|
Synonyms: (R)-ruxolitinib | INC424 | INCB 18424 | INCB018424 | Jakafi® | Jakavi®
ruxolitinib is an approved drug (FDA (2011), EMA (2012))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
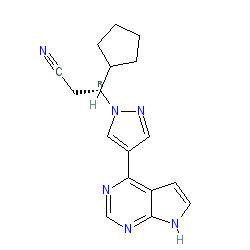
Comment: Ruxolitinib is a Type-1 kinase inhibitor and was first approved by the US FDA in 2011. Ruxolitinib has high potency against Janus kinases 1 and 2 (JAK1, JAK2), as well as against the related family member, tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) [3]. Inhibitory activity against JAK3 is only slightly reduced compared to the other three family kinases.
Marketed formulations may contain ruxolitinib phosphate (PubChem CID 25127112). Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: ruxolitinib |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Used to treat intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis including including primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia vera (post-PV) myelofibrosis and post-essential thrombocythemia (post-ET) myelofibrosis. In 2014 ruxolitinib was approved for use as a treatment for polycythemia vera, a chronic type of bone marrow disease. In May 2019, the FDA approved ruxolitinib as a treatment for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) in patients ≥12 years old. Interesting results from small trials in patients with alopecia areata suggest that by killing the immune cells responsible for hair loss in this disease, ruxolitinib can promote hair re-growth [4,9]. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT03099304 | A Study of INCB018424 Phosphate Cream in Subjects With Vitiligo | Phase 2 Interventional | Incyte Corporation | Topical treatment of vitiligo lesions with ruxolitinib cream is associated with substantial repigmentation. The treatment was well tolerated. | 6 |
| NCT04052425 | Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in Vitiligo Study 1 (TRuE-V1) | Phase 3 Interventional | Incyte Corporation | Phase 3 trials NCT04052425 and NCT04057573 found that topical ruxolitinib produced greater repigmentation of vitiligo lesions than placebo. However, treatment caused acne and pruritus at the site of application. | 7 |
| NCT04057573 | Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in Vitiligo Study 2 (TRuE-V2) | Phase 3 Interventional | Incyte Corporation | 7 | |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com European Medicines Agency (EMA) |