|
Synonyms: albuterol | SCH-13949W | Ventolin®
salbutamol is an approved drug (FDA (1981))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
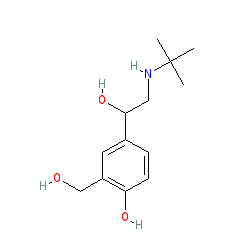
Comment: The approved drug salbutamol is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers: levosalbutamol ((R)-salbutamol) and (S)-salbutamol. The structure shown here does not specify stereochemistry and represents the mixture. The US FDA approved this drug with the name albuterol.
Marketed formulations may contain salbutamol sulfate (PubChem CID 9884233). Salbutamol is termed a 'short-acting beta-agonist' (SABA). Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: salbutamol |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Highly selective β2-adrenoceptor agonist used in the treatment of COPD and asthma. In April 2015, the FDA expanded approval to include treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease and for the treatment of exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB). A first-in-class, fixed-dose combination asthma rescue medication (delivered by a pressurised metered-dose inhaler) containing salbutamol/albuterol and budesonide (an anti-inflammatory inhaled corticosteroid), Airsupra®, was approved by the FDA in 2023. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com |