and function. Furthermore, sodium and guanine nucleotides can modify the functional κ receptor complex and G protein interaction. Also, other G protein-coupled receptors appear to be able to form heterodimers with κ receptors, potentially modifying κ opioid receptor activity. |
| Other Binding Ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Potassium channel Calcium channel |
| References: 6,31,34,46,53,69,98,111 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gi/Go family G12/G13 family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation Other - See Comments |
|
Comments:
Activation of κ opioid receptors stimulates p42/p44 MAP kinase via βγ subunits of Gi/o proteins [10]. κ opioid receptors interact with NHERF-1/EBP50 to stimulate Na+/H+ exchange independent of Gi/o proteins [39]. |
|
| References: 10,39,52,58,72,119 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||
| κ opioid receptors show a fairly widespread distribution although quantitatively they represent only a small percentage of the total opioid receptors in the brain. This contrasts with the guinea-pig brain, where κ opioid receptor expression is far more abundant. In all species, the early receptor autoradiography was carried out with low selectivity ligands such as [3H]ethylketocycazocine and [3H]bremazocine and their cross labelling of μ and δ receptors was supressed by the use of excess cold ligands to displace their binding to μ and δ opioid sites. Since the late 1980s highly selective κ opioid receptor ligands such as [3H]U69,593 and [3H]CI-977 have been used and the distribution is more restrictive when these ligands are employed. For a review of κ opioid receptor expression in the rat see [63]. |
||||||||
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biologically Significant Variant Comments |
| κ1 and κ2 receptor subtypes have been proposed based on in vivo pharmacology showing lack of cross-tolerance between U69,593 and bremazocine and differential antagonism by quadazocine and (-)UPHIT [36-38]. Receptor binding studies have led to suggestions of κ1, κ2 and κ3 subtypes [20,95]. However, only one κ receptor cDNA clone has been reported and no κ receptor variants have been characterised. Interaction between κ and δ receptors in transfected cells has been reported and suggested to result in κ2 subtype pharmacology [43]. Multiple active conformations of the κ receptor are likely to exist. κ receptor subtypes are likely due to interaction of receptor with other proteins or receptors at the level of neuronal circuitry, but not mRNA variants. |
References
1. Adler MW, Geller EB. (1987) Hypothermia and poikilothermia induced by a kappa-agonist opioid and a neuroleptic. Eur J Pharmacol, 140 (2): 233-7. [PMID:2889606]
2. Andreev N, Urban L, Dray A. (1994) Opioids suppress spontaneous activity of polymodal nociceptors in rat paw skin induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Neuroscience, 58 (4): 793-8. [PMID:8190256]
3. Ann DK, Hasegawa J, Ko JL, Chen ST, Lee NM, Loh HH. (1992) Specific reduction of delta-opioid receptor binding in transfected NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem, 267 (11): 7921-6. [PMID:1313812]
4. Arora S, Keenan SM, Peng Y, Welsh W, Zhang Q. (2006) Opioid receptor subtype-selective agents. Patent number: WO2006124687 A1. Assignee: Arora S, Keenan SM, Peng Y, Welsh W, Zhang Q.. Priority date: 12/05/2005. Publication date: 23/11/2006.
5. Arvidsson U, Riedl M, Chakrabarti S, Vulchanova L, Lee JH, Nakano AH, Lin X, Loh HH, Law PY, Wessendorf MW et al.. (1995) The kappa-opioid receptor is primarily postsynaptic: combined immunohistochemical localization of the receptor and endogenous opioids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (11): 5062-6. [PMID:7539141]
6. Attali B, Vogel Z. (1986) Inhibition of adenylate cyclase and induction of heterologous desensitization by kappa agonists in rat spinal cord. NIDA Res Monogr, 75: 141-4. [PMID:2828959]
7. Avidor-Reiss T, Zippel R, Levy R, Saya D, Ezra V, Barg J, Matus-Leibovitch N, Vogel Z. (1995) kappa-Opioid receptor-transfected cell lines: modulation of adenylyl cyclase activity following acute and chronic opioid treatments. FEBS Lett, 361 (1): 70-4. [PMID:7890042]
8. Belkowski SM, Zhu J, Liu-Chen LY, Eisenstein TK, Adler MW, Rogers TJ. (1995) Sequence of kappa-opioid receptor cDNA in the R1.1 thymoma cell line. J Neuroimmunol, 62 (1): 113-7. [PMID:7499487]
9. Besse D, Lombard MC, Besson JM. (1991) Autoradiographic distribution of mu, delta and kappa opioid binding sites in the superficial dorsal horn, over the rostrocaudal axis of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res, 548 (1-2): 287-91. [PMID:1651143]
10. Bohn LM, Belcheva MM, Coscia CJ. (2000) Mitogenic signaling via endogenous kappa-opioid receptors in C6 glioma cells: evidence for the involvement of protein kinase C and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade. J Neurochem, 74 (2): 564-73. [PMID:10646507]
11. Béguin C, Richards MR, Wang Y, Chen Y, Liu-Chen LY, Ma Z, Lee DY, Carlezon Jr WA, Cohen BM. (2005) Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological evaluation of salvinorin A analogues modified at C(2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 15 (11): 2761-5. [PMID:15869877]
12. Chang KJ, Rigdon GC, Howard JL, McNutt RW. (1993) A novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist BW373U86. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 267 (2): 852-7. [PMID:8246159]
13. Chao CC, Gekker G, Hu S, Sheng WS, Shark KB, Bu DF, Archer S, Bidlack JM, Peterson PK. (1996) kappa opioid receptors in human microglia downregulate human immunodeficiency virus 1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93 (15): 8051-6. [PMID:8755601]
14. Chavkin C, Sud S, Jin W, Stewart J, Zjawiony JK, Siebert DJ, Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL. (2004) Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: structural and functional considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 308 (3): 1197-203. [PMID:14718611]
15. Che T, Majumdar S, Zaidi SA, Ondachi P, McCorvy JD, Wang S, Mosier PD, Uprety R, Vardy E, Krumm BE et al.. (2018) Structure of the Nanobody-Stabilized Active State of the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Cell, 172 (1-2): 55-67.e15. [PMID:29307491]
16. Chen Y, Mestek A, Liu J, Yu L. (1993) Molecular cloning of a rat kappa opioid receptor reveals sequence similarities to the mu and delta opioid receptors. Biochem J, 295 ( Pt 3): 625-8. [PMID:8240267]
17. Cometta-Morini C, Maguire PA, Loew GH. (1992) Molecular determinants of mu receptor recognition for the fentanyl class of compounds. Mol Pharmacol, 41 (1): 185-96. [PMID:1310142]
18. Cox BM, Chavkin C. (1983) Comparison of dynorphin-selective Kappa receptors in mouse vas deferens and guinea pig ileum. Spare receptor fraction as a determinant of potency. Mol Pharmacol, 23 (1): 36-43. [PMID:6135144]
19. Dapoigny M, Abitbol JL, Fraitag B. (1995) Efficacy of peripheral kappa agonist fedotozine versus placebo in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. A multicenter dose-response study. Dig Dis Sci, 40 (10): 2244-9. [PMID:7587797]
20. de Costa BR, Rothman RB, Bykov V, Jacobson AE, Rice KC. (1989) Selective and enantiospecific acylation of kappa opioid receptors by (1S,2S)-trans-2-isothiocyanato-N-methyl-N-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl) cyclohexy l] benzeneacetamide. Demonstration of kappa receptor heterogeneity. J Med Chem, 32 (2): 281-3. [PMID:2536435]
21. Dekan Z, Sianati S, Yousuf A, Sutcliffe KJ, Gillis A, Mallet C, Singh P, Jin AH, Wang AM, Mohammadi SA et al.. (2019) A tetrapeptide class of biased analgesics from an Australian fungus targets the µ-opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116 (44): 22353-22358. [PMID:31611414]
22. Di Chiara G, Imperato A. (1988) Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiate agonists on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and in the dorsal caudate of freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 244 (3): 1067-80. [PMID:2855239]
23. Durham RA, Johnson JD, Moore KE, Lookingland KJ. (1996) Evidence that D2 receptor-mediated activation of hypothalamic tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons in the male rat occurs via inhibition of tonically active afferent dynorphinergic neurons. Brain Res, 732 (1-2): 113-20. [PMID:8891275]
24. Fulton BS, Knapp BI, Bidlack JM, Neumeyer JL. (2008) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of hydrophobic esters and ethers of butorphanol at opioid receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 18 (16): 4474-6. [PMID:18674902]
25. Gavériaux C, Peluso J, Simonin F, Laforet J, Kieffer B. (1995) Identification of kappa- and delta-opioid receptor transcripts in immune cells. FEBS Lett, 369 (2-3): 272-6. [PMID:7649271]
26. Gavériaux-Ruff C, Simonin F, Filliol D, Kieffer BL. (2003) Enhanced humoral response in kappa-opioid receptor knockout mice. J Neuroimmunol, 134 (1-2): 72-81. [PMID:12507774]
27. George SR, Zastawny RL, Briones-Urbina R, Cheng R, Nguyen T, Heiber M, Kouvelas A, Chan AS, O'Dowd BF. (1994) Distinct distributions of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptor mRNA in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 205 (2): 1438-44. [PMID:7802680]
28. Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM, Raucci J, Archer S. (1995) Kappa opioid inhibition of morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res, 681 (1-2): 147-52. [PMID:7552272]
29. Gmerek DE, Cowan A. (1988) Role of opioid receptors in bombesin-induced grooming. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 525: 291-300. [PMID:2839069]
30. Gottschlich R, Ackermann KA, Barber A, Bartoszyk GD, Greiner HE. (1994) EMD 61 753 as a favourable representative of structurally novel arylacetamido-type K opiate receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 4 (4): 677–682.
31. Grudt TJ, Williams JT. (1993) kappa-Opioid receptors also increase potassium conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (23): 11429-32. [PMID:7902584]
32. Guerrero M, Urbano M, Kim EK, Gamo AM, Riley S, Abgaryan L, Leaf N, Van Orden LJ, Brown SJ, Xie JY et al.. (2019) Design and Synthesis of a Novel and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor (KOR) Antagonist (BTRX-335140). J Med Chem, 62 (4): 1761-1780. [PMID:30707578]
33. Handler CM, Geller EB, Adler MW. (1992) Effect of mu-, kappa-, and delta-selective opioid agonists on thermoregulation in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 43 (4): 1209-16. [PMID:1361992]
34. Henry DJ, Grandy DK, Lester HA, Davidson N, Chavkin C. (1995) Kappa-opioid receptors couple to inwardly rectifying potassium channels when coexpressed by Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol, 47 (3): 551-7. [PMID:7700253]
35. Hjorth SA, Thirstrup K, Schwartz TW. (1996) Radioligand-dependent discrepancy in agonist affinities enhanced by mutations in the kappa-opioid receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 50 (4): 977-84. [PMID:8863844]
36. Horan P, de Costa BR, Rice KC, Porreca F. (1991) Differential antagonism of U69,593- and bremazocine-induced antinociception by (-)-UPHIT: evidence of kappa opioid receptor multiplicity in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 257 (3): 1154-61. [PMID:1646325]
37. Horan PJ, de Costa BR, Rice K, Haaseth RC, Hruby VJ, Porreca F. (1993) Differential antagonism of bremazocine- and U69,593-induced antinociception by quadazocine: further functional evidence of opioid kappa receptor multiplicity in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 266 (2): 926-33. [PMID:8394923]
38. Horan PJ, Porreca F. (1993) Lack of cross-tolerance between U69,593 and bremazocine suggests kappa-opioid receptor multiplicity in mice. Eur J Pharmacol, 239 (1-3): 93-8. [PMID:8223918]
39. Huang P, Steplock D, Weinman EJ, Hall RA, Ding Z, Li J, Wang Y, Liu-Chen LY. (2004) kappa Opioid receptor interacts with Na(+)/H(+)-exchanger regulatory factor-1/Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 (NHERF-1/EBP50) to stimulate Na(+)/H(+) exchange independent of G(i)/G(o) proteins. J Biol Chem, 279 (24): 25002-9. [PMID:15070904]
40. Hunter JC, Leighton GE, Meecham KG, Boyle SJ, Horwell DC, Rees DC, Hughes J. (1990) CI-977, a novel and selective agonist for the kappa-opioid receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 101 (1): 183-9. [PMID:2178014]
41. Jones RM, Portoghese PS. (2000) 5'-Guanidinonaltrindole, a highly selective and potent kappa-opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol, 396 (1): 49-52. [PMID:10822054]
42. Jongkamonwiwat N, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Sarapoke P, Chetsawang B, Casalotti SO, Forge A, Dodson H, Govitrapong P. (2003) The presence of opioid receptors in rat inner ear. Hear Res, 181 (1-2): 85-93. [PMID:12855366]
43. Jordan BA, Devi LA. (1999) G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization modulates receptor function. Nature, 399 (6737): 697-700. [PMID:10385123]
44. Khroyan TV, Polgar WE, Cami-Kobeci G, Husbands SM, Zaveri NT, Toll L. (2011) The first universal opioid ligand, (2S)-2-[(5R,6R,7R,14S)-N-cyclopropylmethyl-4,5-epoxy-6,14-ethano-3-hydroxy-6-methoxymorphinan-7-yl]-3,3-dimethylpentan-2-ol (BU08028): characterization of the in vitro profile and in vivo behavioral effects in mouse models of acute pain and cocaine-induced reward. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 336 (3): 952-61. [PMID:21177476]
45. Kitchen I, Slowe SJ, Matthes HW, Kieffer B. (1997) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in knockout mice lacking the mu-opioid receptor gene. Brain Res, 778 (1): 73-88. [PMID:9462879]
46. Konkoy CS, Childers SR. (1993) Relationship between kappa 1 opioid receptor binding and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in guinea pig brain membranes. Biochem Pharmacol, 45 (1): 207-16. [PMID:8381004]
47. Kozak CA, Filie J, Adamson MC, Chen Y, Yu L. (1994) Murine chromosomal location of the mu and kappa opioid receptor genes. Genomics, 21 (3): 659-61. [PMID:7959748]
48. Kreek MJ, Schluger J, Borg L, Gunduz M, Ho A. (1999) Dynorphin A1-13 causes elevation of serum levels of prolactin through an opioid receptor mechanism in humans: gender differences and implications for modulation of dopaminergic tone in the treatment of addictions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 288 (1): 260-9. [PMID:9862779]
49. Krulich L, Koenig JI, Conway S, McCann SM, Mayfield MA. (1986) Opioid kappa receptors and the secretion of prolactin (PRL) and growth hormone (GH) in the rat. II. GH and PRL release-inhibiting effects of the opioid kappa receptor agonists bremazocine and U-50,488. Neuroendocrinology, 42: 82-87. [PMID:3001566]
50. Kumar V, Guo D, Daubert JD, Cassel JA, DeHaven RN, Mansson E, DeHaven-Hudkins DL, Maycock AL. (2005) Amino acid conjugates as kappa opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 15 (5): 1279-82. [PMID:15713370]
51. Lahti RA, Mickelson MM, McCall JM, Von Voigtlander PF. (1985) [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 109 (2): 281-4. [PMID:2986999]
52. Lai HW, Minami M, Satoh M, Wong YH. (1995) Gz coupling to the rat kappa-opioid receptor. FEBS Lett, 360 (1): 97-9. [PMID:7875310]
53. Lawrence DM, Bidlack JM. (1993) The kappa opioid receptor expressed on the mouse R1.1 thymoma cell line is coupled to adenylyl cyclase through a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 266 (3): 1678-83. [PMID:8103800]
54. Le Bourdonnec B, Barker WM, Belanger S, Wiant DD, Conway-James NC, Cassel JA, O'Neill TJ, Little PJ, DeHaven RN, DeHaven-Hudkins DL et al.. (2008) Novel trans-3,4-dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidines as mu opioid receptor antagonists with improved opioid receptor selectivity profiles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 18 (6): 2006-12. [PMID:18313920]
55. Le Bourdonnec B, Windh RT, Ajello CW, Leister LK, Gu M, Chu GH, Tuthill PA, Barker WM, Koblish M, Wiant DD et al.. (2008) Potent, orally bioavailable delta opioid receptor agonists for the treatment of pain: discovery of N,N-diethyl-4-(5-hydroxyspiro[chromene-2,4'-piperidine]-4-yl)benzamide (ADL5859). J Med Chem, 51 (19): 5893-6. [PMID:18788723]
56. Le Bourdonnec B, Windh RT, Leister LK, Zhou QJ, Ajello CW, Gu M, Chu GH, Tuthill PA, Barker WM, Koblish M et al.. (2009) Spirocyclic delta opioid receptor agonists for the treatment of pain: discovery of N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxy-4-(spiro[chromene-2,4'-piperidine]-4-yl) benzamide (ADL5747). J Med Chem, 52 (18): 5685-702. [PMID:19694468]
57. Leander JD. (1984) Kappa opioid agonists and antagonists: effects on drinking and urinary output. Appetite, 5 (1): 7-14. [PMID:6091543]
58. Lee JW, Joshi S, Chan JS, Wong YH. (1998) Differential coupling of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors to G alpha16-mediated stimulation of phospholipase C. J Neurochem, 70 (5): 2203-11. [PMID:9572309]
59. Li S, Zhu J, Chen C, Chen YW, Deriel JK, Ashby B, Liu-Chen LY. (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Biochem J, 295 ( Pt 3): 629-33. [PMID:8240268]
60. Linz K, Christoph T, Tzschentke TM, Koch T, Schiene K, Gautrois M, Schröder W, Kögel BY, Beier H, Englberger W et al.. (2014) Cebranopadol: a novel potent analgesic nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide and opioid receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 349 (3): 535-48. [PMID:24713140]
61. Liu HC, Lu S, Augustin LB, Felsheim RF, Chen HC, Loh HH, Wei LN. (1995) Cloning and promoter mapping of mouse kappa opioid receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 209: 639-647. [PMID:7733933]
62. Maisonneuve IM, Archer S, Glick SD. (1994) U50,488, a kappa opioid receptor agonist, attenuates cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Neurosci Lett, 181: 57-60. [PMID:7898771]
63. Mansour A, Fox CA, Akil H, Watson SJ. (1995) Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: anatomical and functional implications. Trends Neurosci, 18: 22-29. [PMID:7535487]
64. Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ. (1987) Autoradiographic differentiation of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors in the rat forebrain and midbrain. J Neurosci, 7 (8): 2445-64. [PMID:3039080]
65. Mansson E, Bare L, Yang D. (1994) Isolation of a human kappa opioid receptor cDNA from placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 202 (3): 1431-7. [PMID:8060324]
66. McCarthy L, Wetzel M, Sliker JK, Eisenstein TK, Rogers TJ. (2001) Opioids, opioid receptors, and the immune response. Drug Alcohol Depend, 62 (2): 111-23. [PMID:11245967]
67. Meng F, Xie GX, Thompson RC, Mansour A, Goldstein A, Watson SJ, Akil H. (1993) Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (21): 9954-8. [PMID:8234341]
68. Minami M, Toya T, Katao Y, Maekawa K, Nakamura S, Onogi T, Kaneko S, Satoh M. (1993) Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the rat kappa-opioid receptor. FEBS Lett, 329 (3): 291-5. [PMID:8103466]
69. Moises HC, Rusin KI, Macdonald RL. (1994) Mu- and kappa-opioid receptors selectively reduce the same transient components of high-threshold calcium current in rat dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons. J Neurosci, 14 (10): 5903-16. [PMID:7931552]
70. Morley JE, Levine AS, Kneip J, Grace M, Zeugner H, Shearman GT. (1985) The kappa opioid receptor and food intake. Eur J Pharmacol, 112 (1): 17-25. [PMID:2990965]
71. Munro TA, Huang XP, Inglese C, Perrone MG, Van't Veer A, Carroll FI, Béguin C, Carlezon Jr WA, Colabufo NA, Cohen BM et al.. (2013) Selective κ opioid antagonists nor-BNI, GNTI and JDTic have low affinities for non-opioid receptors and transporters. PLoS ONE, 8 (8): e70701. [PMID:23976952]
72. Murthy KS, Makhlouf GM. (1996) Opioid mu, delta, and kappa receptor-induced activation of phospholipase C-beta 3 and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase is mediated by Gi2 and G(o) in smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol, 50 (4): 870-7. [PMID:8863832]
73. Nakazawa T, Furuya Y, Kaneko T, Yamatsu K. (1991) Spinal kappa receptor-mediated analgesia of E-2078, a systemically active dynorphin analog, in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 256 (1): 76-81. [PMID:1671100]
74. Neumeyer JL, Zhang A, Xiong W, Gu XH, Hilbert JE, Knapp BI, Negus SS, Mello NK, Bidlack JM. (2003) Design and synthesis of novel dimeric morphinan ligands for kappa and micro opioid receptors. J Med Chem, 46 (24): 5162-70. [PMID:14613319]
75. Neumeyer JL, Zhang B, Zhang T, Sromek AW, Knapp BI, Cohen DJ, Bidlack JM. (2012) Synthesis, binding affinity, and functional in vitro activity of 3-benzylaminomorphinan and 3-benzylaminomorphine ligands at opioid receptors. J Med Chem, 55 (8): 3878-90. [PMID:22439881]
76. Nishi M, Takeshima H, Fukuda K, Kato S, Mori K. (1993) cDNA cloning and pharmacological characterization of an opioid receptor with high affinities for kappa-subtype-selective ligands. FEBS Lett, 330 (1): 77-80. [PMID:8396539]
77. Nishi M, Takeshima H, Mori M, Nakagawara K, Takeuchi T. (1994) Structure and chromosomal mapping of genes for the mouse kappa-opioid receptor and an opioid receptor homologue (MOR-C). Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 205 (2): 1353-7. [PMID:7802669]
78. Nock B, Rajpara A, O'Connor LH, Cicero TJ. (1988) Autoradiography of [3H]U-69593 binding sites in rat brain: evidence for kappa opioid receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol, 154 (1): 27-34. [PMID:2846324]
79. Ohnishi A, Mihara M, Yasuda S, Tomono Y, Hasegawa J, Tanaka T. (1994) Aquaretic effect of the stable dynorphin-A analog E2078 in the human. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 270 (1): 342-7. [PMID:7913498]
80. Pande AC, Pyke RE, Greiner M, Wideman GL, Benjamin R, Pierce MW. (1996) Analgesic efficacy of enadoline versus placebo or morphine in postsurgical pain. Clin Neuropharmacol, 19 (5): 451-6. [PMID:8889289]
81. Patkar KA, Yan X, Murray TF, Aldrich JV. (2005) [Nalpha-benzylTyr1,cyclo(D-Asp5,Dap8)]- dynorphin A-(1-11)NH2 cyclized in the "address" domain is a novel kappa-opioid receptor antagonist. J Med Chem, 48 (14): 4500-3. [PMID:15999987]
82. Payza K. (2003) Binding and activity of opioid ligands at the cloned human delta, mu and kappa receptors. In The Delta Receptor. Edited by Chang KJ (CRC Press) 261-275. [ISBN:0824740319]
83. Pfeiffer A, Braun S, Mann K, Meyer HD, Brantl V. (1986) Anterior pituitary hormone responses to a kappa-opioid agonist in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 62: 181-185. [PMID:3079599]
84. Pfeiffer A, Knepel W, Braun S, Meyer HD, Lohmann H, Brantl V. (1986) Effects of a kappa-opioid agonist on adrenocorticotropic and diuretic function in man. Horm Metab Res, 18 (12): 842-8. [PMID:3028922]
85. Pol O, Palacio JR, Puig MM. (2003) The expression of delta- and kappa-opioid receptor is enhanced during intestinal inflammation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 306 (2): 455-62. [PMID:12724348]
86. Portoghese PS, Larson DL, Ronsisvalle G, Schiller PW, Nguyen TM, Lemieux C, Takemori AE. (1987) Hybrid bivalent ligands with opiate and enkephalin pharmacophores. J Med Chem, 30 (11): 1991-4. [PMID:2444704]
87. Poulain R, Horvath D, Bonnet B, Eckhoff C, Chapelain B, Bodinier MC, Déprez B. (2001) From hit to lead. Combining two complementary methods for focused library design. Application to mu opiate ligands. J Med Chem, 44 (21): 3378-90. [PMID:11585443]
88. Prchalová E, Hin N, Thomas AG, Veeravalli V, Ng J, Alt J, Rais R, Rojas C, Li Z, Hihara H et al.. (2019) Discovery of Benzamidine- and 1-Aminoisoquinoline-Based Human MAS-Related G-Protein-Coupled Receptor X1 (MRGPRX1) Agonists. J Med Chem, 62 (18): 8631-8641. [PMID:31498617]
89. Ravert HT, Scheffel U, Mathews WB, Musachio JL, Dannals RF. (2002) [(11)C]-GR89696, a potent kappa opiate receptor radioligand; in vivo binding of the R and S enantiomers. Nucl Med Biol, 29 (1): 47-53. [PMID:11786275]
90. Remmers AE, Clark MJ, Mansour A, Akil H, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F. (1999) Opioid efficacy in a C6 glioma cell line stably expressing the human kappa opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 288 (2): 827-33. [PMID:9918595]
91. Rimoy GH, Bhaskar NK, Wright DM, Rubin PC. (1991) Mechanism of diuretic action of spiradoline (U-62066E)--a kappa opioid receptor agonist in the human. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 32 (5): 611-5. [PMID:1659438]
92. Rimoy GH, Wright DM, Bhaskar NK, Rubin PC. (1994) The cardiovascular and central nervous system effects in the human of U-62066E. A selective opioid receptor agonist. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 46 (3): 203-7. [PMID:8070500]
93. Rorick-Kehn LM, Witkin JM, Statnick MA, Eberle EL, McKinzie JH, Kahl SD, Forster BM, Wong CJ, Li X, Crile RS et al.. (2014) LY2456302 is a novel, potent, orally-bioavailable small molecule kappa-selective antagonist with activity in animal models predictive of efficacy in mood and addictive disorders. Neuropharmacology, 77: 131-44. [PMID:24071566]
94. Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB. (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99 (18): 11934-9. [PMID:12192085]
95. Rothman RB, France CP, Bykov V, De Costa BR, Jacobson AE, Woods JH, Rice KC. (1989) Pharmacological activities of optically pure enantiomers of the kappa opioid agonist, U50,488, and its cis diastereomer: evidence for three kappa receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol, 167 (3): 345-53. [PMID:2553442]
96. Salemi S, Aeschlimann A, Reisch N, Jüngel A, Gay RE, Heppner FL, Michel BA, Gay S, Sprott H. (2005) Detection of kappa and delta opioid receptors in skin--outside the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 338 (2): 1012-7. [PMID:16263089]
97. Schmauss C, Yaksh TL. (1984) In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 228 (1): 1-12. [PMID:6319664]
98. Schoffelmeer AN, Rice KC, Jacobson AE, Van Gelderen JG, Hogenboom F, Heijna MH, Mulder AH. (1988) Mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor-mediated inhibition of neurotransmitter release and adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain slices: studies with fentanyl isothiocyanate. Eur J Pharmacol, 154: 169-178. [PMID:2906610]
99. Schteingart CD, Menzaghi F, Jiang G, Alexander RV, Sueiras-Diaz J, Spencer RH, Chalmers DT, Luo Z. (2008) Synthetic peptide amides. Patent number: US7402564 B1. Assignee: Cara Therapeutics, Inc.. Priority date: 10/11/2006. Publication date: 22/07/2008.
100. Sengupta JN, Su X, Gebhart GF. (1996) Kappa, but not mu or delta, opioids attenuate responses to distention of afferent fibers innervating the rat colon. Gastroenterology, 111 (4): 968-80. [PMID:8831591]
101. Sharp BM, Roy S, Bidlack JM. (1998) Evidence for opioid receptors on cells involved in host defense and the immune system. J Neuroimmunol, 83 (1-2): 45-56. [PMID:9610672]
102. Shippenberg TS, Herz A. (1987) Place preference conditioning reveals the involvement of D1-dopamine receptors in the motivational properties of mu- and kappa-opioid agonists. Brain Res, 436 (1): 169-72. [PMID:2961413]
103. Simonin F, Gavériaux-Ruff C, Befort K, Matthes H, Lannes B, Micheletti G, Mattéi MG, Charron G, Bloch B, Kieffer B. (1995) kappa-Opioid receptor in humans: cDNA and genomic cloning, chromosomal assignment, functional expression, pharmacology, and expression pattern in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (15): 7006-10. [PMID:7624359]
104. Simonin F, Slowe S, Becker JA, Matthes HW, Filliol D, Chluba J, Kitchen I, Kieffer BL. (2001) Analysis of [3H]bremazocine binding in single and combinatorial opioid receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol, 414 (2-3): 189-95. [PMID:11239918]
105. Simonin F, Valverde O, Smadja C, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Dierich A, Le Meur M, Roques BP, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL. (1998) Disruption of the kappa-opioid receptor gene in mice enhances sensitivity to chemical visceral pain, impairs pharmacological actions of the selective kappa-agonist U-50,488H and attenuates morphine withdrawal. EMBO J, 17 (4): 886-97. [PMID:9463367]
106. Slizgi GR, Ludens JH. (1982) Studies on the nature and mechanism of the diuretic activity of the opioid analgesic ethylketocyclazocine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 220 (3): 585-91. [PMID:6121047]
107. Spanagel R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. (1990) The effects of opioid peptides on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem, 55 (5): 1734-40. [PMID:1976759]
108. Spetea M, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Guerrieri E, Schmidhammer H. (2012) Discovery and pharmacological evaluation of a diphenethylamine derivative (HS665), a highly potent and selective κ opioid receptor agonist. J Med Chem, 55 (22): 10302-6. [PMID:23134120]
109. Stein C, Millan MJ, Shippenberg TS, Peter K, Herz A. (1989) Peripheral opioid receptors mediating antinociception in inflammation. Evidence for involvement of mu, delta and kappa receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 248 (3): 1269-75. [PMID:2539460]
110. Stevens WC, Jones RM, Subramanian G, Metzger TG, Ferguson DM, Portoghese PS. (2000) Potent and selective indolomorphinan antagonists of the kappa-opioid receptor. J Med Chem, 43 (14): 2759-69. [PMID:10893314]
111. Tallent M, Dichter MA, Bell GI, Reisine T. (1994) The cloned kappa opioid receptor couples to an N-type calcium current in undifferentiated PC-12 cells. Neuroscience, 63 (4): 1033-40. [PMID:7700508]
112. Taub DD, Eisenstein TK, Geller EB, Adler MW, Rogers TJ. (1991) Immunomodulatory activity of mu- and kappa-selective opioid agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 88 (2): 360-4. [PMID:1846441]
113. Tempel A, Zukin RS. (1987) Neuroanatomical patterns of the mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors of rat brain as determined by quantitative in vitro autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 84 (12): 4308-12. [PMID:3035579]
114. Thomas JB, Atkinson RN, Rothman RB, Fix SE, Mascarella SW, Vinson NA, Xu H, Dersch CM, Lu Y, Cantrell BE et al.. (2001) Identification of the first trans-(3R,4R)- dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine derivative to possess highly potent and selective opioid kappa receptor antagonist activity. J Med Chem, 44 (17): 2687-90. [PMID:11495579]
115. Togashi Y, Umeuchi H, Okano K, Ando N, Yoshizawa Y, Honda T, Kawamura K, Endoh T, Utsumi J, Kamei J et al.. (2002) Antipruritic activity of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, TRK-820. Eur J Pharmacol, 435 (2-3): 259-64. [PMID:11821035]
116. Toll L, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Polgar WE, Brandt SR, Adapa ID, Rodriguez L, Schwartz RW, Haggart D, O'Brien A, White A et al.. (1998) Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res Monogr, 178: 440-66. [PMID:9686407]
117. Toll L, Khroyan TV, Polgar WE, Jiang F, Olsen C, Zaveri NT. (2009) Comparison of the antinociceptive and antirewarding profiles of novel bifunctional nociceptin receptor/mu-opioid receptor ligands: implications for therapeutic applications. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 331 (3): 954-64. [PMID:19773529]
118. Tyers MB. (1980) A classification of opiate receptors that mediate antinociception in animals. Br J Pharmacol, 69 (3): 503-12. [PMID:6249436]
119. Ueda H, Miyamae T, Fukushima N, Takeshima H, Fukuda K, Sasaki Y, Misu Y. (1995) Opioid mu- and kappa-receptor mediate phospholipase C activation through Gi1 in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 32 (1): 166-70. [PMID:7494457]
120. Unterwald EM, Knapp C, Zukin RS. (1991) Neuroanatomical localization of kappa 1 and kappa 2 opioid receptors in rat and guinea pig brain. Brain Res, 562 (1): 57-65. [PMID:1666016]
121. Varty GB, Lu SX, Morgan CA, Cohen-Williams ME, Hodgson RA, Smith-Torhan A, Zhang H, Fawzi AB, Graziano MP, Ho GD et al.. (2008) The anxiolytic-like effects of the novel, orally active nociceptin opioid receptor agonist 8-[bis(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-3-phenyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol (SCH 221510). J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 326 (2): 672-82. [PMID:18492950]
122. Vergura R, Balboni G, Spagnolo B, Gavioli E, Lambert DG, McDonald J, Trapella C, Lazarus LH, Regoli D, Guerrini R et al.. (2008) Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities of H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2-COOH)-Bid (UFP-512), a novel selective delta opioid receptor agonist. Peptides, 29 (1): 93-103. [PMID:18069089]
123. Vonvoigtlander PF, Lahti RA, Ludens JH. (1983) U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 224 (1): 7-12. [PMID:6129321]
124. Wang Y, Tang K, Inan S, Siebert D, Holzgrabe U, Lee DY, Huang P, Li JG, Cowan A, Liu-Chen LY. (2005) Comparison of pharmacological activities of three distinct kappa ligands (Salvinorin A, TRK-820 and 3FLB) on kappa opioid receptors in vitro and their antipruritic and antinociceptive activities in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 312 (1): 220-30. [PMID:15383632]
125. Wentland MP, Lou R, Lu Q, Bu Y, Denhardt C, Jin J, Ganorkar R, VanAlstine MA, Guo C, Cohen DJ et al.. (2009) Syntheses of novel high affinity ligands for opioid receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 19 (8): 2289-94. [PMID:19282177]
126. Wentland MP, Lu Q, Lou R, Bu Y, Knapp BI, Bidlack JM. (2005) Synthesis and opioid receptor binding properties of a highly potent 4-hydroxy analogue of naltrexone. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 15 (8): 2107-10. [PMID:15808478]
127. Wu H, Wacker D, Mileni M, Katritch V, Han GW, Vardy E, Liu W, Thompson AA, Huang XP, Carroll FI et al.. (2012) Structure of the human κ-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature, 485 (7398): 327-32. [PMID:22437504]
128. Yasuda K, Raynor K, Kong H, Breder CD, Takeda J, Reisine T, Bell GI. (1993) Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (14): 6736-40. [PMID:8393575]
129. Yoshino H, Nakazawa T, Arakawa Y, Kaneko T, Tsuchiya Y, Matsunaga M, Araki S, Ikeda M, Yamatsu K, Tachibana S. (1990) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of dynorphin A-(1-8) amide analogues. J Med Chem, 33 (1): 206-12. [PMID:1967312]
130. Yuferov V, Fussell D, LaForge KS, Nielsen DA, Gordon D, Ho A, Leal SM, Ott J, Kreek MJ. (2004) Redefinition of the human kappa opioid receptor gene (OPRK1) structure and association of haplotypes with opiate addiction. Pharmacogenetics, 14 (12): 793-804. [PMID:15608558]
131. Zaveri NT, Journigan VB, Polgar WE. (2015) Discovery of the first small-molecule opioid pan antagonist with nanomolar affinity at mu, delta, kappa, and nociceptin opioid receptors. ACS Chem Neurosci, 6 (4): 646-57. [PMID:25635572]
132. Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ. (2004) Effect of the endogenous kappa opioid agonist dynorphin A(1-17) on cocaine-evoked increases in striatal dopamine levels and cocaine-induced place preference in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 172 (4): 422-9. [PMID:14712335]
133. Zheng Y, Obeng S, Wang H, Jali AM, Peddibhotla B, Williams DA, Zou C, Stevens DL, Dewey WL, Akbarali HI et al.. (2019) Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of the Third Generation 17-Cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6β-[(4'-pyridyl)carboxamido]morphinan (NAP) Derivatives as μ/κ Opioid Receptor Dual Selective Ligands. J Med Chem, 62 (2): 561-574. [PMID:30608693]
134. Zhou L, Lovell KM, Frankowski KJ, Slauson SR, Phillips AM, Streicher JM, Stahl E, Schmid CL, Hodder P, Madoux F et al.. (2013) Development of functionally selective, small molecule agonists at kappa opioid receptors. J Biol Chem, 288 (51): 36703-16. [PMID:24187130]
135. Zhu J, Chen C, Xue JC, Kunapuli S, DeRiel JK, Liu-Chen LY. (1995) Cloning of a human kappa opioid receptor from the brain. Life Sci, 56: PL201-PL207. [PMID:7869844]
136. Zhu J, Luo LY, Li JG, Chen C, Liu-Chen LY. (1997) Activation of the cloned human kappa opioid receptor by agonists enhances [35S]GTPgammaS binding to membranes: determination of potencies and efficacies of ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 282 (2): 676-84. [PMID:9262330]
137. Zhu J, Luo LY, Mao GF, Ashby B, Liu-Chen LY. (1998) Agonist-induced desensitization and down-regulation of the human kappa opioid receptor expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 285 (1): 28-36. [PMID:9535991]
138. Zhu Y, Pintar JE. (1998) Expression of opioid receptors and ligands in pregnant mouse uterus and placenta. Biol Reprod, 59 (4): 925-32. [PMID:9746745]