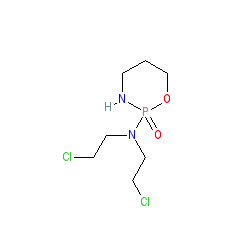
|
Synonyms: cytophosphane | Cytoxan® | Endoxan®
cyclophosphamide is an approved drug (FDA (1959))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Cyclophosphamide is an alkylating agent of the nitrogen mustard type. It is converted in vivo to the active metabolite 4-hydroxy cyclophosphamide by liver cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. It is used mainly as a cancer chemotherapeutic. It can be used to treat autoimmune conditions, but as it has severe and life-threatening side-effects, other less toxic medications may be the preferred option following an acuteautoimmune crisis.
Cyclophosphamide is on the World Health Organisation's List of Essential Medicines. Click here to access the pdf version of the WHO's 21st Essential Medicines list (2019). 
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: cyclophosphamide |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com |